Abstract
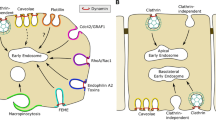
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is the most specific pathway for macromolecules and macromolecular complexes generally designated as ligands to enter cells. Upon binding to their transmembrane receptors, the ligands enter endocytic vesicles that fuse with each other giving rise to the so-called early endosomes. The sorting of ligand-receptor complexes internalized in these endosomes depends on their nature: metabolic receptors are recycled back to the plasma membrane, while signaling receptors and their ligands (e.g. receptor tyrosine kinases or receptors associated with tyrosine kinase) are delivered to internal vesicles of the multivesicular late endosomes and finally are degraded after interaction with lysosomes. During these processes, endosomes undergo translocation from the cell periphery to the juxtanuclear region, which is accompanied by multiple fusion, invagination, tabulation, and membrane fission events. This review considers modern concepts of the sorting mechanisms of ligand-receptor complexes, the crosstalk between endosomes, microtubules, and actin, and the role of this crosstalk in endosome maturation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EE:
-
early endosomes
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- JNR:
-
juxtanuclear region
- LDL:
-
low density lipoproteins
- LE:
-
late endosomes
- MT:
-
microtubules
- MVBs:
-
multivesicular bodies
- PI3P:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3-monophosphate
- TGN:
-
trans-Golgi network
References
Stahl, P., and Schwartz, A. L. (1986) Receptor-mediated endocytosis, J. Clin. Invest., 77, 657–662.
Sorkin, A. (2004) Cargo recognition during clathrin-mediated endocytosis: a team effort, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 16, 392–399.
Marks, M. S., Woodruff, L., Ohio, H., and Bonifacino, J. S. (1996) Protein targeting by tyrosine- and di-leucine-based signals: evidence for distinct saturable components, J. Cell Biol., 135, 341–354.
Shen, D., Wang, X., and Xu, H. (2011) Pairing phosphoinositides with calcium ions in endolysosomal dynamics: phosphoinositides control the direction and specificity of membrane trafficking by regulating the activity of calcium channels in the endolysosomes, Bioessays, 33, 448–457.
Abe, K., and Puertollano, R. (2011) Role of TRP channels in the regulation of the endosomal pathway, Physiology (Bethesda), 26, 14–22.
Vina-Vilaseca, A., Bender-Sigel, J., Sorkina, T., Closs, E. I., and Sorkin, A. (2011) Protein kinase C-dependent ubiquitination and clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 8697–8706.
Mousavi, S. A., Malerod, L., Berg, T., and Kjeken, R. (2004) Clathrin-dependent endocytosis, Biochem. J., 377, 1–16.
Gruenberg, J., Griffiths, G., and Howell, K. E. (1989) Characterization of the early endosome and putative endocytic carrier vesicles in vivo and with an assay of vesicle fusion in vitro, J. Cell Biol., 108, 1301–1316.
Ali, N., and Evans, W. H. (1990) Priority targeting of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins to the bilecanalicular (apical) plasma membrane of hepatocytes. Involvement of “late” endosomes, Biochem. J., 271, 193–199.
Sorkin, A., Krolenko, S., Kudrjavtceva, N., Lazebnik, J., Teslenko, L., Soderquist, A. M., and Nikolsky, N. (1991) Recycling of epidermal growth factor-receptor complexes in A431 cells: identification of dual pathways, J. Cell Biol., 112, 55–63.
Scott, C. C., Vacca, F., and Gruenberg, J. (2014) Endosome maturation, transport and functions, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., pii: S1084-9521(14)00070-6.
Linderman, J. J., and Lauffenburger, D. A. (1986) Analysis of intracellular receptor/ligand sorting. Calculation of mean surface and bulk diffusion times within a sphere, Biophys. J., 50, 295–305.
Forgac, M., Cantley, L., Wiedenmann, B., Altstiel, L., and Branton, D. (1983) Clathrin-coated vesicles contain an ATP-dependent proton pump, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 80, 1300–1303.
Ostlund, R. E., Jr., Pfleger, B., and Schonfeld, G. (1979) Role of microtubules in low density lipoprotein processing by cultured cells, J. Clin. Invest., 63, 75–84.
