-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Samer Jabbour, Elio Kechichian, Barbara Hersant, Philippe Levan, Lena El Hachem, Warren Noel, Marwan Nasr, Labia Majora Augmentation: A Systematic Review of the Literature, Aesthetic Surgery Journal, Volume 37, Issue 10, November-December 2017, Pages 1157–1164, https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx056
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Currently, there is no standardized approach for labia majora augmentation and controversies still exist regarding this subject.
This systematic review aimed to assess the evidence in the literature regarding labia majora augmentation.
On November 20, 2016, we conducted an online search of published articles in the Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases. All articles describing labia majora augmentation were included in this review.
Nine studies were selected for inclusion in the systematic review. Only 2 studies were prospective trials. The most commonly used technique was fat grafting with a total of 4 articles and 183 patients. The mean total injected fat volume ranged from 18 mL to 120 mL per session. Two articles described hyaluronic acid injection techniques. The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid ranged from 2 to 6 mL per session. Three articles used surgical techniques for labia majora augmentation. All included articles did not report any major or life-threatening complications. All techniques demonstrated high satisfaction rates.
Labia majora augmentation appears to be a safe, efficient technique with a high satisfaction rate and no reported major complications. However, further randomized controlled trials are warranted.

With the prevalent media coverage of explicit material and “external genitalia grooming,” the demand for female genital aesthetic procedures has been steadily increasing.1,2 According to the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 8745 labiaplasty procedures were done in 2015, with a 15% increase compared to 2014.3
Like other body areas, female genitalia are affected by the normal process of aging.4 The decrease in hyaluronic acid, collagen, and fat result in volume loss, rhytids development, and an increased minora to majora ratio with a seemingly prominent labia minora.5 These age-related changes not only affect the physical appearance of the female external genitalia but also disrupt sexual functioning.6,7 The sexual self-esteem decreases, resulting in a significant psychosocial impairment.6,8-10 To address these issues, the number of publications devoted to external genitalia rejuvenation is constantly growing. Most of the articles describe labiaplasty techniques and vaginal tightening procedures with a good outcome and a low complication rate.1,4,11-13 However, the approach of female genitalia rejuvenation is marked by a relatively low number of articles devoted to labia majora augmentation procedures. Currently, there is no standardized approach for labia majora augmentation and controversies still exist regarding this subject. This systematic review aims to summarize and compare all available data to guide current practice and provide a road map for future research.
METHODS
On November 20, 2016, the first 2 authors (S.J. and E.K.) conducted an online search of published articles in the Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases. The initial search was done using the following combination of keywords: (“labia majora” OR “labium majus”) AND (augmentation OR enhancement OR enlargement). All articles published before the search date were evaluated for inclusion. Studies related to the augmentation of labia majora were selected based on their titles and abstracts and were obtained and read in full. The reference list of each study was manually screened for additional articles. All articles describing labia majora augmentation were included in this review. Excluded studies were those lacking a detailed description of the augmentation technique. The first 2 authors (S.J. and E.K.) unanimously agreed on the final selection of the included studies.
RESULTS
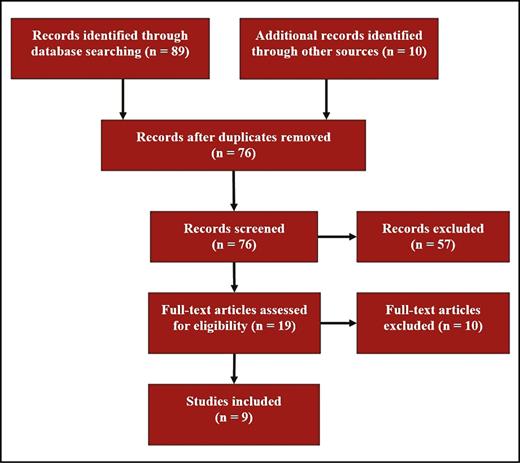
The initial search of the database and the manual screening of the references yielded 89 results, 23 of which were duplicates. Of the 76 unique articles, 19 were retained based on assessments of their titles and abstracts and 57 were excluded because they were not related to labia majora augmentation. Following full-text review, 10 articles were excluded because they did not provide a clear description of the augmentation technique and 9 studies were selected for inclusion in the systematic review (Figure 1).
The stepwise approach used to select the final articles included in the systematic review.
All included studies were published between 2007 and 2016 with a total of 226 patients. The mean age of patients was 43.6 years (range, 17-68 years). Only 2 studies were prospective trials.12,14 Two were retrospective cohorts,5,15 3 were case reports,6,16,17 and 2 only described a technique for labial augmentation.18,19 None of the included studies had a control group. Three studies were done in Europe,5,12,16 2 in Turkey,14,15 2 in Brazil,19 1 in Egypt,17 and 1 in the United States6 (Table 1).
