Abstract
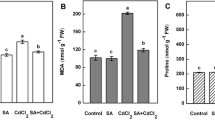
As a widespread pollutant in the environment, cadmium (Cd) would be accumulated in leaves and cause phytotoxic effect on plants. Salicylic acid (SA), a natural signal molecule, plays an important role in eliciting specific responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. In our case, the effect of SA on Cd-induced photochemical damage and cell death in Arabidopsis was studied. The results illustrated that Cd could cause a series of physiological events such as chloroplast structure change (e.g. irregular mesophyll cell as well as ultrastructure change), reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and cell death. Furthermore, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters (Fv/Fm, qN and ETR) showed a rapid decrease in wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis after treatment with 50 µM CdCl2, identical with the change in chlorophyll delayed fluorescence (DF) intensity. The changes of these parameters showed the damage of Cd toxicity to photosynthetic apparatus. We found that cell death might be autophagic cell death, which might be caused by Cd toxicity induced oxidative stress just like photosynthetic damage. The NahG plants with lower SA accumulation level showed more sensitivity to Cd toxicity, although they exhibited a decrease both in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and DF intensity. Exogenously SA prevented the Cd-induced photochemical efficiency decrease and mitigated Cd toxicity. Additionally, SA pretreatment could alleviate Cd-induced ROS overproduction. In conclusion, our results suggested that SA could prevent Cd-induced photosynthetic damage and cell death, which might be due to the inhibition of ROS overproduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Alice, A. K. Elizabeth and I. S. Julian, An improved grafting technique for mature Arabidopsis plants demonstrates long-distance shoot-to-root transport of phytochelatins in Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 2006, 141, 108–120.
M. K. Joshi and P. Mohanty, Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a probe of heavy metal ion toxicity in plants, in: G. C. Papageorgiou (ed.): Chlorophyll a Fluorescence: Signature of Photosynthesis. Springer, Dordrecht, 2004, pp. 637–637.
E. Franco, S. Alessandrelli, J. Masojidek, A. Margonelli and M. T. Giardi, Modulation of D1 protein turnover under cadmium and heat stresses monitored by [35S] methionine incorporation, Plant Sci., 1999, 144, 53–61.
C. M. Lu, N. W. Qiu, B. S. Wang and J. H. Zhang, Salinity treatment shows no effects on photosystem II photochemistry, but increases the resistance of photosystem II to heat stress in halophyte Suaeda salsa, J. Exp. Bot., 2003, 54, 851–860.
H. Küpper, F. Küpper and M. Spiller, Environmental relevance of heavy metal substituted chlorophylls using the example of water plants, J. Exp. Bot., 1996, 47, 259–266.
T. Baszynski, L. Wajda, M. Krol, D. Wolinska, Z. Krupa and A. Tukendrof, Photosynthetic activities of cadmium treated tomato plants, Plant Physiol., 1980, 98, 365–370.
M. C. Romero-Puertas, M. Rodriguez-Serrano, F. J. Corpas, M. Gómez, L. A. Delrío and L. M. Sandalio, Cadmium-induced subcel-lular accumulation of O2-and H2O2 in pea leaves, Plant, Cell Environ., 2004, 27, 1122–1134.
R. Mittle, Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance [J], Trends Plant Sci., 2002, 7, 405–410.
A. Krantev, R. Yordanova, T. Janda, G. Szalaib and L. Popova, Treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effect of cadmium on photosynthesis in maize plants, J. Plant Physiol., 2008, 165, 920–931.
O. Borsani, V. Valpuesta and M. A. Botella, Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings, Plant Physiol., 2001, 126, 1024–1030.
J. F. Dat, C. H. Foyer and I. M. Scott, Changes in salicylic acid and antioxidants during induced thermotolerance in mustard seedlings, Plant Physiol., 1998, 118, 1455–1461.
T. Senaratna, D. Touchell, E. Bunns and K. Dixon, Acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) and salicylic acid induce multiple stress tolerance in bean and tomato plants, Plant Growth Regul., 2000, 30, 157–161.