Hopkins, C. R., Miller, K., and Beardmore, J. M. (1985) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and epidermal growth factor receptors: a comparison of constitutive and ligand-induced uptake, J. Cell. Sci. Suppl., 3, 173–186.
Felder, S., Miller, K., Moehren, G., Ullrich, A., Schlessinger, J., and Hopkins, C. R. (1990) Kinase activity controls the sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor within the multivesicular body, Cell, 61, 623–634.
Van Weering, J. R., and Cullen, P. J. (2014) Membrane-associated cargo recycling by tubule-based endosomal sorting, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., pii: S1084-9521(14)00043-3.
Woodman, P. G., and Futter, C. E. (2008) Multivesicular bodies: coordinated progression to maturity, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 20, 408–414.
Gonnord, P., Blouin, C. M., and Lamaze, C. (2012) Membrane trafficking and signaling: two sides of the same coin, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 23, 154–164.
Luzio, J. P., Gray, S. R., and Bright, N. A. (2010) Endosome-lysosome fusion, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 38, 1413–1416.
Aniento, F., Emans, N., Griffiths, G., and Gruenberg, J. (1993) Cytoplasmic dynein-dependent vesicular transport from early to late endosomes, J. Cell Biol., 123, 1373–1387.
Herman, B., and Albertini, D. F. (1984) A time-lapse video image intensification analysis of cytoplasmic organelle movements during endosome translocation, J. Cell Biol., 98, 565–576.
Wacker, I., Kaether, C., Kromer, A., Migala, A., Almers, W., and Gerdes, H. H. (1997) Microtubule-dependent transport of secretory vesicles visualized in real time with a GFP-tagged secretory protein, J. Cell Sci., 110, 1453–1463.
Bryantseva, S. A., and Zhapparova, O. N. (2012) Bidirectional transport of organelles: unity and struggle of opposing motors, Cell Biol. Int., 36, 1–6.
Barr, F., and Lambright, D. G. (2010) Rab GEFs and GAPs, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 22, 461–470.
Pfeffer, S. R. (2001) Rab GTPases: specifying and deciphering organelle identity and function, Trends Cell Biol., 11, 487–491.
Cai, H., Reinisch, K., and Ferro-Novick, S. (2007) Coats, tethers, Rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle, Dev. Cell, 12, 671–682.
Markgraf, D. F., Peplowska, K., and Ungermann, C. (2007) Rab cascades and tethering factors in the endomembrane system, FEBS Lett., 581, 2125–2130.
Hutagalung, A. H., and Novick, P. J. (2011) Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology, Physiol. Rev., 91, 119–149.
Sonnichsen, B., De Renzis, S., Nielsen, E., Rietdorf, J., and Zerial, M. J. (2000) Distinct membrane domains on endosomes in the recycling pathway visualized by multicolor imaging of Rab4, Rab5, and Rab11, Cell Biol., 149, 901–914.
Stenmark, H., Parton, R. G., Steele-Mortimer, O., Lutcke, A., Gruenberg, J., and Zerial, M. (1994) Inhibition of rab5 GTPase activity stimulates membrane fusion in endocytosis, EMBO J., 13, 1287–1296.
Zeigerer, A., Gilleron, J., Bogorad, R. L., Marsico, G., Nonaka, H., Seifert, S., Epstein-Barash, H., Kuchimanchi, S., Peng, C. G., Ruda, V. M., Del Conte-Zerial, P., Hengstler, J. G., Kalaidzidis, Y., Koteliansky, V., and Zerial, M. (2012) Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo, Nature, 485, 465–470.
Rink, J., Ghigo, E., Kalaidzidis, Y., and Zerial, M. (2005) Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes, Cell, 122, 735–749.
Chaineau, M., Ioannou, M. S., and McPherson, P. S. (2013) Rab35: GEFs, GAPs and effectors, Traffic, 14, 1109–1117.
Zhu, H., Liang, Z., and Li, G. (2009) Rabex-5 is a Rab22 effector and mediates a Rab22-Rab5 signaling cascade in endocytosis, Mol. Biol. Cell, 20, 4720–4729.
