Abstract
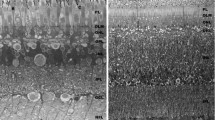
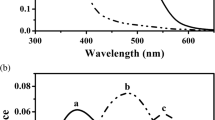
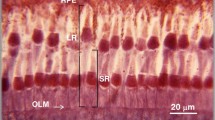
Photoreceptor composition and retinal visual pigments in three newt (Caudata, Salamandridae, Pleurodelinae) species (Pleurodeles waltl, Lissotriton (Triturus) vulgaris, and Cynops orientalis) were studied by light microscopy and single-cell microspectrophotometry. Retinas of all three species contain “red” (rhodopsin/porphyropsin) rods, large and small single cones, and double cones. Large single cones and both components of double cones contain red-sensitive (presumably LWS) visual pigment whose absorption spectrum peaks between 593 and 611 nm. Small single cones are either blue- (SWS2, maximum absorption between 470 and 489 nm) or UV-sensitive (SWS1, maximum absorption between 340 and 359 nm). Chromophore composition of visual pigments (A1 vs. A2) was assessed both from template fitting of absorption spectra and by the method of selective bleaching. All pigments contained a mixture of A1 (11-cis retinal) and A2 (11-cis-3,4-dehydroretinal) chromophore in the proportion depending on the species and cell type. In all cases, A2 was dominant. However, in C. orientalis rods the fraction of A1 could reach 45%, while in P. waltl and L. vulgaris cones it did not exceed 5%. Remarkably, the absorption of the newt blue-sensitive visual pigment was shifted by up to 45 nm toward the longer wavelength, as compared with all other amphibian SWS2-pigments. We found no “green” rods typical of retinas of Anura and some Caudata (ambystomas) in the three newt species studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohun, S.M., Davies, W.L., Bowmaker, J.K., Pisani, D., Himstedt, W., Gower, D.J., Hunt, D.M., and Wilkinson, M., Identification and Characterization of Visual Pigments in Caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona), an Order of Limbless Vertebrates with Rudimentary Eyes, J. Exp. Biol., 2010, vol. 213, pp. 3586–3592.
Walls, G.L., The Vertebrate Eye and Its Adaptive Radiation, Bloomfield Hills, Mich. Cranbrook Institute of Science, 1942, 785 p.
Crescitelli, F., The Visual Cells and Visual Pigments of the Vertebrate Eye, Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol. VII/1, Dartnall, H.J.A., Ed., Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer Verlag, 1972, pp. 245–363.
Sherry, D.M., Bui, D.D., and DeGrip, W.J., Identification and Distribution of Photoreceptor Subtypes in the Neotenic Tiger Salamander Retina, Vis. Neurosci., 1998, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 1175–1187.
Röhlich, P. and Szél, A., Photoreceptor Cells in the Xenopus Retina, Microsc. Res. Tech., 2000, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 327–337.
Zhang, J. and Wu, S.M., Immunocytochemical Analysis of Photoreceptors in the Tiger Salamander Retina, Vision Res., 2009, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 64–73.
Yokoyama, S., Molecular Evolution of Vertebrate Visual Pigments, Prog. Retin. Eye Res., 2000, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 385–419.
Bowmaker, J.K., Evolution of Vertebrate Visual Pigments, Vision Res., 2008, vol. 48, no. 20, pp. 2022–2041.
Collin, S.P.., Davies, W.L., Hart, N.S., and Hunt, D.M., The Evolution of Early Vertebrate Photoreceptors, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci., 2009, vol. 364, no. 1531, pp. 2925–2940.
Shichida, Y. and Matsuyama, T., Evolution of Opsins and Phototransduction, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci., 2009, vol. 364, no. 1531, pp. 2881–2895.
Bridges, C.D.B., The Rhodopsin-Porphyropsin Visual System, Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol. VII/1, Ed. H.J.A. Dartnall, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer Verlag, 1972, pp. 417–480.
