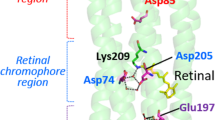
Abstract
In this work, TcaR rhodopsin from the cyanobacterium Tolypothrix campylonemoides was characterized. Analysis of the amino acid sequence of TcaR revealed that this protein possesses a TSD motif that differs by only one amino acid from the TSA motif of the known halorhodopsin chloride pump. The TcaR protein was expressed in E. coli, purified, and incorporated into proteoliposomes and nanodiscs. Functional activity was measured by electric current generation through the planar bilayer lipid membranes (BLMs) with proteoliposomes adsorbed on one side of the membrane surface, as well as by fluorescence using the voltage-dependent dye oxonol VI. We have shown that TcaR rhodopsin functions as a powerful anion pump. Our results show that the novel microbial anion transporter, TcaR, deserves deeper investigation and may be of interest both for fundamental studies of membrane proteins and as a tool for optogenetics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BLM:
-
planar bilayer lipid membrane
- CCCP:
-
carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone
- PLs:
-
proteoliposomes
References
Gushchin, I., and Gordeliy, V. (2018) Microbial rhodopsins, Subcell Biochem., 87, 19-56, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7757-9_2.
Gomez-Consarnau, L., Raven, J. A., Levine, N. M., Cutter, L. S., Wang, D., Seegers, B., Aristegui, J., Fuhrman, J. A., Gasol, J. M., and Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S. A. (2019) Microbial rhodopsins are major contributors to the solar energy captured in the sea, Sci. Adv., 8, eaaw8855, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw8855.
Spudich, J. L., Sineshchekov, O. A., and Govorunova, E. G. (2014) Mechanism divergence in microbial rhodopsins, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1837, 546-552, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.06.006.
Mukherjee, S., Hegemann, P., and Broser, M. (2019) Enzymerhodopsins: novel photoregulated catalysts for optogenetics, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 57, 118-126, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.02.003.
Kirpichnikov, M. P. and Ostrovskiy, M. A. (2019) Optogenetics and vision, Herald Russ. Acad. Sci., 89, 34-38, https://doi.org/10.1134/S1019331619010039.
Luecke, H., Schobert, B., Richter, H. T., Cartailler, J. P., and Lanyi, J. K. (1999) Structure of bacteriorhodopsin at 1.55 A resolution, J. Mol. Biol., 291, 899-911, https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.3027.
Das, S., Singh, D., Madduluri, M., Chandrababunaidu, M. M., Gupta, A., Adhikary, S. P., and Tripathy, S. (2015) Draft genome sequence of bioactive-compound-producing cyanobacterium Tolypothrix campylonemoides strain VB511288, Genome Announc., 3, e00226-15, https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00226-15.
Hasemi, T., Kikukawa, T., Watanabe, Y., Aizawa, T., Miyauchi, S., Kamo, N., and Demura, M. (2019) Photochemical study of a cyanobacterial chloride-ion pumping rhodopsin, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1860, 136-146, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.12.001.
Yun, J. H., Park, J. H., Jin, Z., Ohki, M., Wang, Y., Lupala, C. S., Liu, H., Park, S. Y., and Lee, W. (2020) Structure-based functional modification study of a cyanobacterial chloride pump for transporting multiple anions, J. Mol. Biol., 432, 5273-5286, https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143061.
Astashkin, R., Kovalev, K., Bukhdruker, S., Vaganova, S., Kuzmin, A., Alekseev, A., Balandin, T., Zabelskii, D., Gushchin, I., Royant, A., Volkov, D., Bourenkov, G., Koonin, E., Engelhard, M., Bamberg, E., and Gordeliy, V. (2022) Structural insights into light-driven anion pumping in cyanobacteria, Nat. Commun., 13, 6460, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34019-9.
Oesterhelt, D., Tittor, J., and Bamberg, E. (1992) A unifying concept for ion translocation by retinal proteins, J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 24, 181-191, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762676.
Drachev, L. A., Jasaitis, A. A., Kaulen, A. D., Kondrashin, A. A., Liberman, E. A., Nemecek, I. B., Ostroumov, S. A., Semenov, A. Yu., and Skulachev, V. P. (1974) Direct measurement of electric current generation by cytochrome oxidase, H+-ATPase and bacteriorhodopsin, Nature, 249, 321-324, https://doi.org/10.1038/249321a0.
Drachev, L. A., Frolov, V. N., Kaulen, A. D., Liberman, E. A., Ostroumov, S. A., Plakunova, V. G., Semenov, A. Y., and Skulachev, V. P. (1976) Reconstitution of biological molecular generators of electric current. Bacteriorhodopsin, J. Biol. Chem., 251, 7059-7065, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)32940-X.