Zhang, C., Li, A., Zhang, X., and Xiao, H. (2011) A novel TIP30 protein complex regulates EGF receptor signaling and endocytic degradation, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 9373–9381.
Barbieri, M. A., Fernandez-Pol, S., Hunker, C., Horazdovsky, B. H., and Stahl, P. D. (2004) Role of rab5 in EGF receptor-mediated signal transduction, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 83, 305–314.
Shin, H. W., Hayashi, M., Christoforidis, S., Lacas-Gervais, S., Hoepfner, S., Wenk, M. R., Modregger, J., Uttenweiler-Joseph, S., Wilm, M., Nystuen, A., Frankel, W. N., Solimena, M., De Camilli, P., and Zerial, M. (2005) An enzymatic cascade of Rab5 effectors regulates phosphoinositide turnover in the endocytic pathway, J. Cell Biol., 170, 607–618.
Birkeland, H. C., and Stenmark, H. (2004) Protein targeting to endosomes and phagosomes via FYVE and PX domains, Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol., 282, 89–115.
Lawe, D. C., Chawla, A., Merithew, E., Dumas, J., Carrington, W., Fogarty, K., Lifshitz, L., Tuft, R., Lambright, D., and Corvera, S. (2002) Sequential roles for phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate and Rab5 in tethering and fusion of early endosomes via their interaction with EEA1, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 8611–8617.
Hickey, C. M., and Wickner, W. (2010) HOPS initiates vacuole docking by tethering membranes before trans-SNARE complex assembly, Mol. Biol. Cell, 21, 2297–2305.
Haft, C. R., de la Luz Sierra, M., Barr, V. A., Haft, D. H., and Taylor, S. I. (1998) Identification of a family of sorting nexin molecules and characterization of their association with receptors, Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 7278–7287.
Van Weering, J. R., Verkade, P., and Cullen, P. J. (2010) SNX-BAR proteins in phosphoinositide-mediated, tubular-based endosomal sorting, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 21, 371–380.
Carlton, J., Bujny, M., Peter, B. J., Oorschot, V. M., Rutherford, A., Mellor, H., Klumperman, J., McMahon, H. T., and Cullen, P. J. (2004) Sorting nexin-1 mediates tubular endosome-to-TGN transport through coincidence sensing of high-curvature membranes and 3-phosphoinositides, Curr. Biol., 14, 1791–1800.
Skanland, S. S., Walchli, S., Brech, A., and Sandvig, K. (2009) SNX4 in complex with clathrin and dynein: Implications for endosome movement, PLoS ONE, 4, e5935.
Gullapalli, A., Garrett, T. A., Paing, M. M., Griffin, C. T., Yang, Y., and Trejo, J. (2004) A role for sorting nexin 2 in epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation: evidence for distinct functions of sorting nexin 1 and 2 in protein trafficking, Mol. Biol. Cell, 15, 2143–2155.
Chin, L. S., Raynor, M. C., Wei, X., Chen, H. Q., and Li, L. (2001) Hrs interacts with sorting nexin 1 and regulates degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 7069–7078.
Traer, C. J., Rutherford, A. C., Palmer, K. J., Wassmer, T., Oakley, J., Attar, N., Carlton, J. G., Kremerskothen, J., Stephens, D. J., and Cullen, P. J. (2007) SNX4 coordinates endosomal sorting of TfnR with dynein-mediated transport into the endocytic recycling compartment, Nat. Cell Biol., 9, 1370–1380.
Wassmer, T., Attar, N., Harterink, M., van Weering, J. R., Traer, C. J., Oakley, J., Goud, B., Stephens, D. J., Verkade, P., Korswagen, H. C., and Cullen, P. J. (2009) The retromer coat complex coordinates endosomal sorting and dyneinmediated transport, with carrier recognition by the tans-Golgi network, Dev. Cell, 17, 110–122.
Bowtell, D. D., and Langdon, W. Y. (1995) The protein product of the c-cbl oncogene rapidly complexes with the EGF receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated following EGF stimulation, Oncogene, 11, 1561–1567.
Huang, F., Kirkpatrick, D., Jiang, X., Gygi, S., and Sorkin, A. (2006) Differential regulation of EGF receptor internalization and degradation by multiubiquitination within the kinase domain, Mol. Cell, 21, 737–748.
