Abstract
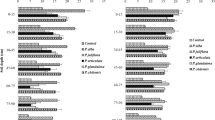
The understanding of relationships between the plants and environmental variables is important for ecological restoration. The objective of this research was to investigate the controlling soil factor in plant growth and salt tolerance of leguminous plant Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. (A. sparsifolia) in a saline desert ecosystem of western China. Results showed that coverage of A. sparsifolia was positively linked to soil total K. A. sparsifolia accumulated the toxic Na+ in either roots or stems and thus reduced their allocation in the leaves to adapt the salt stress. The most important factor that determined Na+ uptake of A. sparsifolia was soil total K content, which suggests that total K can alleviate toxic Na+ accumulation in A. sparsifolia. In addition, there was a significant negative correlation among toxic Cl− concentration in A. sparsifolia, soil total K and pH. Overall, soil total K accounted for 18.2% of plant growth and salt tolerance of A. sparsifolia, followed by soil pH 13.1%, and soil total P 11.6%. In order to restore A. sparsifolia in the degraded desert ecosystems on salinized soil, first we need to consider the effects of soil total K, and then synergistically consider the soil pH and total P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Karaki, G.N., Barley response to salt stress at varied levels of phosphorus, J. Plant Nutr., 1997, vol. 20, pp. 1635–1643.
Antione, G., and Niklaus, E.Z., Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology, Ecol. Model., 2000, vol. 135, pp. 147–186.
Arndt, S.K., Arampatsis, C., Foetzki, A, Li, X.Y., and Zhang, X.M., Contrasting patterns of leaf solute accumulation and salt adaptation in four phreatophytic desert plants in a hyperarid desert with saline groundwater, J. Arid Environ., 2004, vol. 59, pp. 259–270.
Ashworth, L.J., Gaona, S.A., and Surber, E., Nutritional diseases of pistachio trees: potassium and phosphorus deficiencies and chloride and boron toxicities, Phytopathology, 1985, vol. 75, pp. 1084–1091.
Bai, H.X., The response of artificially planted Suaeda corniculata (C.A.Mey.) Bunge. populations to grassland salinization, MSc Thesis, Neimenggu: Inner Mongolia Normal Univ., 2013.
Bao, S.D., Analysis Method of Soil and Agricultural Chemicals, Beijing: Chin. Agric. Sci. Technol. Press, 2000.
Belkheiri, O., and Mulas, M., The effects of salt stress on growth, water relations and ion accumulation in two halophyte Atriplex species, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2013, vol. 86, pp. 17–28.
Eviner, V.T., and Hawkes, C.V., Embracing variability in the application of plant-soil interactions to the restoration of communities and ecosystems, Restor. Ecol., 2008, vol. 16, pp. 713–729.
Fu, B.J., Liu, S.L., Ma, K.M., and Zhu, Y.G., Relationships between soil characteristics, topography and plant diversity in a heterogeneous deciduous broad-leaved forest near Beijing, China, Plant Soil, 2004, vol. 261, pp. 47–54.
Garthwaite, A.J., von Bothmer, R., and Colmer, T.D., Salt tolerance in wild Hordeum species is associated with restricted entry of Na+ and Cl- into the shoots, J. Exp. Bot., 2005, vol. 56, pp. 2365–2378.
Ge, Y.W., Li, Y.C., Bunting, M.J., Li, Z.T., and Wang, J.T., Relation between modern pollen rain, vegetation and climate in northern China: implications for quantitative vegetation reconstruction in a steppe environment, Sci. Total Environ., 2017, vol. 586, pp. 25–41.
Gong, L, Li, C.J., and Tiyip, T., Relations between soil heterogeneity and common reed (Phragmites australis Trin. ex Steud.) colonization in Keriya River Basin, Xinjiang of China, J. Arid Land, 2014, vol. 6, pp. 753–761.
Grattan, S.R., and Grieve, C.M., Salinity-mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops, Sci. Hortic., 1999, vol. 78, 127–157.
