Abstract
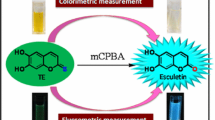
The interaction of the cupric ion with esculetin, a dihydroxy coumarin derivative, was studied by absorption and fluorescence spectroscopic methods in aqueous medium. Esculetin formed a complex in the presence of the cupric ion which was characterised by the shift in its absorption band from 350 nm to 389 nm and the quenching of its fluorescence intensity at 466 nm. From Job's plot and fluorescence quenching studies, the stoichiometry of the copper ion and esculetin in the complex was estimated to be 1: 2 respectively. Interestingly, the incubation of the Cu(ii)–esculetin complex with a thiol peptide, glutathione (GSH), showed restoration of the fluorescence intensity as well as absorption maxima to that of pure esculetin. Incubation with other common thiol and non-sulphur amino acids did not show a similar restoration of the photophysical properties of the complex except in the case of cysteine. Mechanistically, it was evident that two molecules of GSH were consumed in reducing the Cu(ii)–esculetin complex, which subsequently split into the copper ion and esculetin. In this process GSH was converted into oxidised GSH (GSSG) as evident from the mass spectroscopy and HPLC studies. The above florescence regeneration behaviour of the copper–esculetin system in the presence of GSH was also observed in the cellular system using Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) as model cells. In conclusion, these studies may find application in developing sensors for detecting the cellular thiol level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Kumar, E. V. Anslyn, A selective turn-on fluorescent sensor for sulfur mustard simulants, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6338–6344.
L. Zhang, S. Dong, L. Zhu, Fluorescent dyes of the esculetin and alizarin families respond to zinc ions ratiometrically, Chem. Commun., 2007, 1891–1893.
K. Żamojć, M. Zdrowowicz, W. Wiczk, D. Jacewicz, L. Chmurzyński, Dihydroxycoumarins as highly selective fluorescent probes for the fast detection of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO in aqueous solution, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 63807–63812.
T. Sarwar, M. A. Husain, S. U. Rehman, H. M. Ishqi, M. Tabish, Multi-spectroscopic and molecular modelling studies on the interaction of esculetin with calf thymus DNA, Mol. BioSyst., 2015, 11, 522–531.
R. L. Atkins, D. E. Bliss, Substituted coumarins and azacoumarins synthesis and fluorescent properties, J. Org. Chem., 1978, 43, 1975–1980.
G. A. Reynolds, K. H. Drexhage, New coumarin dyes with rigidized structure for flashlamp-pumped dye lasers, Opt. Commun., 1975, 13, 222–225.
K. Rechthaler, G. Köhler, Excited state properties and deactivation pathways of 7-aminocoumarins, Chem. Phys., 1994, 189, 99–116.
D. G. Crosby, R. V. Berthold, Fluorescence spectra of some simple coumarins, Anal. Biochem., 1962, 4, 349–357.
W. Jivaramonaikul, P. Rashatasakhon, S. Wanichwecharungruang, UVA absorption and photostability of coumarins, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, 9, 1120–1125.
S. Dragojević, V. Šunjić, V. Bencetić-Mihaljević, J. Ralić, M. Mesić, I. J. Elenkov, A. F. Sučić, A. Č. Klonkay, L. Lerman, M. Ilijaš, V. Gabelica-Marković, I. Malnar, Determination of aqueous stability and degradation products of series of coumarin dimers, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2011, 54, 37–47.
H. M. Revankar, S. N. A. Bukhari, G. B. Kumar, H. Qin, Coumarins scaffolds as COX inhibitors, Bioorg. Chem., 2017, 71, 146–159.
B. D. Wagner, The use of coumarins as environmentally-sensitive fluorescent probes of heterogeneous inclusion systems, Molecules, 2009, 14, 210–237.
M. A. Haidekker, T. P. Brady, D. Lichlyter, E. A. Theodorakis, Effects of solvent polarity and solvent viscosity on the fluorescent properties of molecular rotors and related probes, Bioorg. Chem., 2005, 33, 415–425.
T. Moriya, Excited-state reaction of coumarins VII. The solvent-dependent fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarins, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1988, 61, 1873–1886.
N. Li, Y. Xiang, A. Tong, Highly sensitive and selective “turn-on” fluorescent chemodosimeter for Cu2+ in water via Cu2+-promoted hydrolysis of lactone moiety in coumarin, Chem. Commun., 2010, 3363–3365.
M. H. Kim, H. H. Jang, S. Yi, S. Chang, M. S. Han, Coumarin-derivative-based off–on catalytic chemodosimeter for Cu2+ ions, Chem. Commun., 2009, 4838–4840.
Z. Yang, Z. Liu, Y. Chen, X. Wang, W. He, Y. Lu, A new ratiometric and colorimetric chemosensor for cyanide anion based on Coumarin–hemicyanine hybrid, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 5073–5076.
