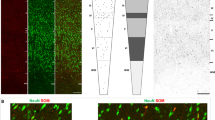
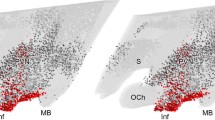
Abstract
The location and neurochemical composition of somatostatin (SOM)-immunoreactive (ir) neurons in the tuberal region of the rat hypothalamus were studied using immunohistochemical method in young (2–3-month-old), adult (1-year-old), and aged (2–2.5-year-old) male and female rats. The highest percentage of SOM-ir neurons was found in the arcuate nucleus (AN) and ventrolateral part of the ventromedial nucleus (VMNvl). A smaller part of them was observed in the dorsomedial (DMN) and medial tuberal (MTu) nuclei, as well as in the VMN shell. Single SOM-ir neurons occurred in the dorsomedial part of the ventromedial nucleus (VMNdm), periventricular (PeV) and perifornical (PeF) nuclei. No age-related changes were found in the number of SOM-ir neurons. The percentage of SOM-ir neurons colocalizing calbindin (CB), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) increased in the AN during aging. In the VMNvl, from one third to one half of SOM-ir neurons in all rats colocalized nNOS, and only from 7.9 to 18.6% of them colocalized CB and NPY. In the DMN of males, a significantly higher percentage of SOM-ir neurons colocalizing NPY was observed in all age groups when compared with females. Thus, aging is accompanied by neurochemical changes in the SOM-ergic system of the tuberal hypothalamic nuclei, mainly in the arcuate nuclei.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kumar U, Singh S (2020) Role of Somatostatin in the Regulation of Central and Peripheral Factors of Satiety and Obesity. Int J Mol Sci 21(7):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072568
Patel YC (1999) Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 20:157–198.https://doi.org/10.1006/frne.1999.0183
Shamsi BH, Chatoo M, Xu XK, Xu X, Chen XQ (2021) Versatile Functions of Somatostatin and Somatostatin Receptors in the Gastrointestinal System. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:652363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.652363
Kumar U (2007) Colocalization of somatostatin receptor subtypes (SSTR1-5) with somatostatin, NADPH-diaphorase (NADPH-d), and tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 504(2):185-205. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21444
Zou SL, Somvanshi RK, Paik S, Kumar U (2015) Colocalization of Cannabinoid Receptor 1 with Somatostatin and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Rat Brain Hypothalamus. J Mol Neurosci 55: 480–491.
Stepanyan Z, Kocharyan A, Behrens M, Koebnick C, Pyrski M, Meyerhof W (2007) Somatostatin, a negative-regulator of central leptin action in the rat hypothalamus. J Neurochem 100(2):468-78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04219.x
Barrios V, Frago LM, Canelles S, Guerra-Cantera S, Arilla-Ferreiro E, Chowen JA, Argente J (2021) Leptin Modulates the Response of Brown Adipose Tissue to Negative Energy Balance: Implication of the GH/IGF-I Axis. Int J Mol Sci 22(6):2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062827
Dufourny L, Delmas O, Teixeira-Gomes AP, Decourt C, Sliwowska JH (2018) Neuroanatomical connections between kisspeptin neurones and somatostatin neurones in female and male rat hypothalamus: a possible involvement of SSTR1 in kisspeptin release. J Neuroendocrinol 15:e12593. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12593
Proudan N, Peroski M, Grignol G, Merchenthaler I, Dudas B (2015) Juxtapositions between the somatostatinergic and growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) neurons in the human hypothalamus. Neuroscience 297:205-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.054
Masliukov PM, Nozdrachev AD (2021) Hypothalamic Regulatory Mechanisms of Aging. J Evol Biochem Phys 57:473–491. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093021030030
Liu T, Xu Y, Yi CX, Tong Q, Cai D (2021) The hypothalamus for whole-body physiology: from metabolism to aging. Protein Cell 12:1-28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00834-x
Kim K, Choe HK (2019) Role of hypothalamus in aging and its underlying cellular mechanisms. Mech Ageing Dev 177:74-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.04.008
Moiseev KY, Vishnyakova PA, Porseva VV, Masliukov AP, Spirichev AA, Emanuilov AI, Masliukov PM (2020) Changes of nNOS expression in the tuberal hypothalamic nuclei during ageing. Nitric Oxide 100-101:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.04.002
Vishnyakova PA, Moiseev KY, Spirichev AA, Emanuilov AI, Nozdrachev AD, Masliukov PM (2021) Expression of calbindin and calretinin in the dorsomedial and ventromedial hypothalamic nuclei during aging. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 304:1094-1104. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24536
Nozdrachev AD, Masliukov PM (2011) Neuropeptide Y and autonomic nervous system. J Evol Biochem Phys 47:121–130. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1134/S0022093011020010
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 5th Edition. Elsevier Acad Press.
