Abstract
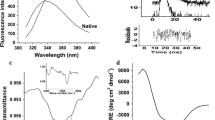
Functionally important multidomain bacterial protein bS1 is the largest ribosomal protein of subunit 30S. It interacts with both mRNA and proteins and is prone to aggregation, although this process has not been studied in detail. Here, we obtained bacterial strains overproducing ribosomal bS1 protein from Thermus thermophilus and its stable fragment bS1(49) and purified these proteins. Using fluorescence spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering, and high-performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometric analysis of products of protein limited proteolysis, we demonstrated that disordered regions at the N- and C-termini of bS1 can play a key role in the aggregation of this protein. The truncated fragment bS1(49) was less prone to aggregation compared to the full-size bS1. The revealed properties of the studied proteins can be used to obtain protein crystals for elucidating the structure of the bS1 stable fragment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bS1(49):
-
a fragment of Thermus thermophilus bS1 protein with a molecular mass of ∼49 kDa
- CD:
-
circular dichroism
- CSD:
-
cold shock domain
- DLS:
-
dynamic light scattering
- EM:
-
electron microscopy
- HPLC/MS:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry
- I320/I380 :
-
ratio of fluorescence intensities at 320 and 380 nm
- m/z :
-
mass-to-charge ratio
References
Chiti, F., and Dobson, C. M. (2006) Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 75, 333–366.
Dovidchenko, N. V., and Galzitskaya, O. V. (2015) Computational approaches to identification of aggregation sites and the mechanism of amyloid growth, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 855, 213–239.
Galzitskaya, O. (2019) New mechanism of amyloid fibril formation, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 20, 630–640.
Solovyov, K. V., Gasteva, A. A., Egorov, V. V., Aleinikova, T. D., Sirotkin, A. K., Shvartsman, A. L., and Shavlovsky, M. M. (2006) Role of the C-terminal fragment of human transthyretin in abnormal fibrillogenesis, Biochemistry (Moscow), 71, 543–549.
Pilla, S. P., Thomas, A., and Bahadur, R. P. (2019) Dissecting macromolecular recognition sites in ribosome: implication to its self-assembly, RNA Biol., 16, 1300–1312.
Pechmann, S., Willmund, F., and Frydman, J. (2013) The ribosome as a hub for protein quality control, Mol. Cell, 49, 411–421.
Chaillou, T. (1985) Ribosome specialization and its potential role in the control of protein translation and skeletal muscle size, J. Appl. Physiol., 127, 599–607.
Schieber, G. L., and O’Brien, T. W. (1982) Extraction of proteins from the large subunit of bovine mitochondrial ribosomes under nondenaturing conditions, J. Biol. Chem., 257, 8781–8787.
Wittmann, H. G., Stofflet, G., Hindennach, I., Kurland, C. G., Birge, E. A., Randall-Hazelbauer, L., Nomura, M., Kaltschmidt, E., Mizushima, S., Traut, R. R., and Bickle, T. A. (1971) Correlation of 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli isolated in different laboratories, Mol. Gen. Genet., 111, 327–330.
Ban, N., Beckmann, R., Cate, J. H., Dinman, J. D., Dragon, F., Ellis, S. R., Lafontaine, D. L., Lindahl, L., Liljas, A., Lipton, J. M., McAlear, M. A., Moore, P. B., Noller, H. F., Ortega, J., Panse, V. G., Ramakrishnan, V., Spahn, C. M., Steitz, T. A., Tchorzewski, M., Tollervey, D., Warren, A. J., Williamson, J. R., Wilson, D., Yonath, A., and Yusupov, M. (2014) A new system for naming ribosomal proteins, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 24, 165–169.
Giri, L., and Subramanian, A. R. (1977) Hydrodynamic properties of protein S1 from Escherichia coli ribosome, FEBS Lett., 81, 199–203.
Laughrea, M., and Moore, P. B. (1977) Physical properties of ribosomal protein S1 and its interaction with the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli, J. Mol. Biol., 112, 399–421.