T. G. Janda, I. T. Szalai and E. Padi, Hydroponic treatment with salicylic acid decrease the effects of chilling injury in maize (Zea mays L.) plant, Planta, 1999, 208, 175–180.
A. Mishra and M. A. Chudhuri, Effect of salicylic acid on heavy metal-induced membrane deterioration in rice, Biol. Plant., 1999, 42, 409–415.
A. Metwally, I. Finkermeier, M. Georgi and K. J. Dietz, Salicylic acid alleviates the cadmium toxicity in barley seedlings, Plant Physiol., 2003, 132, 272–281.
M. Pal, G. Szalai, E. Horvath, T. Janda and E. Paldi, Effect of salicylic acid during heavy metal stress, Proc. 7th Hungarian Congress Plant Physiol., 2002, 46, 119–120.
G. Drazic and N. Mihailovic, Modification of cadmium toxicity in soybean seedlings by salicylic acid, Plant Sci., 2005, 168, 511–517.
K. Yoshimoto, Y. Takano and Y. Sakai, Autophagy in plants and phytopathogens, FEBS Lett., 2010, 584, 1350–1358.
H. E. Tao, H. J. Wang and Y. Z. Tan, The roles of autophagy in cell survival and cell death, Prog. Physiol. Sci., 2008, 39, 37–40.
B. Mauch-Mani and A. J. Slusarenko, Production of salicylic acid precursors is a major function of phenylalanine ammonialyase in the resistance of Arabidopsis to Peronospora parasitica, Plant Cell, 1996, 8, 203–212.
L. R. Zhang, D. Xing and J. S. Wang, A non-invasive and real-time monitoring of the regulation of photosynthetic metabolism biosensor based on measurement of delayed fluorescence in vivo, Sensors, 2007, 7, 52–66.
K. B. Bonfig, U. Schreiber, A. Gabler, T. Roitsch and S. Berger, Infection with virulent and avirulent P.syringae strains differentially affects photosynthesis and sink metabolism in Arabidopsis leaves, Planta, 2006, 225, 1–12.
L. R. Zhang, Q. X. Xu, D. Xing, C. J. Gao and H. W. Xiong, Realtime detection of Caspase-3-like protease activation in vivo using fluorescence resonance energy transfer during plant programmed cell death induced by ultraviolet C overexposure, Plant Physiol., 2009, 150, 1773–1783.
Y. H. Bi, W. L. Chen, W. N. Zhang, Q. Zhou, L. J. Yun and D. Xing, Production of reactive oxygen species, impairment of photosynthetic function and dynamic changes in mitochondria are early events in cadmium induced cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana, Biol. Cell, 2009, 101, 629–643.
C. J. Gao, D. Xing, L. L. Li and L. R. Zhang, Implication of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction in the early stages of plant programmed cell death induced by ultraviolet-C overexposure, Planta, 2007, 227, 755–767.
Y. Moriyasu, M. Hattori, G. Y. Jauh and J. C. Rogers, Alpha tonoplast intrinsic protein is specifically associated with vacuole membrane involved in an autophagic process, Plant Cell Physiol., 2003, 44, 795–802.
L. P. Popova, L. T. Maslenkova, R. Y. Yordanova, A. P. Ivanova, A. P. Krantev, G. Szalai and T. Janda, Exogenous treatment with salicylic acid attenuates cadmium toxicity in pea seedlings, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2009, 47, 224–231.
L. A. Belkhadi, H. Hediji, Z. Abbes, I. Nouairi, Z. Barhoumi, M. Zarrouk, W. ChaIbi and W. Djebali, Effects of exogenous salicylic acid pre-treatment on cadmium toxicity and leaf lipid content in Linum usitatissimum L, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2010, 73, 1004–1011.
H. R. Moussa and S. M. El-Gamal, Effect of salicylic acid pretreatment on cadmium toxicity in wheat, Biol. Plant., 2010, 54, 315–320.
K. Apel and H. Hirt, Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2004, 55, 373–399.
W. Jakubowski and G. Bartosz, 2,7-Dichlorofluorescein oxidation and reactive oxygen species: what does it measure?, Cell Biol. Int., 2000, 24, 757–760.