De Melker, A. A., van der Horst, G., Calafat, J., Jansen, H., and Borst, J. (2001) c-Cbl ubiquitinates the EGF receptor at the plasma membrane and remains receptor associated throughout the endocytic route, J. Cell Sci., 114, 2167–2178.
Melikova, M. S., Kondratov, K. A., and Kornilova, E. S. (2006) Two different stages of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor endocytosis are sensitive to free ubiquitin depletion produced by proteasome inhibitor MG132, Cell Biol. Int., 30, 31–43.
Wright, M. H., Berlin, I., and Nash, P. D. (2011) Regulation of endocytic sorting by ESCRT-DUB-mediated deubiquitination, Cell Biochem. Biophys., 60, 39–46.
Kondratov, K. A., Chernorudsky, A. L., Amosova, A. P., and Kornilova, E. S. (2009) Analysis of the effect of Tyrphostin AF1478 on the behavior of internalized EGF receptor at different stages of endocytosis, Tsitologiya, 51, 520–525.
Raiborg, C., Bremnes, B., Mehlum, A., Gillooly, D. J., D’Arrigo, A., Stang, E., and Stenmark, H. (2001) FYVE and coiled-coil domains determine the specific localization of Hrs to early endosomes, J. Cell Sci., 114, 2255–2263.
Mageswaran, S. K., Dixon, M. G., Curtiss, M., Keener, J. P., and Babst, M. (2014) Binding to any ESCRT can mediate ubiquitin-independent cargo sorting, Traffic, 15, 212–229.
Lim, J., Son, W. S., Park, J. K., Kim, E. E., Lee, B. J., and Ahn, H. C. (2011) Solution structure of UIM and interaction of tandem ubiquitin binding domains in STAM1 with ubiquitin, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 405, 24–30.
Kato, M., Miyazawa, K., and Kitamura, N. (2000) A deubiquitinating enzyme UBPY interacts with the Src homology 3 domain of Hrs-binding protein via a novel binding motif PX(V/I)(D/N)RXXKP, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 37481–37487.
Raiborg, C., Wesche, J., Malerd, L., and Stenmark, H. (2006) Flat clathrin coats on endosomes mediate degradative protein sorting by scaffolding Hrs in dynamic microdomains, J. Cell Sci., 119, 2414–2424.
Chin, L. S., Raynor, M. C., Wei, X., Chen, H. Q., and Li, L. (2001) Hrs interacts with sorting nexin 1 and regulates degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 7069–7078.
Stern, K. A., Visser-Smit, G. D., Place, T. L., Winistorfer, S., Piper, R. C., and Lill, N. L. (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor fate is controlled by Hrs tyrosine phosphorylation sites that regulate Hrs degradation, Mol. Cell Biol., 27, 888–898.
Hoeller, D., Crosetto, N., Blagoev, B., Raiborg, C., Tikkanen, R., Wagner, S., Kowanetz, K., Breitling, R., Mann, M., Stenmark, H., and Dikic, I. (2006) Regulation of ubiquitin-binding proteins by monoubiquitination, Nat. Cell Biol., 8, 163–169.
Sun, W., Yan, Q., Vida, T. A., and Bean, A. J. (2003) Hrs regulates early endosome fusion by inhibiting formation of an endosomal SNARE complex, J. Cell Biol., 162, 125–137.
Yan, Q., Sun, W., McNew, J. A., Vida, T. A., and Bean, A. J. (2004) Ca2+ and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor differentially regulate disassembly of SNARE complexes on early endosomes, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 18270–18276.
Hurley, J. H. (2008) ESCRT complexes and the biogenesis of multivesicular bodies, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 20, 4–11.
Slagsvold, T., Pattni, K., Malerod, L., and Stenmark, H. (2006) Endosomal and non-endosomal functions of ESCRT proteins, Trends Cell Biol., 16, 317–326.
Hurley, J. H., and Emr, S. D. (2006) The ESCRT complexes: structure and mechanism of a membrane-trafficking network, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 35, 277–298.