Characteristics of Included Studies
| Study (year) . | Country . | Study design . | Procedure . | Number of patients . | Mean age in years (range) . | Follow up in months . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola (2016)5 | Italy | Retrospective cohort | HA filler | 31 | 45 (36-68) | 12 |
| Hexsel et al (2016)18 | Brazil | Technique description | HA filler | NR | NR | NR |
| Cihantimur and Herold (2013)14 | Turkey | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 124 | NR | 12 |
| Felicio (2007)19 | Brazil | Technique description | Lipofilling | 31 | NR | NR |
| Gress (2007)12 | Germany | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 27 | NR | 6 |
| Vogt et al (2011)16 | Germany | Case report | Lipofilling | 1 | NR | 8 |
| El Danaf (2010)17 | Egypt | Case report | Surgery - flap | 1 | 48 | 10 |
| Karabağlı et al (2015)15 | Turkey | Retrospective case-series | Surgery - flap | 10 | 39.9 ± 13.9 (17-63) | 14.5 ± 3.4 |
| Salgado et al (2012)6 | United States | Case report | Surgery - dermal graft | 1 | 33 | 6 |
| Study (year) . | Country . | Study design . | Procedure . | Number of patients . | Mean age in years (range) . | Follow up in months . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola (2016)5 | Italy | Retrospective cohort | HA filler | 31 | 45 (36-68) | 12 |
| Hexsel et al (2016)18 | Brazil | Technique description | HA filler | NR | NR | NR |
| Cihantimur and Herold (2013)14 | Turkey | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 124 | NR | 12 |
| Felicio (2007)19 | Brazil | Technique description | Lipofilling | 31 | NR | NR |
| Gress (2007)12 | Germany | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 27 | NR | 6 |
| Vogt et al (2011)16 | Germany | Case report | Lipofilling | 1 | NR | 8 |
| El Danaf (2010)17 | Egypt | Case report | Surgery - flap | 1 | 48 | 10 |
| Karabağlı et al (2015)15 | Turkey | Retrospective case-series | Surgery - flap | 10 | 39.9 ± 13.9 (17-63) | 14.5 ± 3.4 |
| Salgado et al (2012)6 | United States | Case report | Surgery - dermal graft | 1 | 33 | 6 |
HA, hyaluronic acid; NR, not reported.
Characteristics of Included Studies
| Study (year) . | Country . | Study design . | Procedure . | Number of patients . | Mean age in years (range) . | Follow up in months . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola (2016)5 | Italy | Retrospective cohort | HA filler | 31 | 45 (36-68) | 12 |
| Hexsel et al (2016)18 | Brazil | Technique description | HA filler | NR | NR | NR |
| Cihantimur and Herold (2013)14 | Turkey | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 124 | NR | 12 |
| Felicio (2007)19 | Brazil | Technique description | Lipofilling | 31 | NR | NR |
| Gress (2007)12 | Germany | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 27 | NR | 6 |
| Vogt et al (2011)16 | Germany | Case report | Lipofilling | 1 | NR | 8 |
| El Danaf (2010)17 | Egypt | Case report | Surgery - flap | 1 | 48 | 10 |
| Karabağlı et al (2015)15 | Turkey | Retrospective case-series | Surgery - flap | 10 | 39.9 ± 13.9 (17-63) | 14.5 ± 3.4 |
| Salgado et al (2012)6 | United States | Case report | Surgery - dermal graft | 1 | 33 | 6 |
| Study (year) . | Country . | Study design . | Procedure . | Number of patients . | Mean age in years (range) . | Follow up in months . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola (2016)5 | Italy | Retrospective cohort | HA filler | 31 | 45 (36-68) | 12 |
| Hexsel et al (2016)18 | Brazil | Technique description | HA filler | NR | NR | NR |
| Cihantimur and Herold (2013)14 | Turkey | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 124 | NR | 12 |
| Felicio (2007)19 | Brazil | Technique description | Lipofilling | 31 | NR | NR |
| Gress (2007)12 | Germany | Prospective cohort | Lipofilling | 27 | NR | 6 |
| Vogt et al (2011)16 | Germany | Case report | Lipofilling | 1 | NR | 8 |
| El Danaf (2010)17 | Egypt | Case report | Surgery - flap | 1 | 48 | 10 |
| Karabağlı et al (2015)15 | Turkey | Retrospective case-series | Surgery - flap | 10 | 39.9 ± 13.9 (17-63) | 14.5 ± 3.4 |
| Salgado et al (2012)6 | United States | Case report | Surgery - dermal graft | 1 | 33 | 6 |
HA, hyaluronic acid; NR, not reported.