Donner, K.O. and Reuter, T., Visual Pigments and Photoreceptor Function, Llinas, R. and Precht, W., Eds., Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer, 1976, pp. 251–277.
Lythgoe, J.N., List of Vertebrate Pigments, Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol. VII/1, Dartnall, H.J.A., Ed., Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer Verlag, 1972, pp. 604–624.
Sakakibara, S., Hiramatsu, H., Takahashi, Y., Hisatomi, O., Kobayashi, Y., Sakami, S., Saito, T., and Tokunaga, F., Opsin Expression in Adult, Developing, and Regenerating Newt Retinas, Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 2002, vol. 103, no. 1–2, pp. 28–35.
Makino, C.L., Taylor, W.R., and Baylor, D.A., Rapid Charge Movements and Photosensitivity of Visual Pigments in Salamander Rods and Cones, J. Physiol., 1991, vol. 442, pp. 761–780.
Perry, R.J. and McNaughton, P.A., Response Properties of Cones from the Retina of the Tiger Salamander, J. Physiol., 1991, vol. 433, pp. 561–587.
Govardovskii, V.I., Fyhrquist, N., Reuter, T., Kuzmin, D.G., and Donner, K., In Search of the Visual Pigment Template, Vis. Neurosci., 2000, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 509–528.
Deutschlander, M.E. and Phillips, J.B., Characterization of an Ultraviolet Photoreception Mechanism in the Retina of an Amphibian, the Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum), Neurosci. Lett., 1995, vol. 197, no. 2, pp. 93–96.
Govardovskii, V.P., Zueva, L.V., Kiseleva, E.I., and Margulis, S.E., Organ zreniya, Sibirskii uglozub: zoogeografiya, sistematika, morfologiya (Vision Organ, Siberian Salamander: Zoogeography, Taxonomy, Morphology), Vorobieva, E.I., Ed., Moscow, Nauka, 1994, pp. 296–307.
Koskelainen, A., Hemilä, S., and Donner, K., Spectral Sensitivities of Short- and Long-Wavelength Sensitive Cone Mechanisms in the Frog Retina, Acta. Physiol. Scand., 1994, vol. 152, no. 1, pp. 115–124.
Ma, J., Znoiko, S., Othersen, K.L., Ryan, J.C., Das, J., Isayama, T., Kono, M., Oprian, D.D., Corson, D.W., Cornwall, M.C., Cameron, D.A., Harosi, F.I., Makino, C.L., and Crouch, R.K., A Visual Pigment Expressed in both Rod and Cone Photoreceptors, Neuron, 2001, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 451–461.
Takahashi, Y., Hisatomi, O., Sakakibara, S., Tokunaga, F., and Tsukahara, Y., Distribution of Blue-Sensitive Photoreceptors in Amphibian Retinas, FEBS Lett., 2001, vol. 501, no. 2–3, pp. 151–155.
Chen, Y., Znoiko, S., DeGrip, W.J., Crouch, R.K., and Ma, J.X., Salamander Blue-Sensitive Cones Lost during Metamorphosis, Photochem. Photobiol., 2008, vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 855–862.
Denton, E.J. and Wyllie, J.H., Study of the Photosensitive Pigments in the Pink and Green Rods of the Frog, J. Physiol., 1955, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 81–89.
Dartnall, H.J., The Visual Pigment of the Green Rods, Vision Res., 1967, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–16.
Liebman, P.A., Microspectrophotometry of Photoreceptors, Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol. VII/1, Dartnall, H.J.A., Ed., Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer Verlag, 1972, pp. 481–528.
Witkovsky, P., Yang, C.Y., and Ripps, H., Properties of a Blue-Sensitive Rod in the Xenopus Retina, Vision Res., 1981, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 875–883.
Matthews, G., Physiological Characteristics of Single Green Rod Photoreceptors from Toad Retina, J. Physiol., 1983, vol. 342, pp. 347–359.
Makino-Tasaka, M. and Suzuki, T., The Green Rod Pigment of the Bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, Vision Res., 1984, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 309–322.