Jafari, M., Chahouki, M.A., Tavili, A., Azarnivand, H., and Amiri, G.Z., Effective environmental factors in the distribution of vegetation types in Poshtkouh rangelands of Yazd Province (Iran)., J. Arid Environ., 2004, vol. 56, pp. 627–641.
Jin, Q.H., A study on the characters of content and distribution of K, Na, Ca, Mg elements in Alhagi sparsifolia, Acta Phytoecol. Sin., 1996, vol. 20, pp. 80–84.
Kaya, C., Tuna, A.L., Ashraf, M., and Altunlu, H., Improved salt tolerance of melon (Cucumis melo L.) by the addition of proline and potassium nitrate, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2007, vol. 60, pp. 397–403.
Lenis, J.M., Ellerisieck, M., Blevins, D.G., Selper, D.A., Nguyen, H.T., Dunn, D., Lee, J.D., and Shannon, J.G., Differences in ion accumulation and salt tolerance among glycine accessions, J. Agron. Crop Sci., 2011, vol. 197, pp. 302–310.
Li, C.J., Zeng, F.J., Zhang, B., Liu, B., Guo, Z.C., Gao, H.H., and Tiyip, T., Optimal root system strategies for desert phreatophytic seedlings in the search for groundwater, J. Arid Land, 2015, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 462–474.
Li, H.F., Zeng, F.J., Gui, D.W., Zhang, L.G., Song, C., Luo, W.C., and Peng, S.L., Effects of cutting and burning on regeneration of Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. on the southern fringe of the Taklamakan desert, Northwest China, Rangeland J., 2013, vol. 34, pp. 389–397.
Li, X.F., Wang, J., Huang, D., Wang, L.X., and Wang, K., Allelopathic potential of Artemisia frigida and successional changes of plant communities in the northern China steppe, Plant Soil, 2011, vol. 341, pp. 383–398.
Liu, B., Zeng, F.J., Arndt, S.K., He, J.X., Luo, W.C., and Song, C., Patterns of root architecture adaptation of a phreatophytic perennial desert plant in a hyperarid desert, S. Afr. J. Bot., 2013, vol. 86, pp. 56–62.
Liu, G.F., Freschet, G.T., Pan, X., Cornelissen, J.H.C., Li, Y., and Dong, M., Coordinated variation in leaf and root traits across multiple spatial scales in Chinese semi-arid and arid ecosystems, New Phytol., 2010, vol. 188, pp. 543–553.
Liu, P.L., Hao, L., Pan, C., Zhou, D.H., Liu, Y.Q., and Sun, G., Combined effects of climate and land management on watershed vegetation dynamics in an arid environment, Sci. Total Environ., vol. 589, pp. 73–88.
Liu, X.P., Zhang, W.J., Yang, F., Zhou, X., Liu, Z.J., Qu, F., Lian, S.Q., Wang, C.L., and Tang, X.G., Changes in vegetation-environment relationships over long-term natural restoration process in Middle Taihang Mountain of North China, Ecol. Eng., 2012, vol. 49, pp. 193–200.
Liu, Z., Root distribution of Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. response to different water conditions, MSc Thesis, Xinjiang: Xinjiang Inst. Ecol. Geogr., Chin. Acad. Sci., 2011.
Lu, R.K., Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry, Beijing: Chin. Agric. Sci. Technol. Press, 1999.
Moya, J.L., Primo-Millo, E., and Talon, M., Morphological factors determining salt tolerance in citrus seedlings: the shoot to root ratio modulates passive root uptake of chloride ions and their accumulation in leaves, Plant Cell Environ., 1999, vol. 22, pp. 1425–1433.
Munns, R., Comparative physiology of salt and water stress, Plant Cell Environ., 2002, vol. 25, pp. 239–250.
Munns, R., Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together, New Phytol., 2005, vol. 167, pp. 645–653.