K. Kaur, R. Saini, A. Kumar, V. Luxami, N. Kaur, P. Singh, S. Kumar, Chemodosimeters: An approach for detection and estimation of biologically and medically relevant metal ions, anions and thiols, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2012, 256, 1992–2028.
J. Du, M. Hu, J. Fan, X. Peng, Fluorescent chemodosimeters using “mild” chemical events for the detection of small anions and cations in biological and environmental media, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 4511–4535.
M. G. Choi, Y. H. Kim, J. E. Namgoong, S. Chang, Hg2+-selective chromogenic and fluorogenic chemodosimeter based on thiocoumarins, Chem. Commun., 2009, 3560–3562.
J. E. Park, M. G. Choi, S. Chang, Colorimetric and fluorescent signaling of Au3+ by desulfurization of thiocoumarin, Inorg. Chem., 2012, 51, 2880–2884.
C. Wu, J. Wang, J. Shen, C. Bi, H. Zhou, Coumarin-based Hg2+ fluorescent probe: synthesis and turn-on fluorescence detection in neat aqueous solution, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 243, 678–683.
D. Maity, T. Govindaraju, A differentially selective sensor with fluorescence turn-on response to Zn2+ and dual-mode ratiometric response to Al3+ in aqueous medium, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 1039–1041.
J. Wu, W. Liu, X. Zhuang, F. Wang, P. Wang, S. Tao, X. Zhang, S. Wu, S. Lee, Fluorescence turn on of coumarin derivatives by metal cations: A new signaling mechanism based on C=N isomerization, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 33–36.
H. S. Jung, P. S. Kwon, J. W. Lee, J. I. Kim, C. S. Hong, J. W. Kim, S. Yan, J. Y. Lee, J. H. Lee, T. Joo, J. S. Kim, Coumarin-derived Cu2+-selective fluorescence sensor: Synthesis, mechanisms, and applications in living cells, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 2008–2012.
R. J. P. Williams, Role of transition metal ions in biological processes, R. Inst. Chem., Rev., 1968, 1, 13–38.
M. Bost, S. Houdart, M. Oberli, E. Kalonji, J. Huneau, I. Margaritis, Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., 2016, 35, 107–115.
R. N. Mukherjee, The bioinorganic chemistry of copper, Indian J. Chem., Sect. A: Inorg., Bio-inorg., Phys., Theor. Anal. Chem., 2003, 42, 2175–2184.
A. Gupte, R. J. Mumper, Elevated copper and oxidative stress in cancer cells as a target for cancer treatment, Cancer Treat. Rev., 2009, 35, 32–46.
C. T. Sheline, E. H. Choi, J. S. Kim-Han, L. L. Dugan, D. W. Choi, Cofactors of mitochondrial enzymes attenuate copper-induced death in vitro and in vivo, Ann. Neurol., 2002, 52, 195–204.
S. Puig, D. J. Thiele, Molecular mechanisms of copper uptake and distribution, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2002, 6, 171–180.
M. Zeeshan, A. Murugadas, S. Ghaskadbi, R. B. Rajendran, M. A. Akbarsha, ROS dependent copper toxicity in Hydra-biochemical andmolecular study, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2016, 185–186, 1–12.
C. Saporito-Magriñá, R. Musacco-Sebio, J. M. Acosta, S. Bajicoff, P. Paredes-Fleitas, A. Boveris, M. G. Repetto, Rat liver mitochondrial dysfunction by addition of copper(II) or iron(III) ions, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2017, 166, 5–11.
V. Kumar, J. Kalita, H. K. Bora, U. K. Misra, Relationship of antioxidant and oxidative stress markers in different organs following copper toxicity in a rat model, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2016, 293, 37–43.
K. Lee, J. Park, H. Park, Y. K. Chung, S. B. Park, H. Kim, I. Shin, J. Hong, Regenerative fluorescence “turn-on” probe for biothiols through Cu(II)/Cu(I) redox conversion, Sens. Actuators, B, 2016, 237, 256–261.
C. Sivasankar, N. Sadhukhan, J. K. Bera, A. G. Samuelson, Is copper(I) hard or soft? A density functional study of mixed ligand complexes, New J. Chem., 2007, 31, 385–393.
H. K. Baek, R. A. Holwerda, An S-bonded adduct of cysteine with the [Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine]copper(II) ion, Inorg. Chem., 1983, 22, 3452–3456.
H. B. Singh, R. K. Negi, S. Srivastava, Binary and ternary complexes of copper(II) with some dihydroxycoumarins, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), 1981, 90, 141–146.
G. He, J. Li, L. Yang, C. Hou, T. Ni, Z. Yang, X. Qian, C. Li, The synthesis of a coumarin carbohydrazide dinuclear copper complex based fluorescence probe and its detection of thiols, PLoS One, 2016, 11, e0148026, DOI: 10.1371/journal.
