Abstract
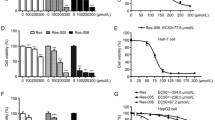
Liver cancer is one of the commonly detected malignancy and third highest cause of deaths caused by cancer worldwide. The current study investigated the effect of triethylsilyl resveratrol on HuH7 and hep3B cell proliferation and explored the underlying mechanism. The viability of HuH7 and hep3B cells was suppressed to 23 and 18%, respectively on exposure to 2 µM triethylsilyl resveratrol for 72 h. Triethylsilyl resveratrol treatment of HuH7 cells led to a prominent increase in expression of Atg-5, LC3B-II and Beclin proteins. In triethylsilyl resveratrol treated HuH7 cells expression of activated PI3K and Akt proteins showed a prominent decrease compared to the control cells. Moreover, p-mTOR protein expression was also suppressed in HuH7 cells on treatment with 2 µM triethylsilyl resveratrol. In triethylsilyl resveratrol treated cells a marked increase in ERK1/2 phosphorylation was observed compared to the control cells. Treatment with 2 µM triethylsilyl resveratrol for 72 h led to a significant (p < 0.05) increase in GFP-LC3B labelling in HuH7 cells compared to the control cells. Thus, triethylsilyl resveratrol reduced liver cancer cell viability through increase expression of proteins associated with autophagy. Moreover, it increased p-ERK1/2 expression and targeted activation of PI3K/Akt protein in HuH7 cells. Therefore, triethylsilyl resveratrol may be studied further as a promising therapeutic agent for treatment of liver cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Fremont, L., Minireview: biological effects of resveratrol, Life Sci., 2000, vol. 66, no. 8, pp. 663–673.
Vervandier-Fasseur, D. and Latruffe, N., The potential use of resveratrol for cancer prevention, Molecules, 2019, vol. 24.
Zhang, L, Yu, X., Ji, M., Liu, S., Wu, X., Wang, Y., and Liu, R., Resveratrol alleviates motor and cognitive deficits and neuropathology in the A53T a-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, Food Funct., 2018, vol. 9, pp. 6414–6426.
Hernandez‑Gea, V., Turon, F., Berzigotti, A., and Villanueva, A., Management of small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: focus on portal hypertension, World J. Gastroenterol., 2013, vol. 19, pp. 1193–1199.
Yang, L.Y., Fang, F., Ou, D.P., Wu, W., Zeng, Z.J., and Wu, F., Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: a specific subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma with good outcome after hepatic resection, Ann. Surg., 2009, vol. 249, pp. 118–123.
Lee, T.K., Castilho, A., Ma, S., and Ng, I.O., Liver cancer stem cells: implications for a new therapeutic target, Liver Int., 2009, vol. 29, pp. 955–965.
Chuang, W.-L., Su, C.-C., Lin, P.-Y., Lin, C.-C., and Chen, Y.-L., Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang induces autophagy in HepG2 cells via regulation of the phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, Mol. Med. Rep., 2015, vol. 12, pp. 1677–1684.
Yamamoto, M, Suzuki, S.O., and Himeno, M., Resveratrol‑induced autophagy in human U373 glioma cells, Oncol. Lett., 2010, vol. 1, pp. 489–493.
Zhang, D.M., Liu, J.S., Deng, L.J., et al., Arenobufagin, a natural bufadienolide from toad venom, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, Carcinogenesis, 2013, vol. 34, pp. 1331–1342.
Miao, Q., Bi, L.L., Li, X., et al., Anticancer effects of bufalin on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells: roles of apoptosis and autophagy, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013, vol. 14, pp. 1370–1382.
Shimizu, S., Yoshida, T., Tsujioka, M., and Arakawa, S., Autophagic cell death and cancer, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2014, vol. 15, pp. 3145–3153.
Hu, W., Chen, S.S., Zhang, J.L., Lou, X.E., and Zhou, H.J., Dihydroartemisinin induces autophagy by suppressing NF‑κB activation, Cancer Lett., 2014, vol. 343, pp. 239–248.
Hu, C., Zou, M.J., Zhao, L., et al., E Platinum, a newly synthesized platinum compound, induces autophagy via inhibiting phosphorylation of mTOR in gastric carcinoma BGC‑823 cells, Toxicol. Lett., 2012, vol. 210, pp. 78–86.
Bincoletto, C., Bechara, A., Pereira, G.J., et al., Interplay between apoptosis and autophagy, a challenging puzzle: new perspectives on antitumor chemotherapies, Chem. Biol. Interact., 2013, vol. 206, pp. 279–288.
Wu, Y.T., Tan, H.L., Huang, Q., Ong, C.N., and Shen, H.M., Activation of the PI3K‑Akt‑mTOR signaling pathway promotes necrotic cell death via suppression of autophagy, Autophagy, 2009, vol. 5, pp. 824–834.
Fan, M. and Chambers, T.C., Role of mitogen‑activated protein kinases in the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy, Drug Resist. Updat., 2001, vol. 4, pp. 253–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Li, J. Inhibition of Liver Cancer Cell Growth by Triethylsilyl Resveratrol through Targeting Phosphoinositide-3 Kinase Pathway. Dokl Biochem Biophys 501, 449–453 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672921060065
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672921060065