Williams, R. L., and Urbe, S. (2007) The emerging shape of the ESCRT machinery, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 8, 355–368.
Vaccari, T., Rusten, T. E., Menut, L., Nezis, I. P., Brech, A., Stenmark, H., and Bilder, D. (2009) Comparative analysis of ESCRT-I, ESCRT-II and ESCRT-III function in Drosophila by efficient isolation of ESCRT mutants, J. Cell Sci., 122, 2413–2423.
Adell, M. A. Y., and Teis, D. (2011) Assembly and disassembly of the ESCRT-III membrane scission complex, FEBS Lett., 585, 3191–3196.
Horgan, C. P., and McCaffrey, M. W. (2011) Rab GTPases and microtubule motors, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 39, 1202–1206.
Schonteich, E., Wilson, G. M., Burden, J., Hopkins, C. R., Anderson, K., Goldenring, J. R., and Prekeris, R. (2008) The Rip11/Rab11-FIP5 and kinesin II complex regulates endocytic protein recycling, J. Cell Sci., 121, 3824–3833.
Hoepfner, S., Severin, F., Cabezas, A., Habermann, B., Runge, A., Gillooly, D., Stenmark, H., and Zerial, M. (2005) Modulation of receptor recycling and degradation by the endosomal kinesin KIF16B, Cell, 121, 437–450.
Bielli, A., Thornqvist, P. O., Hendrick, A. G., Finn, R., Fitzgerald, K., and McCaffrey, M. W. (2001) The small GTPase Rab4A interacts with the central region of cytoplasmic dynein light intermediate chain-1, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 281, 1141–1153.
Horgan, C. P., Hanscom, S. R., Jolly, R. S., Futter, C. E., and McCaffrey, M. W. (2010) Rab11-FIP3 binds dynein light intermediate chain 2 and its overexpression fragments the Golgi complex, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 394, 387–392.
Horgan, C. P., Hanscom, S. R., Jolly, R. S., Futter, C. E., and McCaffrey, M. W. (2010) Rab11-FIP3 links the Rab11 GTPase and cytoplasmic dynein to mediate transport to the endosomal-recycling compartment, J. Cell Sci., 123, 181–191.
Jordens, I., Fernandez-Borja, M., Marsman, M., Dusseljee, S., Janssen, L., Calafat, J., Janssen, H., Wubbolts, R., and Neefjes, J. (2001) The Rab7 effector protein RILP controls lysosomal transport by inducing the recruitment of dynein-dynactin motors, Curr. Biol., 11, 1680–1685.
Mooren, O. L., Galletta, B. J., and Cooper, J. A. (2012) Roles for actin assembly in endocytosis, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 81, 661–686.
Moughamian, A. J., Osborn, G. E., Lazarus, J. E., Maday, S., and Holzbaur, E. L. (2013) Ordered recruitment of dynactin to the microtubule plus-end is required for efficient initiation of retrograde axonal transport, J. Neurosci., 33, 13190–13203.
Lomakin, A. J., Semenova, I., Zaliapin, I., Kraikivski, P., Nadezhdina, E., Slepchenko, B. M., Akhmanova, A., and Rodionov, V. (2009) CLIP-170-dependent capture of membrane organelles by microtubules initiates minus-end directed transport, Dev. Cell., 17, 323–333.
Pierre, P., Pepperkok, R., and Kreis, T. E. (1994) Molecular characterization of two functional domains of CLIP-170 in vivo, J. Cell Sci., 107, 1909–1920.
Nielsen, E., Severin, F., Backer, J. M., Hyman, A. A., and Zerial, M. (1999) Rab5 regulates motility of early endosomes on microtubules, Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 376–382.
Zhang, J., Li, S., Fischer, R., and Xiang, X. (2003) Accumulation of cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin at microtubule plus ends in Aspergillus nidulans is kinesin dependent, Mol. Biol. Cell, 14, 1479–1488.
Huckaba, T. M., Gennerich, A., Wilhelm, J. E., Chishti, A. H., and Vale, R. D. (2011) Kinesin-73 is a processive motor that localizes to Rab5-containing organelles, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 7457–7467.
