Summary
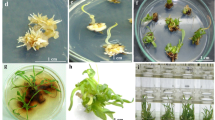
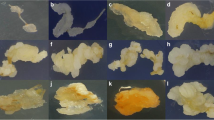
A highly efficient protocol for callus induction and plant regeneration in Sorghum bicolor was developed by varying the concentrations of copper (0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1, 1.5, 2.5 μM) in Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium. The mature embryos of Sorghum bicolor were cultured on MS medium containing 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (9μM), kinetin (2.3 μM), and 3% (w/v) sucrose for embryogenic callus induction. Plant regeneration from this callus occurred on MS medium containing kinetin (9.2 μM) and indole-3-acetic acid (2.85 μM). A much greater response was noted on these media with higher levels of copper. Frequency of plant regeneration and number of regenerants dramatically increased with an optimal amount of copper (2 μM) in the MS medium. Rooting of the regenerated shoots readily occurred on half-strength MS medium supplemented with α-naphthaleneacetic acid (10.7 μM) and 3% (w/v) sucrose. Well-developed plantlets were transferred to the field where 100% survival and normal seed setting was noted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baillie, A. M. R.; Rossnagel, B. G.; Kartha, K. K. Evaluation of 10 Canadian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars for tissue culture response. Can. J. Plant Sci. 73:171–174; 1993.
Brettell, R.; Wernicke, W.; Thomas, E. Embryogenesis from cultured immature inflorescences of Sorghum bicolor. Protoplasma 104:141–148; 1980.
Dahleen, L. S. Improved plant regeneration from barley callus cultures by increased copper levels. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 43:267–269; 1995.
Gamborg, O. L.; Shyluk, J. P.; Brar, D. S.; Constabel, F. Morphogenesis and plant regeneration from callus of immature embryos of sorghum. Plant Sci. Lett. 10:67–74; 1977.
Lidon, F. C. M.; Da Graca Barreiro, M.; Santos Henriquest, F. Interactions between biomass production and ethylene biosynthesis in copper treated rice. J. Plant Nut. 18:1301–1314; 1995.
Luhrs, R.; Lorz, H. Plant regeneration in vitro from embryogenic cultures of spring and winter-type barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 75:16–25; 1987.
Lusardi, M. C.; Lupotto, E. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in sorghum species. Maydica 35:59–66; 1990.
Ma, H.; Gu, M.; Liang, G. H. Plant regeneration from cultured immature embryos of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Theor. Appl. Genet. 73:389–394; 1987.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Nahdi, S.; de Wet, J. M. J. In vitro regeneration of Sorghum bicolor lines from shoot apices. Int. Sorghum Millets Newsl. 36:88–90; 1995.
Purnhauser, L. Stimulation of shoot and root regeneration in wheat (Triticum aestivum) callus cultures by copper. Cereal Res. Commun. 19:419–423; 1991.
Purnhauser, L.; Gyulai, G. Effect of copper on shoot and root regeneration in wheat, triticale, rape and tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 35:131–139; 1993.
Sharma, V.; Kothari, S. L.; Chandra, N. In vitro regeneration, field transfer of plantlets and growth to maturity of plants of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Curr. Sci. 58:586–588; 1989.
Smith, R. H.; Bhaskaran, S. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). In: Bajaj, Y. P. S., ed. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry crops I. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1986.
Thomas, E.; King, P. J.; Potrykus, I. Shoot and embryo like structure formation from cultured tissues of Sorghum bicolor. Naturwissenschaften 64:587; 1977.
Wernicke, W.; Brettell, R. I. S. Somatic embryogenesis from Sorghum bicolor leaves. Nature 287:138–139; 1980.
Wernicke, W.; Brettell, R. I. S. Morphogenesis from cultured leaf tissue of Sorghum bicolor. Culture initiation. Auxins. Protoplasma 111:19–27; 1982.
Zhong, H.; Wang, W.; Sticklen, M. In vitro morphogenesis of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Efficient plant regeneration from shoot apices. J. Plant Physiol. 153:719–726; 1998.
Zhu, H.; Muthukrishna, S.; Krishnaveni, S.; Wild, G.; Jeoung, J. M.; Liang, G. H. Biolistic transformation of sorghum using a rice chitinase gene. J. Genet. Breed. 52:243–252; 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nirwan, R.S., Kothari, S.L. High copper levels improve callus induction and plant regeneration in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 39, 161–164 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2002385
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2002385