Hisatomi, O., Takahashi, Y., Taniguchi, Y., Tsukahara, Y., and Tokunaga, F., Primary Structure of a Visual Pigment in Bullfrog Green Rods, FEBS Lett., 1999, vol. 447, no. 1, pp. 44–48.
Darden, A.G., Wu, B.X., Znoiko, S.L., Hazard, E.S. 3rd, Kono, M., Crouch, R.K., and Ma, J.X., A Novel Xenopus SWS2, P434 Visual Pigment: Structure, Cellular Location, and Spectral Analyses, Mol. Vis., 2003, vol. 9, pp. 191–199.
Nilsson, S.E., An Electron Microscopic Classification of the Retinal Receptors of the Leopard Frog (Rana pipiens), J. Ultrastruct. Res., 1964, vol. 10, pp. 390–416.
Ala-Laurila, P., Kolesnikov, A.V., Crouch, R.K., Tsina, E., Shukolyukov, S.A., Govardovskii, V.I., Koutalos, Y., Wiggert, B., Estevez, M.E., and Cornwall, M.C., Visual Cycle: Dependence of Retinol Production and Removal on Photoproduct Decay and Cell Morphology, J. Gen. Physiol., 2006, vol. 128, no. 2, pp. 153–169.
Liebman, P.A. and Entine, G., Visual Pigments of Frog and Tadpole (Rana pipiens), Vision Res., 1968, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 761–775.
Harosi, F.I., Recent Results from Single-Cell Microspectrophotometry: Cone Pigments in Frog, Fish, and Monkey, Color Res. Appl., 1982, vol. 7, pp. 135–141.
Babu, K.R., Dukkipati, A., Birge, R.R., and Knox, B.E., Regulation of Phototransduction in Short-Wavelength Cone Visual Pigments via the Retinylidene Schiff Base Counterion, Biochemistry, 2001, vol. 40, no. 46, pp. 13760–13766.
Muntz, W.R.A., Phototaxis and Green Rods in Urodeles, Nature, 1963, vol. 199, p. 620.
Himstedt, W., Helas, A., and Sommer, T.J., Projections of Color Coding Retinal Neurons in Urodele Amphibians, Brain Behavol. Evol., 1981, vol. 18, no. 1–2, pp. 19–32.
Przyrembel, C., Keller, B., and Neumeyer, C., Trichromatic Color Vision in the Salamander (Salamandra salamandra), J. Comp. Physiol. A, 1995, vol. 176, pp. 575–586.
Govardovskii, V.I. and Zueva, L.V., High-Rate Microspectrophotometer for Study of Photolysis of Visual Pigments in situ, Sensor. Sist., 2000, vol. 14, pp. 288–296.
Denton, E.J. and Pirenne, M.H., Green Coloured Rods and Retinal Sensitivity, J. Physiol., 1952, vol. 116, no. 3, pp. 33–34.
Donner, K.O. and Rushton, W.A., Rod-Cone Interaction in the Frog’s Retina Analysed by the Stilles-Crawford Effect and by Dark Adaptation, J. Physiol., 1959, vol. 149, pp. 303–317.
Takahashi, Y. and Ebrey, T.G., Molecular Basis of Spectral Tuning in the Newt Short Wavelength Sensitive Visual Pigment, Biochemistry, 2003, vol. 42, no. 20, pp. 6025–6034.
Harosi, F.I., Absorption Spectra and Linear Dichroism of Some Amphibian Photoreceptors, J. Gen. Physiol., 1975, vol. 66, no. 3, pp. 357–382.
Keefe, J.R., The Fine Structure of the Retina in the Newt, Triturus viridescens, J. Exp. Zool., 1971, vol. 177, no. 3, pp. 263–293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.A. Korenyak, V.I. Govardovskii, 2013, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2013, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 264–271.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korenyak, D.A., Govardovskii, V.I. Photoreceptors and visual pigments in three species of newts. J Evol Biochem Phys 49, 399–407 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093013040038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093013040038