L. S. di Toppi and R. Gabbrielli, Response to cadmium in higher plants, Environ. Exp. Bot., 1999, 41, 105–130.
I. McCarthy, M. C. Romero-Puertas, J. M. Palma, L. M. Sandalio, F. J. Corpas, M. Gómez and L. A. Delrío, Cadmium induces senescence symptoms in leaf peroxisomes of pea plants, Plant, Cell Environ., 2001, 24, 1065–1073.
B. Guo, Y. C. Liang and Y. G. Zhu, Does salicylic acid regulate antioxidant defense system, cell death, cadmium uptake and partitioning to acquire cadmium tolerance in rice?, J. Plant Physiol., 2009, 166, 20–31.
G. Ouzounidou, M. Moustakas and E. P. Eleftheriou, Physiological and ultrastructural effects of cadmium on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1997, 32, 154–160.
D. H. Yang, The effects of heavy metals on the structure and function of photosynthetic membranes in higher plants, Chin. Bull. Bot., 1991, 8, 26–29.
L. M. Sandalio, H. C. Dalurzo, M. Gomez, M. C. Romero-Puertas and L. A. del Rio, Cadmiun-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants, J. Exp. Bot., 2001, 52, 2115–2126.
J. Soukupová, S. Smatanová, L. Nedbal and A. Jegorov, Plant response to destruxins visualized by imaging of chlorophyll fluorescence, Physiol. Plant., 2003, 118, 399–405.
B. Gielen, H. J. De Boeck, C. M. H. M. Lemmens, R. Valcke, I. Nijs and R. Ceulemans, Grassland species will not necessarily benefit from future elevated air temperatures: a chlorophyll fluorescence approach to study autumn physiology, Physiol. Plant., 2005, 125, 52–63.
B. Guo, Y. C. Liang, Y. G. Zhu and F. J. Zhao, Role of salicylic acid in alleviating oxidative damage in rice roots (Oryza sativa) subjected to cadmium stress, Environ. Pollut., 2007, 147, 743–749.
M. J. Lenardo, C. K. McPhee and L. Yu, Autophagic cell death, Methods Enzymol., 2009, 453, 71–31.
Q. H. Shi and Z. J. Zhu, Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on manganese toxicity, element contents and antioxidantive system in cucumber, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2008, 63, 317–326.
T. P. Delaney, S. Uknes, B. Vernooij, L. Friedrich, K. Weymann, D. Negrotto, T. Gaffney, M. Gut-Rella, H. Kessmann, E. Ward and J. Ryals, A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance, Science, 1994, 266, 1247–1246.
T. C. Dinis, V. M. Maderia and L. M. Almeida, Action of phenolic derivates (acetaminophen, salicylate, and 5-aminosalicylate) as inhibitors of membrane lipid peroxidation and as peroxyl radical scavengers, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1994, 315, 161–169.
L. P. Popova, L. T. Maslenkova, R. Y. Yordanova, A. P. Ivanova, A. P. Krantev, G. Szalai and T. Janda, Exogenous treatment with salicylic acid attenuates cadmium toxicity in pea seedlings, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2009, 47, 224–231.
M. S. Zawoznik, M. D. Groppa, M. L. Tomaro and M. P. Benavides, Endogenous salicylic acid potentiates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana, Plant Sci., 2007, 173, 190–197.
D. Bassham, Plant autophagy—more than a starvation response, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2007, 10, 587–593.
S. Shimizu, T. Kanaseki, N. Mizushima, T. Mizuta, S. Arakawa-Kobayashi, C. B. Thompson and Y. Tsujimoto, Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes, Nat. Cell Biol., 2004, 6, 1221–1228.
L. Yu, A. Alva, H. Su, P. Dutt, E. Freundt, S. Welsh, E. H. Baehrecke and M. J. Lenardo, Regulation of an ATG7-beclin1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8, Science, 2004, 304, 1500–1502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c0pp00305k
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Chen, W. Role of salicylic acid in alleviating photochemical damage and autophagic cell death induction of cadmium stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Photochem Photobiol Sci 10, 947–955 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00305k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00305k