Munns, R., and Tester, M., Mechanisms of salinity tolerance, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2008, vol.59, pp. 651–681.
Nelson, D.W., and Sommers, L.E., A rapid and accurate method for estimating organic carbon in soil, P. Indiana Acad. Sci., 1975, vol. 84, pp. 456–462.
Olsen, S.R., Cole, C.V., Watanabe, F.S., and Dean, L.A., Estimation of available organic carbon in soil, P. Indiana Acad. Sci., 1954, vol. 84, pp. 456–462.
Parkinson, J.A., and Allen, S.E., A wet oxidation procedure suitable for determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material, Commun. Soil Sci. Plan., 1975, vol. 6, pp. 1–11.
Ramoliya, P.J., Patel, H.M., and Pandey, A.N., Effect of salinization of soil on growth and macro- and micronutrient accumulation in seedlings of Salvadora persica (Salvadoraceae), For. Ecol. Manage., 2004, vol. 202, pp. 181–193.
Schelfhout, S., Schrijver, A.D., Bolle, S.D., Gelder, L.D., Demey, A., Pré, T.D., Neve, S.D., Haesaert, G., Verheyen, K., and Mertens, J., Phosphorus mining for ecological restoration on former agricultural land, Restor. Ecol., 2015, vol. 23, pp. 842–851.
Siebert, S., Gries, D., Zhang, X.M., Runge, M., and Buerkert, A., Non-destructive dry matter estimation of Alhagi sparsifolia vegetation in a desert oasis of Northwest China, J. Veg. Sci., 2004, vol. 15, pp. 365–372.
Sonmez, S., Buyuktas, D., Okturen, F., and Citak, S., Assessment of different soil to water ratios (1: 1, 1: 2.5, 1: 5) in soil salinity studies, Geoderma, 2008, vol. 144, pp. 361–369.
Tan, Y., Zhang, H.C., and Fang, S.Z., Distribution of K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in poplar rhizosphere system under NaCl stress, J. Plant Resour. Environ., 2003, vol. 27, pp. 5–9.
Zeng, F.J., Zhang, X.M., Foetzki, A., Li, X.Y., Li, X.M., and Runge, M., Water relation characteristics of Alhagi sparsifolia and consequences for a sustainable management, Sci. China, 2002, vol. 45, pp. 126–131.
Zeng, F.J., Lu, Y., Guo, H.F., Liu, B., Zeng, J., and Zhang, L.G., Ecological characteristics of Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. seedling roots under different irrigation treatments, Russ. J. Ecol., 2012, vol. 43, pp. 196–203.
Zeng, J., Zeng, F.J., Arndt, S.K., Guo, H.F., Yan, H.L., Xing, W.J., and Liu, B., Growth, physiological characteristics and ion distribution of NaCl stressed Alhagi sparsifolia seedlings, Chin. Sci. Bull., 2008, vol. 53, pp. 169–176.
Zhao, Y., Li, X.R., Zhang, Z.S., Hu, Y.G., and Wu, P., Soil-plant relationships in the Hetao irrigation region drainage ditch banks, northern China, Arid Land Res. Manage., 2014, vol. 28, pp. 74–86.
Zheng, Y.H., Ning, T.Y., Jia, A.J., Li, Z.J., Han, B., Jiang, X.D., and Li, W.D., Amortizing functions of potassium nutrition on different genotypes wheat seedling under NaCI stress, Plant Nutr. Ferilt. Sci., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 381–386.
Zuo, X.A., Zhao, X.Y., Zhao, H.L., Zhang, T.H., Guo, Y.R., Li, Y.Q., and Huang, Y.X., Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation-soil relationships following vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China, Plant Soil, 2009, vol. 318, pp. 153–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Gui, D., Gao, X. et al. Controlling Soil Factor in Plant Growth and Salt Tolerance of Leguminous Plant Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. in Saline Deserts, Northwest China. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 11, 111–121 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551801002X
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551801002X