Bamberg, E., Apell, H. J., Dencher, N. A., Sperling, W., Stieve, H., and Lauger, P. (1979) Photocurrents generated by bacteriorhodopsin on planar bilayer membranes, Biophys. Struct. Mech., 5, 277-292, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426663.
Bamberg, E., Butt, H. J., Eisenrauch, A., and Fendler, K. (1993) Charge transport of ion pumps on lipid bilayer membranes, Q. Rev. Biophys., 26, 1-25, https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033583500003942.
Friedrich, T., Geibel, S., Kalmbach, R., Chizhov, I., Ataka, K., Heberle, J., Engelhard, M., and Bamberg, E. (2002) Proteorhodopsin is a light-driven proton pump with variable vectoriality, J. Mol. Biol., 321, 821-838, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00696-4.
Shevchenko, V., Mager, T., Kovalev, K., Polovinkin, V., Alekseev, A., Juettner, J., Chizhov, I., Bamann, C., Vavourakis, C., Ghai, R., Gushchin, I., Borshchevskiy, V., Rogachev, A., Melnikov, I., Popov, A., Balandin, T., Rodriguez-Valera, F., Manstein, D. J., Bueldt, G., Bamberg, E., and Gordeliy, V. (2017) Inward H+ pump xenorhodopsin: mechanism and alternative optogenetic approach, Sci. Adv., 3, e1603187, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1603187.
Schuler, M. A., Denisov, I. G., and Sligar, S. G. (2013) Nanodiscs as a new tool to examine lipid-protein interactions, Methods Mol. Biol., 974, 415-433, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-275-9_18.
Rokitskaya, T. I., Maliar, N. L., Siletsky, S. A., Gordeliy, V., and Antonenko, Y. N. (2022) Electrophysiological characterization of microbial rhodopsin transport properties: electrometric and ΔpH measurements using planar lipid bilayer, collodion film, and fluorescent probe approaches, Methods Mol. Biol., 2501, 259-275, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2329-9_12.
Rokitskaya, T. I., Maliar, N., Kovalev, K. V., Volkov, O., Gordeliy, V. I., and Antonenko, Y. N. (2021) Rhodopsin channel activity can be evaluated by measuring the photocurrent voltage dependence in planar bilayer lipid membranes, Biochemistry (Moscow), 86, 409-419, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921040039.
Selwyn, M. J., Dawson, A. P., Stockdale, M., and Gains, N. (1970) Chloride-hydroxide exchange across mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial lipid membranes mediated by trialkyl-and triphenyltin compounds, Eur. J. Biochem., 14, 120-126, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00268.x.
Antonenko, Y. N. (1990) Electrically silent anion transport through bilayer lipid membrane induced by tributyltin and triethyllead, J. Membr. Biol., 113, 109-113, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872884.
Sato, T., Konno, H., Tanaka, Y., Kataoka, T., Nagai, K., Wasserman, H. H., and Ohkuma, S. (1998) Prodigiosins as a new group of H+/Cl– symporters that uncouple proton translocators, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 21455-21462, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.34.21455.
Bamberg, E., Hegemann, P., and Oesterhelt, D. (1984) Reconstitution of the light-driven electrogenic ion-pump halorhodopsin in black lipid membranes, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 773, 53-60, https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(84)90549-2.
Bamberg, E., Tittor, J., and Oesterhelt, D. (1993) Light-driven proton or chloride pumping by halorhodopsin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 639-643, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.2.639.
Antonenko, Y. N., Denisov, S. S., Silachev, D. N., Khailova, L. S., Jankauskas, S. S., Rokitskaya, T. I., Danilina, T. I., Kotova, E. A., Korshunova, G. A., Plotnikov, E. Y., and Zorov, D. B. (2016) A long-linker conjugate of fluorescein and triphenylphosphonium as mitochondria-targeted uncoupler and fluorescent neuro- and nephroprotector, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1860, 2463-2473, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.07.014.
Steiner, M., Oesterhelt, D., Ariki, M., and Lanyi, J. K. (1984) Halide binding by the purified halorhodopsin chromoprotein. I. Effects on the chromophore, J. Biol. Chem., 259, 2179-2184, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)43334-5.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grants 23-24-00038, 21-64-00018) and by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (project AAAA-A19-119031390114-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.I.G. concept of the study; A.A.A., T.I.R., Y.N.A., S.M.B., F.M.Ts. conducting experiments; Y.N.A., V.I.G., T.I.R. writing text of the paper. All authors participated in discussion of the obtained results and editing of the final text of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interests in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rokitskaya, T.I., Alekseev, A.A., Tsybrov, F.M. et al. Retinal-Based Anion Pump from the Cyanobacterium Tolypothrix campylonemoides. Biochemistry Moscow 88, 1571–1579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297923100127
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297923100127