In all the included articles, the main indication was cosmetic except for one report that used fat grafting for labia majora reconstruction.16
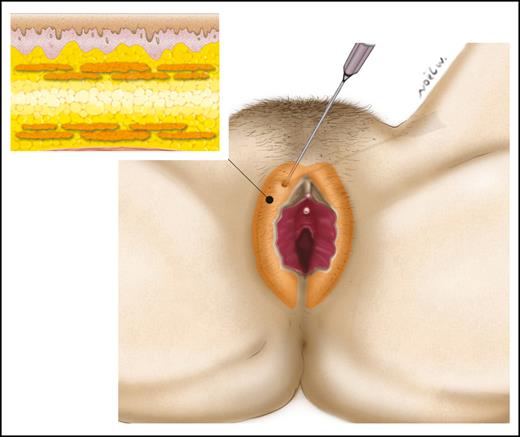
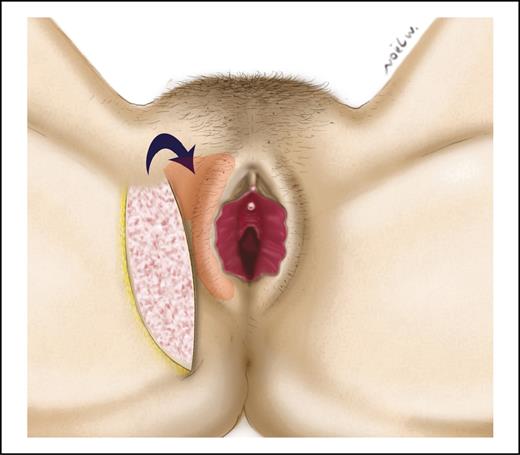
The most commonly used technique was fat grafting with a total of 4 articles and 183 patients.12,14,16,19 The mean total injected fat volume ranged from 18 mL to 120 mL per session. To increase the fat graft survival, the injection was done in multiple layers (Figure 2). If additional volume was needed, new injections were done after a period of 4 to 6 months.16,19 Wound dehiscence was observed when lipofilling was associated with a labia minora reduction procedures.14
Fat injection for labia majora augmentation. The injection of fat should be done in multiple layers.
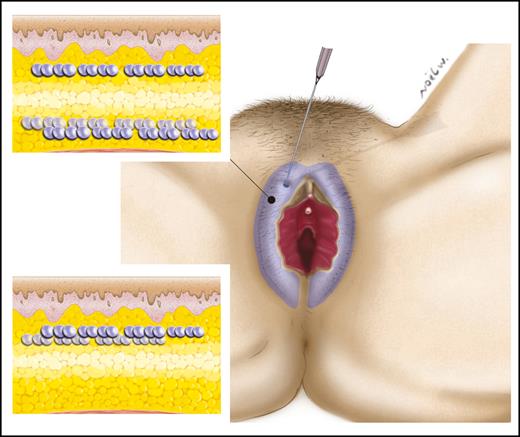
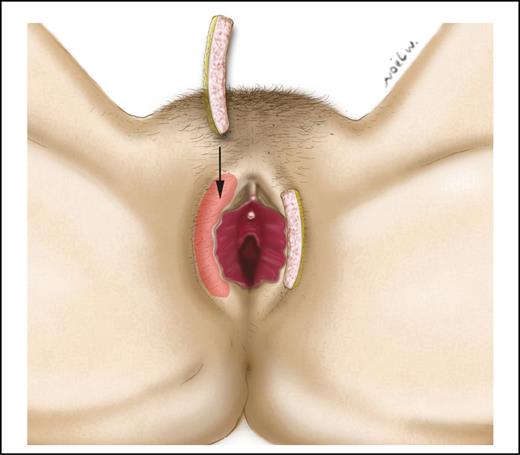
Two articles described hyaluronic acid injection techniques for labia majora augmentation.5,18 The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid ranged from 2 to 6 mL per session. The concentration of the injected hyaluronic acid was 19 to 20 mg/mL. The site of injection was the subcutaneous tissue with or without deeper injection under the Dartos muliebris fascia of the labia majora (Figure 3). If additional volume was needed, the injection was repeated after a duration of 2 to 4 months. Only mild and transient adverse events were noted with hyaluronic acid injections such as hyperemia, edema, ecchymosis, and palpable nodules.
Hyaluronic acid injection for labia majora augmentation. Hyaluronic acid can be injected subcutaneously only or can be associated with deep injections under the Dartos fascia.