Tedin, K., Resch, A., and Blasi, U. (1997) Requirements for ribosomal protein S1 for translation initiation of mRNAs with and without a 5′ leader sequence, Mol. Microbiol., 25, 189–199.
Wower, I. K. (2000) Binding and cross-linking of tmRNA to ribosomal protein S1, on and off the Escherichia coli ribosome, EMBO J., 19, 6612–6621.
Deryusheva, E. I., Machulin, A. V., Selivanova, O. M., and Galzitskaya, O. V. (2017) Taxonomic distribution, repeats, and functions of the S1 domain-containing proteins as members of the OB-fold family, Proteins, 85, 602–613.
Bycroft, M., Hubbard, T. J. P., Proctor, M., Freund, S. M. V., and Murzin, A. G. (1997) The solution structure of the S1 RNA binding domain: a member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding fold, Cell, 88, 235–242.
Mihailovich, M., Militti, C., Gabaldyn, T., and Gebauer, F. (2010) Eukaryotic cold shock domain proteins: highly versatile regulators of gene expression, BioEssays, 32, 109–118.
Machulin, A. V., Deryusheva, E. I., Selivanova, O. M., and Galzitskaya, O. V. (2019) The number of domains in the ribosomal protein S1 as a hallmark of the phylogenetic grouping of bacteria, PLoS One, 14, e0221370.
Deriusheva, E. I., Machulin, A. V., Selivanova, O. M., and Serdiuk, I. N. (2010) Family of ribosomal proteins S1 contains unique conservative domain, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 44, 728–734.
Machulin, A., Deryusheva, E., Lobanov, M., and Galzitskaya, O. (2019) Repeats in S1 proteins: flexibility and tendency for intrinsic disorder, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20, 2377.
Subramanian, A. R. (1983) Structure and functions of ribosomal protein S1, Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 28, 101–142.
Sengupta, J., Agrawal, R. K., and Frank, J. (2001) Visualization of protein S1 within the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interaction with messenger RNA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 11991–11996.
Boni, I. V., Artamonova, V. S., and Dreyfus, M. (2000) The last RNA-binding repeat of the Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 is specifically involved in autogenous control, J. Bacteriol., 182, 5872–5879.
Salah, P., Bisaglia, M., Aliprandi, P., Uzan, M., Sizun, C., and Bontems, F. (2009) Probing the relationship between gram-negative and gram-positive S1 proteins by sequence analysis, Nucleic Acids Res., 37, 5578–5588.
Loveland, A. B., and Korostelev, A. A. (2018) Structural dynamics of protein S1 on the 70S ribosome visualized by ensemble cryo-EM, Methods, 137, 55–66.
Cava, F., Hidalgo, A., and Berenguer, J. (2009) Thermus thermophilus as biological model, Extremophiles, 13, 213–231.
Sedelnikova, S. E., Agalarov, S. C., Garber, M. B., and Yusupov, M. M. (1987) Proteins of the Thermus thermophilus ribosome. Purification of several individual proteins and crystallization of protein TL7, FEBS Lett., 220, 227–230.
Shiryaev, V. M., Selivanova, O. M., Hartsch, T., Nazimov, I. V., and Spirin, A. S. (2002) Ribosomal protein S1 from Thermus thermophilus: its detection, identification and overproduction, FEBS Lett., 525, 88–92.
Selivanova, O. M., Shiryaev, V. M., Tiktopulo, E. I., Potekhin, S. A., and Spirin, A. S. (2003) Compact globular structure of Thermus thermophilus ribosomal protein S1 in solution: sedimentation and calorimetric study, J. Biol. Chem., 278, 36311–36314.
Selivanova, O. M., Fedorova, Y. Y., and Serduyk, I. N. (2007) Proteolysis of ribosomal protein S1 from Escherichia coli and Thermus thermophilus leads to formation of two different fragments, Biochemistry (Moscow), 72, 1225–1232.
Timchenko, A. A., Shiriaev, V. M., Fedorova, Yu. Yu., Kikhara, H., Kimura, K., Willumeit, R., Garamus, V. M., and Selivanova, O. M. (2007) Conformation of the ribosomal protein S1 of Thermus thermophilus in solution under different ionic conditions, Biofizika, 52, 216–222.