Loubery, S., Wilhelm, C., Hurbain, I., Neveu, S., Louvard, D., and Coudrier, E. (2008) Different microtubule motors move early and late endocytic compartments, Traffic, 9, 492–509.
Ligon, L. A., Tokito, M., Finklestein, J. M., Grossman, F. E., and Holzbaur, E. L. (2004) A direct interaction between cytoplasmic dynein and kinesin I may coordinate motor activity, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 19201–19208.
Zlobina, M. V., Kharchenko, M. V., and Kornilova, E. S. (2013) Analysis of the dynamics of EGF receptor endocytosis by the images of confocal light microscopy on fixed cells, Tsitologiya, 55, 348–357.
Pringle, J., Muthukumar, A., Tan, A., Crankshaw, L., Conway, L., and Ross, J. L. (2013) Microtubule organization by kinesin motors and microtubule crosslinking protein MAP65, J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 25, 374103.
Zlobina, M. V., Kharchenko, M. V., Latkin, D. S., and Kornilova, E. S. (2010) Acetylation of microtubules during endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor (c-ErbB1) receptor in interphasic HeLa cells, Tsitologiya, 52, 466–476.
Yan, Q., Sun, W., Kujala, P., Lotfi, Y., Vida, T. A., and Bean, A. J. (2005) CART: An Hrs/actinin-4/BERP/myosin V protein complex required for efficient receptor recycling, Mol. Biol. Cell., 16, 2470–2482.
Li, L., and Cohen, S. N. (1996) Tsg101: a novel tumor susceptibility gene isolated by controlled homozygous functional knockout of allelic loci in mammalian cells, Cell, 85, 319–329.
Lovric, J., Dammeier, S., Kieser, A., Mischak, H., and Kolch, W. (1998) Activated raf induces the hyperphosphorylation of stathmin and the reorganization of the microtubule network, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 22848–22855.
Allison, R., Lumb, J. H., Fassier, C., Connell, J. W., Ten Martin, D., Seaman, M. N., Hazan, J., and Reid, E. (2013) An ESCRT-spastin interaction promotes fission of recycling tubules from the endosome, J. Cell Biol., 202, 527–543.
Chua, J., Rikhy, R., and Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (2009) Dynamin 2 orchestrates the global actomyosin cytoskeleton for epithelial maintenance and apical constriction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 20770–20775.
Helgeson, L. A., and Nolen, B. J. (2013) Mechanism of synergistic activation of Arp2/3 complex by cortactin and N-WASP, Elife, 2, e00884.
Gomez, T. S., Gorman, J. A., de Narvajas, A. A., Koenig, A. O., and Billadeau, D. D. (2012) Trafficking defects in WASH-knockout fibroblasts originate from collapsed endosomal and lysosomal networks, Mol. Biol. Cell., 23, 3215–3228.
Pal, A., Severin, F., Hopfner, S., and Zerial, M. (2008) Regulation of endosome dynamics by Rab5 and Huntingtin-HAP40 effector complex in physiological versus pathological conditions, Methods Enzymol., 438, 239–257.
Deribe, Y. L., Wild, P., Chandrashaker, A., Curak, J., Schmidt, M. H., Kalaidzidis, Y., Milutinovic, N., Kratchmarova, I., Buerkle, L., Fetchko, M. J., Schmidt, P., Kittanakom, S., Brown, K. R., Jurisica, I., Blagoev, B., Zerial, M., Stagljar, I., and Dikic, I. (2009) Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor trafficking by lysine deacetylase HDAC6, Sci. Signal., 2, ra84.
Gao, Y. S., Hubbert, C. C., and Yao, T. P. (2010) The microtubule-associated histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) regulates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytic trafficking and degradation, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 11219–11226.
Purev, E., Neff, L., Horne, W. C., and Baron, R. (2009) c-Cbl and Cbl-b act redundantly to protect osteoclasts from apoptosis and to displace HDAC6 from β-tubulin, stabilizing microtubules and podosomes, Mol. Biol. Cell, 20, 4021–4030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E. S. Kornilova, 2014, published in Biokhimiya, 2014, Vol. 79, No. 9, pp. 1079–1094.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kornilova, E.S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis and cytoskeleton. Biochemistry Moscow 79, 865–878 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914090041
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914090041