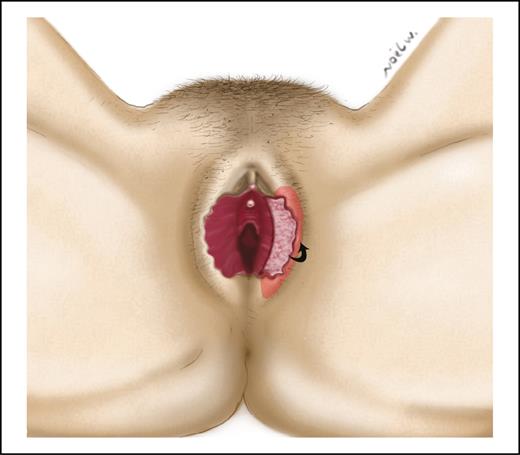
Three articles used surgical techniques for labia majora augmentation.6,15,17 Of those, 2 studies described flaps for labia majora augmentation.15,17 Both were associated with additional procedures. One study described a labia majora flap augmentation associated with labia minora reduction.15 The protruding part of the labia minora was not resected but instead it was de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora (Figure 4). The other study reported a labia majora flap augmentation associated with a thigh lift.17 An adipofascial flap was raised from the inner thigh and transposed to the labia majora (Figure 5). Adverse events reported with these techniques included hematomas, flap necrosis, and pain. One article described the use of dermal fat grafts for labia majora augmentation.6 Two 10 × 2 cm grafts were crafted from the resected abdominoplasty skin island. These grafts were inserted into the labia majora (Figure 6).
The protruding part of the labia minora can be de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora.
When combined with a thigh lift, labia majora augmentation can be done using a de-epithelialized adipofacial flap raised from the inner thigh. The flap is transposed to a pocket created into the labia majora.
The 10 × 2 cm dermal fat grafts can be created from the de-epithelialized skin and inserted into pockets dissected into the labia majora.
All included articles did not report any major or life-threatening complications. Hyaluronic acid related adverse events were: transient hyperaemia during the first 30 minutes posttreatment,5,18 transient oedema for a few days,5 mild ecchymosis,5,18 and small bumps that were corrected with light massage,5 intralesional corticosteroid,18 or hyaluronidase injection.18 Lipofilling was associated with swelling16 and wound dehiscence when combined to labia minora reduction.14 An inner thigh flap was only used in one patient for labial augmentation. It resulted in a unilateral hematoma that was evacuated using forceps which led to the flap necrosis. The resulting deformity was corrected with lipofilling.17 Thirty percent of patients who had a labia minora flaps for labia majora augmentation complained of transient pain, pruritus, and discomfort.15 Two lipofilling articles did not mention the adverse events but were included in the review because they clearly described the augmentation technique.12,19 All techniques demonstrated good satisfaction rates. Fasola and Gazzola used the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale to evaluate the results.5 Cihantimur used a visual analogue scale to evaluate patient satisfaction (9-10: very happy, 6-8: happy, 0-5: unhappy).14 Vogt et al,16 El Danaf,17 and Salgado et al6 reported single cases and all 3 patients were satisfied with their results. Krabagli et al did not use a satisfaction questionnaire but noted that all patients were satisfied with the results.15 Three included studies did not evaluate the patient satisfaction12,18,19 (Table 2). Table 3 summarizes the important findings of this review. The quality of this systematic review was assessed using the PRISMA checklist (Appendix A, available online as Supplementary Material at www.aestheticsurgeryjournal.com).
Techniques and Outcomes
| Study . | Procedure . | Technique description . | Associated procedure . | Indication . | Satisfaction . | Adverse events (number of patients) . | Interval between treatments (months) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola5 | HA filler | 2 mL of 19 mg/mL HA injection for mild to moderate hypotrophy and 21 mg/mL HA for severe hypotrophy. Injection in two layers: 1/3 of volume subcutaneously and 2/3 deep to the Dartos fascia | None | Aesthetic: hypotrophy of the labia majora | 65% increase in patient GAIS and 42 % improvement in doctor GAIS | Transient hyperemia (15) transient edema (1) ecchymosis (2) transient bump (1) | >4 |
| Hexsel et al18 | HA filler | 5-6 mL of Macrolane VRF 20 a injected subcutaneously to fill the mons pubis and the labia majora | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | Ecchymosis palpable nodules | >2 |
| Cihantimur and Herold14 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat and PRP injection: (1) superior and lateral to the cranial part of the labia majora with a mean injected volume of 18 mL (range, 14-30 mL); (2) 3 mL on each side superficially within the labial edge | Labia minora reduction, labial brightening by laser ± mons pubis liposuction and vaginal tightening | Aesthetic: genital beautification | Satisfaction rate: 98% | Wound dehiscence (10) | NR |
| Felicio19 | Lipofilling | 60 mL of fat is injected in each labia majora and 20 mL in each labia minora | Labia minora lipofilling | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | 6 |