Theobald, D. L., Mitton-Fry, R. M., and Wuttke, D. S. (2003) Nucleic acid recognition by OB-fold proteins, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 32, 115–133.
Selivanova, O. M., Guryanov, S. G., Enin, G. A., Skabkin, M. A., Ovchinnikov, L. P., and Serdyuk, I. N. (2010) YB-1 is capable of forming extended nanofibrils, Biochemistry (Moscow), 75, 115–120.
Guryanov, S. G., Selivanova, O. M., Nikulin, A. D., Enin, G. A., Melnik, B. S., Kretov, D. A., Serdyuk, I. N., and Ovchinnikov, L. P. (2012) Formation of amyloid-like fibrils by Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) is mediated by its cold shock domain and modulated by disordered terminal domains, PLoS One, 7, e36969.
William Studier, F., Rosenberg, A. H., Dunn, J. J., and Dubendorff, J. W. (1990) Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes, Methods Enzymol., 185, 60–89.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein—dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 72, 248–254.
Gill, S. C., and von Hippel, P. H. (1989) Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data, Anal. Biochem., 182, 319–326.
Savitzky, A., and Golay, M. J. E. (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures, Anal. Biochem., 36, 1627–1639.
Micsonai, A., Wien, F., Bulyaki, E., Kun, J., Moussong, E., Lee, Y.-H., Goto, Y., Refregiers, M., and Kardos, J. (2018) BeStSel: a web server for accurate protein secondary structure prediction and fold recognition from the circular dichroism spectra, Nucleic Acids Res., 46, 315–322.
Balobanov, V. A., Katina, N. S., Finkelstein, A. V., and Bychkova, V. E. (2017) Intermediate states of apomyoglobin: are they parts of the same area of conformations diagram? Biochemistry (Moscow), 82, 625–631.
Surin, A. K., Grishin, S. Yu., and Galzitskaya, O. V. (2019) Identification of amyloidogenic regions in the spine of insulin fibrils, Biochemistry (Moscow), 84, 47–55.
Zhang, J., Xin, L., Shan, B., Chen, W., Xie, M., Yuen, D., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Lajoie, G. A., and Ma, B. (2012) PEAKS DB: de novo sequencing assisted database search for sensitive and accurate peptide identification, Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 11, M111.010587.
Katina, N. S., Suvorina, M. Yu., Grigorashvili, E. I., Marchenkov, V. V., Ryabova, N. A., Nikulin, A. D., and Surin, A. K. (2017) Identification of regions in apomyoglobin which form intermolecular interactions in amyloid aggregates using high-performance mass spectrometry, J. Anal. Chem., 72, 1271–1279.
Selivanova, O. M., Grishin, S. Yu., Glyakina, A. V., Sadgyan, A. S., Ushakova, N. I., and Galzitskaya, O. V. (2018) Analysis of insulin analogues and a strategy for their further development, Biochemistry (Moscow), 83 (Suppl 1), 146–162.
Yusupov, M. M., Garber, M. B., Vasiliev, V. D., and Spirin, A. S. (1991) Thermus thermophilus ribosomes for crystallographic studies, Biochimie, 73, 887–897.
Tung, C. S., and Sanbonmatsu, K. Y. (2004) Atomic model of the Thermus thermophilus 70S ribosome developed in silico, Biophys. J., 87, 2714–2722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project 18-14-00321) with participation of the Center for Collective Use “Structural and Functional Studies of Proteins and RNA” of the Institute of Protein Research, Russian Academy of Sciences (584307). EM studies were carried out using equipment of the Center for Collective Use (no. 670266).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethical standards
This article does not contain any research involving humans or animals as research subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grishin, S.Y., Dzhus, U.F., Selivanova, O.M. et al. Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of Thermus thermophilus Ribosomal Protein bS1 and Its Stable Fragment. Biochemistry Moscow 85, 344–354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920030104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920030104