Luo SX, Huang J, Li Q, Mohammad H, Lee CY, Krishna K, Kok AM, Tan YL, Lim JY, Li H, Yeow LY, Sun J, He M, Grandjean J, Sajikumar S, Han W, Fu Y (2018) Regulation of feeding by somatostatin neurons in the tuberal nucleus. Science 361(6397):76-81. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar4983
Jais A, Brüning JC (2021). Arcuate nucleus-dependent regulation of metabolism - pathways to obesity and diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev 42:bnab025. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnab025
Chandrasekharan B, Nezami BG, Srinivasan S (2013) Emerging neuropeptide targets in inflammation: NPY and VIP. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 304(11):G949-G957.
Tewari D, Sah AN, Bawari S, Nabavi SF, Dehpour AR, Shirooie S, Braidy N, Fiebich BL, Vacca RA, Nabavi SM (2021) Role of Nitric Oxide in Neurodegeneration: Function, Regulation, and Inhibition. Curr Neuropharmacol 19(2):114-126. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200429001549
Campbell JN, Macosko EZ, Fenselau H, Pers TH, Lyubetskaya A, Tenen D, Goldman M, Verstegen AM, Resch JM, McCarroll SA, Rosen ED, Lowell BB, Tsai LT (2017) A molecular census of arcuate hypothalamus and median eminence cell types. Nat Neurosci 20(3):484-496. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4495
Yoo ES, Yu J, Sohn JW (2021) Neuroendocrine control of appetite and metabolism. Exp Mol Med 53(4):505-516. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00597-9
Khodai T, Luckman SM (2021) Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Neurons Under the Magnifying Glass. Endocrinology 162(10):bqab141. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqab141
Mele P, Zammaretti F, Longo A, Panzica G, Oberto A, Eva C (2016) Sex-dependent regulation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor gene expression in leptin treated obese (ob/ob) or lean mice. Brain Res 1649:102-109.
Shi Z, Cassaglia PA, Pelletier NE, Brooks VL (2019) Sex differences in the sympathoexcitatory response to insulin in obese rats: role of neuropeptide Y. J Physiol 597(6):1757-1775. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP277517
Bi S, Kim YJ, Zheng F (2012) Dorsomedial hypothalamic NPY and energy balance control. Neuropeptides 46(6):309-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2012.09.002
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 19-15-00039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and experimental design (P.M.M., A.D.N.); data collection (P.A.V., K.Yu.M.); data processing (A.F.B., V.V.P., L.G.P.); writing and editing the manuscript (P.M.M., V.V.P.).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have neither evident nor potential conflict of interest related to the publication of this article.
Additional information
Translated by A. Polyanovsky
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2021, published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 2021, Vol. 107, No. 12, pp. 1530–1541https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869813921120116.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vishnyakova, P.A., Moiseev, K.Y., Porseva, V.V. et al. Somatostatin-Expressing Neurons in the Tuberal Region of Rat Hypothalamus during Aging. J Evol Biochem Phys 57, 1480–1489 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093021060247
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093021060247