| Gress12 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat was injected in multiple layers into the labia majora. A mean of 70 mL of fat was injected in each patient | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | NR |
| Vogt et al16 | Lipofilling | Labia majora reconstruction with fat injection. The reconstructed labium majus was injected with 17 mL in the first session and 35 mL in the second session | None | Reconstruction: labium majus reconstruc tion after ablative surgery for Bowen’s disease | Satisfied | Swelling (1) | 4 |
| El Danaf17 | Surgery - flap | Superiorly based de-epithelized adipofascial flap (raised from the inner thigh lift excision crescent) is inserted into a pocket created in the labium majus | Inner thigh lift | Aesthetic: Inner thigh laxity and labia majora atrophy | Satisfied | Hematoma (1) flap necrosis | NR |
| Karabağlı et al15 | Surgery - flap | The protruding part of the labia minora is de-epithelized and transposed into a pocket created in the labium majus | Labia minora reduction | Aesthetic: bilateral labia minora hypertrophy with simultaneous labia majora atrophy | Satisfaction rate: 100% | Pain, pruritus and transient discomfort (3) | NR |
| Salgado et al6 | Surgery - dermal graft | Two de-epithelialized dermal fat grafts (10 × 2 cm) are inserted into tunnels created bluntly on the medial aspect of the labia majora | Abdominoplasty and breast augmentation | Aesthetic: Abdominoplasty, breast augmentation and vaginal rejuvenation | Satisfied | None | NR |
| Study . | Procedure . | Technique description . | Associated procedure . | Indication . | Satisfaction . | Adverse events (number of patients) . | Interval between treatments (months) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola5 | HA filler | 2 mL of 19 mg/mL HA injection for mild to moderate hypotrophy and 21 mg/mL HA for severe hypotrophy. Injection in two layers: 1/3 of volume subcutaneously and 2/3 deep to the Dartos fascia | None | Aesthetic: hypotrophy of the labia majora | 65% increase in patient GAIS and 42 % improvement in doctor GAIS | Transient hyperemia (15) transient edema (1) ecchymosis (2) transient bump (1) | >4 |
| Hexsel et al18 | HA filler | 5-6 mL of Macrolane VRF 20 a injected subcutaneously to fill the mons pubis and the labia majora | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | Ecchymosis palpable nodules | >2 |
| Cihantimur and Herold14 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat and PRP injection: (1) superior and lateral to the cranial part of the labia majora with a mean injected volume of 18 mL (range, 14-30 mL); (2) 3 mL on each side superficially within the labial edge | Labia minora reduction, labial brightening by laser ± mons pubis liposuction and vaginal tightening | Aesthetic: genital beautification | Satisfaction rate: 98% | Wound dehiscence (10) | NR |
| Felicio19 | Lipofilling | 60 mL of fat is injected in each labia majora and 20 mL in each labia minora | Labia minora lipofilling | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | 6 |
| Gress12 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat was injected in multiple layers into the labia majora. A mean of 70 mL of fat was injected in each patient | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | NR |
| Vogt et al16 | Lipofilling | Labia majora reconstruction with fat injection. The reconstructed labium majus was injected with 17 mL in the first session and 35 mL in the second session | None | Reconstruction: labium majus reconstruc tion after ablative surgery for Bowen’s disease | Satisfied | Swelling (1) | 4 |
| El Danaf17 | Surgery - flap | Superiorly based de-epithelized adipofascial flap (raised from the inner thigh lift excision crescent) is inserted into a pocket created in the labium majus | Inner thigh lift | Aesthetic: Inner thigh laxity and labia majora atrophy | Satisfied | Hematoma (1) flap necrosis | NR |
| Karabağlı et al15 | Surgery - flap | The protruding part of the labia minora is de-epithelized and transposed into a pocket created in the labium majus | Labia minora reduction | Aesthetic: bilateral labia minora hypertrophy with simultaneous labia majora atrophy | Satisfaction rate: 100% | Pain, pruritus and transient discomfort (3) | NR |
| Salgado et al6 | Surgery - dermal graft | Two de-epithelialized dermal fat grafts (10 × 2 cm) are inserted into tunnels created bluntly on the medial aspect of the labia majora | Abdominoplasty and breast augmentation | Aesthetic: Abdominoplasty, breast augmentation and vaginal rejuvenation | Satisfied | None | NR |
HA, hyaluronic acid; NR, not reported; PRP, platelet-rich plasma.
aGalderma Labs (Fort Worth, TX).
Techniques and Outcomes
| Study . | Procedure . | Technique description . | Associated procedure . | Indication . | Satisfaction . | Adverse events (number of patients) . | Interval between treatments (months) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola5 | HA filler | 2 mL of 19 mg/mL HA injection for mild to moderate hypotrophy and 21 mg/mL HA for severe hypotrophy. Injection in two layers: 1/3 of volume subcutaneously and 2/3 deep to the Dartos fascia | None | Aesthetic: hypotrophy of the labia majora | 65% increase in patient GAIS and 42 % improvement in doctor GAIS | Transient hyperemia (15) transient edema (1) ecchymosis (2) transient bump (1) | >4 |
| Hexsel et al18 | HA filler | 5-6 mL of Macrolane VRF 20 a injected subcutaneously to fill the mons pubis and the labia majora | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | Ecchymosis palpable nodules | >2 |
| Cihantimur and Herold14 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat and PRP injection: (1) superior and lateral to the cranial part of the labia majora with a mean injected volume of 18 mL (range, 14-30 mL); (2) 3 mL on each side superficially within the labial edge | Labia minora reduction, labial brightening by laser ± mons pubis liposuction and vaginal tightening | Aesthetic: genital beautification | Satisfaction rate: 98% | Wound dehiscence (10) | NR |
| Felicio19 | Lipofilling | 60 mL of fat is injected in each labia majora and 20 mL in each labia minora | Labia minora lipofilling | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | 6 |
| Gress12 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat was injected in multiple layers into the labia majora. A mean of 70 mL of fat was injected in each patient | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | NR |
| Vogt et al16 | Lipofilling | Labia majora reconstruction with fat injection. The reconstructed labium majus was injected with 17 mL in the first session and 35 mL in the second session | None | Reconstruction: labium majus reconstruc tion after ablative surgery for Bowen’s disease | Satisfied | Swelling (1) | 4 |
| El Danaf17 | Surgery - flap | Superiorly based de-epithelized adipofascial flap (raised from the inner thigh lift excision crescent) is inserted into a pocket created in the labium majus | Inner thigh lift | Aesthetic: Inner thigh laxity and labia majora atrophy | Satisfied | Hematoma (1) flap necrosis | NR |
| Karabağlı et al15 | Surgery - flap | The protruding part of the labia minora is de-epithelized and transposed into a pocket created in the labium majus | Labia minora reduction | Aesthetic: bilateral labia minora hypertrophy with simultaneous labia majora atrophy | Satisfaction rate: 100% | Pain, pruritus and transient discomfort (3) | NR |
| Salgado et al6 | Surgery - dermal graft | Two de-epithelialized dermal fat grafts (10 × 2 cm) are inserted into tunnels created bluntly on the medial aspect of the labia majora | Abdominoplasty and breast augmentation | Aesthetic: Abdominoplasty, breast augmentation and vaginal rejuvenation | Satisfied | None | NR |
| Study . | Procedure . | Technique description . | Associated procedure . | Indication . | Satisfaction . | Adverse events (number of patients) . | Interval between treatments (months) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasola and Gazzola5 | HA filler | 2 mL of 19 mg/mL HA injection for mild to moderate hypotrophy and 21 mg/mL HA for severe hypotrophy. Injection in two layers: 1/3 of volume subcutaneously and 2/3 deep to the Dartos fascia | None | Aesthetic: hypotrophy of the labia majora | 65% increase in patient GAIS and 42 % improvement in doctor GAIS | Transient hyperemia (15) transient edema (1) ecchymosis (2) transient bump (1) | >4 |
| Hexsel et al18 | HA filler | 5-6 mL of Macrolane VRF 20 a injected subcutaneously to fill the mons pubis and the labia majora | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | Ecchymosis palpable nodules | >2 |
| Cihantimur and Herold14 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat and PRP injection: (1) superior and lateral to the cranial part of the labia majora with a mean injected volume of 18 mL (range, 14-30 mL); (2) 3 mL on each side superficially within the labial edge | Labia minora reduction, labial brightening by laser ± mons pubis liposuction and vaginal tightening | Aesthetic: genital beautification | Satisfaction rate: 98% | Wound dehiscence (10) | NR |
| Felicio19 | Lipofilling | 60 mL of fat is injected in each labia majora and 20 mL in each labia minora | Labia minora lipofilling | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | 6 |
| Gress12 | Lipofilling | Liposuctionned fat was injected in multiple layers into the labia majora. A mean of 70 mL of fat was injected in each patient | None | Aesthetic: labia majora atrophy | NR | NR | NR |
| Vogt et al16 | Lipofilling | Labia majora reconstruction with fat injection. The reconstructed labium majus was injected with 17 mL in the first session and 35 mL in the second session | None | Reconstruction: labium majus reconstruc tion after ablative surgery for Bowen’s disease | Satisfied | Swelling (1) | 4 |
| El Danaf17 | Surgery - flap | Superiorly based de-epithelized adipofascial flap (raised from the inner thigh lift excision crescent) is inserted into a pocket created in the labium majus | Inner thigh lift | Aesthetic: Inner thigh laxity and labia majora atrophy | Satisfied | Hematoma (1) flap necrosis | NR |
| Karabağlı et al15 | Surgery - flap | The protruding part of the labia minora is de-epithelized and transposed into a pocket created in the labium majus | Labia minora reduction | Aesthetic: bilateral labia minora hypertrophy with simultaneous labia majora atrophy | Satisfaction rate: 100% | Pain, pruritus and transient discomfort (3) | NR |
| Salgado et al6 | Surgery - dermal graft | Two de-epithelialized dermal fat grafts (10 × 2 cm) are inserted into tunnels created bluntly on the medial aspect of the labia majora | Abdominoplasty and breast augmentation | Aesthetic: Abdominoplasty, breast augmentation and vaginal rejuvenation | Satisfied | None | NR |
HA, hyaluronic acid; NR, not reported; PRP, platelet-rich plasma.
aGalderma Labs (Fort Worth, TX).
Key Points
| Labia majora augmentation is not only an anti-aging intervention but also a beautification procedure |
| Fat grafting is the most commonly used technique for labia majora augmentation |
| The mean total injected fat volume ranges from 18 mL to 120 mL per session |
| The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid (19-20 mg/mL) ranges from 2 to 6 mL per session |
| With hyaluronic acid, retouching can be done as soon as 2 to 4 months after the initial injection whereas retouching with fat grafting should be done 4 to 6 months after |
| The used flaps for labia majora augmentation are: (1) the protruding part of the labia minora can be de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora, (2) when combined with a thigh lift, labia majora augmentation can be done using a de-epithelialized adipofascial flap raised from the inner thigh |
| A more general approach to the female genitalia treatment is possible by combining multiple procedures |
| In patients with mild labia minora hypertrophy, the augmentation of the labia majora can help mask the labia minora |
| Adverse events reported in all included studies were minor and transient |
| Labia majora augmentation is not only an anti-aging intervention but also a beautification procedure |
| Fat grafting is the most commonly used technique for labia majora augmentation |
| The mean total injected fat volume ranges from 18 mL to 120 mL per session |
| The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid (19-20 mg/mL) ranges from 2 to 6 mL per session |
| With hyaluronic acid, retouching can be done as soon as 2 to 4 months after the initial injection whereas retouching with fat grafting should be done 4 to 6 months after |
| The used flaps for labia majora augmentation are: (1) the protruding part of the labia minora can be de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora, (2) when combined with a thigh lift, labia majora augmentation can be done using a de-epithelialized adipofascial flap raised from the inner thigh |
| A more general approach to the female genitalia treatment is possible by combining multiple procedures |
| In patients with mild labia minora hypertrophy, the augmentation of the labia majora can help mask the labia minora |
| Adverse events reported in all included studies were minor and transient |
Key Points
| Labia majora augmentation is not only an anti-aging intervention but also a beautification procedure |
| Fat grafting is the most commonly used technique for labia majora augmentation |
| The mean total injected fat volume ranges from 18 mL to 120 mL per session |
| The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid (19-20 mg/mL) ranges from 2 to 6 mL per session |
| With hyaluronic acid, retouching can be done as soon as 2 to 4 months after the initial injection whereas retouching with fat grafting should be done 4 to 6 months after |
| The used flaps for labia majora augmentation are: (1) the protruding part of the labia minora can be de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora, (2) when combined with a thigh lift, labia majora augmentation can be done using a de-epithelialized adipofascial flap raised from the inner thigh |
| A more general approach to the female genitalia treatment is possible by combining multiple procedures |
| In patients with mild labia minora hypertrophy, the augmentation of the labia majora can help mask the labia minora |
| Adverse events reported in all included studies were minor and transient |
| Labia majora augmentation is not only an anti-aging intervention but also a beautification procedure |
| Fat grafting is the most commonly used technique for labia majora augmentation |
| The mean total injected fat volume ranges from 18 mL to 120 mL per session |
| The total injected volume of hyaluronic acid (19-20 mg/mL) ranges from 2 to 6 mL per session |
| With hyaluronic acid, retouching can be done as soon as 2 to 4 months after the initial injection whereas retouching with fat grafting should be done 4 to 6 months after |
| The used flaps for labia majora augmentation are: (1) the protruding part of the labia minora can be de-epithelialized and transposed into the labia majora, (2) when combined with a thigh lift, labia majora augmentation can be done using a de-epithelialized adipofascial flap raised from the inner thigh |
| A more general approach to the female genitalia treatment is possible by combining multiple procedures |
| In patients with mild labia minora hypertrophy, the augmentation of the labia majora can help mask the labia minora |
| Adverse events reported in all included studies were minor and transient |
DISCUSSSION
Labia majora augmentation is a relatively new technique. In 2007, Felicio was the first to describe the enhancement of deficient labia using autogenous fat grafting. 19 Since then, a wide range of different techniques has been reported. This practice has spread geographically as our included studies originated from Asia, Europe, Africa, North and South America.
We found that the mean age was 43.6 years. In fact, the greatest demand for labia majora augmentation is in the fifth decade of life, when the early signs of aging begin to appear.5 Some younger women can also benefit from this procedure as the youngest reported patient in our review was 17 years old. Therefore, labia majora augmentation is not only an antiaging intervention but also a beautification procedure.
The most commonly used labial augmentation technique was lipofilling. Injected volumes varied widely between studies. The volume of injected fat ranged from 18 mL to 120 mL per treatment session. Multiple sites can be injected such as the mons pubis, the anterior and lateral labia majora, and the posterior labia majora. The injection should be done in multiple layers to increase the fat survival (Figure 2). Lipofilling can be used either for cosmetic enhancement of the labia majora or reconstruction of an ablated labium. In the latter case, lipofilling offers a natural appearance with the improvement of both skin and preexisting scar quality with no additional scarring.16 Cosmetic labia majora augmentation may also offer some functional benefits as some patient may report greater sexual satisfaction with intercourse.19
The hyaluronic acid injection can be done in a subcutaneous plane only (Figure 3). Good injection technique is crucial to avoid common palpable nodules and bumps. The concentration of the hyaluronic acid used for labia augmentation should be high: 19 to 20 mg/mL. Hyaluronic acid has many advantages when compared to other filler products. It has a low risk of allergic and immunogenic reactions20 and it can be reversed with hyaluronidase if the patient requests it or in the case of ischemic complications.21 With hyaluronic acid, retouching can be done as soon as 2 to 4 months after the initial injection whereas retouching with lipofilling should be done 4 to 6 months after. Fat grafts suffer from the unavoidable loss of a certain amount of volume.6 The injected fat will be slowly and partially resorbed within the first few months. Thus, when using fat grafting, more time is needed to assess the final result and decide if additional volume is needed.
In comparison to fat grafting and hyaluronic acid, dermal grafts may offer an advantage in terms of longevity.6 These grafts are slowly replaced by fibrosis.22
Some authors choose to combine various aesthetic approaches to the female genitalia treatment. Felicio reported his 17 years of experience in more than 500 labial procedures.19 He described the concomitant injection of fat in both the labia majora and the labia minora. Cihantimur and Herold performed genital beautification by combining labia minora reduction, labia majora augmentation, brightening by laser, mons pubis liposuction, and vaginal tightening.14 Similarly, Karabgli et al enhanced the female genitalia by performing additional labia minora reduction.15 Laser labioplasty, can also be used in adjunct to other surgical gynecologic interventions without increased adverse events.23
Adverse events reported in all included studies were minor and transient. In addition to hyperemia, edema, and ecchymosis that are common to all treatment modalities, surgery carried the additional risk of wound dehiscence, hematoma, and flap necrosis. Pulmonary embolism has also been described with hyaluronic acid injection into the vulva.24
In this reviewer’s opinion, tailoring the treatment to specific patient anatomy is key to optimize results. When facing a minor hypertrophy of the labia minora and a marked labia majora tissue loss, hyaluronic acid injection or autologous fat transplantation are both attractive options. Augmentation of the labia majora in these cases can help mask the labia minora. In the case of major labia minora hypertrophy, a reduction labiaplasty can be done with concomitant labia majora augmentation1,11,14,15 (Figures 7 and 8). Surgery is also warranted when different procedures are needed such as concomitant thigh lift.17
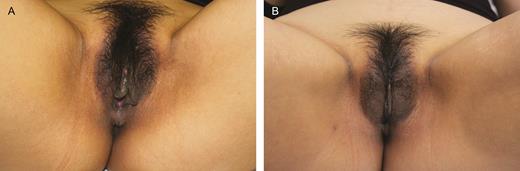
(A) Preoperative photograph of a 35-year-old woman. The patient had a deflated and aged appearance of the labia majora with a mild labia minora hypertrophy. (B) Four-month postoperative photograph of the same patient after the injection of 20 mL of fat in each labium majus and wedge ressection of the labia minora.
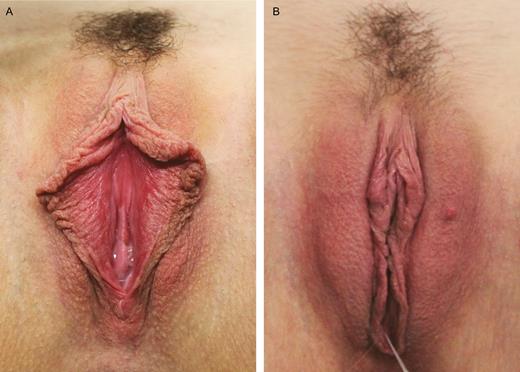
(A) Preoperative photograph of a 28-year-old woman. (B) Twelve-month postoperative photograph of the same patient after the injection of 20 mL of fat in each labium majus and wedge ressection of the labia minora.
There are many limitations to this review. Only 2 of the included studies were prospective trials. The absence of a randomized controlled trial prevented us from doing a traditional meta-analysis to compare the different techniques and limited our systematic review to a form of pooled analysis. The large amount of variability between studies, especially in the satisfaction measurement methods restricted the interstudy comparison. Another important bias was the publication bias, as only published articles were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS
Labia majora augmentation appears to be a safe, efficient technique with a high satisfaction rate. It can be done for aesthetic, reconstructive, or functional indications, alone or in conjunction with other procedures. Future adequately designed randomized controlled trials are needed to compare the different techniques and assess their impact on functional outcomes.
Supplementary Material
This article contains supplementary material located online at www.aestheticsurgeryjournal.com.
Disclosures
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
REFERENCES