K. An, K. H. Park, K. Jun, A new coumarin-based colorimetric and fluorometric sensor for Cu2+, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2014, 35, 2183–2185.
N. Roy, S. Nath, A. Dutta, P. Mondal, P. C. Paul, T. S. Singh, A highly efficient and selective coumarin based fluorescent probe for colorimetric detection of Fe3+ and fluorescence dual sensing of Zn2+ and Cu2+, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 63837–63847.
Z. Hu, L. Sun, Y. Gu, Y. Jiang, A sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for detection of glutathione in the presence of Cu2+ and its application to biological imaging, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 212, 220–224.
C. Xu, H. Li, B. Yin, A colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe for selective detection and cellular imaging of glutathione, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 72, 275–281.
C. Chen, W. Liu, C. Xu, W. Liu, A colorimetric and fluorescent probe for detecting intracellular GSH, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 71, 68–74.
P. V. Kumar, B. G. Singh, A. Kunwar, M. Iwaoka, K. I. Priyadarsini, Degradation of peroxynitrite by simple, recyclable selenolanes, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2016, 89, 490–497.
P. Verma, A. Kunwar, K. Arai, M. Iwaoka, K. I. Priyadarsini, Alkyl chain modulated cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity of bioinspired amphiphilic selenolanes, Toxicol. Res., 2016, 5, 434–445.
Y. Zhang, Y. Fang, N. Xu, M. Zhang, G. Wu, C. Yao, A colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor based on furan-pyrene for selective and sensitive sensing Al3+, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2016, 27, 1673–1678.
A. L. Person, A. Moncomble, J. Cornard, The complexation of AlIII, PbII, and CuII metal ions by esculetin: A spectroscopic and theoretical approach, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118, 2646–2655.
L. Zhang, S. Dong, L. Zhu, Fluorescent dyes of the esculetin and alizarin families respond to zinc ions ratiometrically, Chem. Commun., 2007, 1891–1893.
M. J. Sever, J. J. Wilker, Visible absorption spectra of metal–catecholate and metal–tironate complexes, Dalton Trans., 2004, 1061–1072.
A. E. Bolzán, Electrodeposition of copper on glassy carbon electrodes in the presence of picolinic acid, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 113, 706–718.
Y. Samuni, S. Goldstein, O. M. Dean, M. Berk, The chemistry and biological activities of N-acetylcysteine, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2013, 1830, 4117–4129.
L. B. Poole, The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry, Free Radicals Biol. Med., 2015, 80, 148–157.
M.-H. Chau, J. W. Nelson, Direct measurement of the equilibrium between glutathione and dithiothreitol by high performance liquid chromatography, FEBS Lett., 1991, 291, 296–298.
A. K. Tummanapelli, S. Vasudevan, Ab Initio MD simulations of the Brønsted acidity of glutathione in aqueous solutions: Predicting pKa shifts of the cysteine residue, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, 119, 15353–15358.
L. Königsberger, E. Königsberger, G. Hefte, P. M. May, Formation constants of copper(I) complexes with cysteine, penicillamine and glutathione: implications for copper speciation in the human eye, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 20413–20425.
M. J. Walsh, S. D. Goodnow, G. E. Vezeau, L. V. Richter, B. A. Ahner, Cysteine enhances bioavailability of copper to marine phytoplankton, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 12145–12152.
M. J. Walsh, B. A. Ahner, Determination of stability constants of Cu(I), Cd(II) & Zn(II) complexes with thiols using fluorescent probes, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2013, 128, 112–123.
M.-Z. Zhang, H.-H. Han, S.-Z. Zhang, C.-Y. Wang, Y.-X. Lu, W.-H. Zhu, A new colorimetric and fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for rapid and specific detection of biothiols and its application in living cells, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017, 5, 8780–8785.
M. E. Aliaga, C. López-Alarcón, R. Bridi, H. Speisky, Redox-implications associated with the formation of complexes between copper ions and reduced or oxidized glutathione, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2016, 154, 78–88.
H. Speisky, M. Gómez, C. Carrasco-Pozo, E. Pastene, C. Lopez-Alarcón, C. Olea-Azar, Cu(I)–Glutathione complex: A potential source of superoxide radicals generation, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 6568–6574.
M. E. Aliaga, C. Carrasco-Pozo, C. López-Alarcón, H. Speisky, The Cu(I)–glutathione complex: factors affecting its formation and capacity to generate reactive oxygen species, Transition Met. Chem., 2010, 35, 321–329.
A. Katayamat, T. Kamidate, M. Morita, H. Watanabe, Spectrophotometric determination of aliphatic thiols based on redox color reaction with Copper(II) complex of 1,10-Phenanthroline in dimethyl sulfoxide, Anal. Sci., 1991, 7, 633–636.
M. E. Aliaga, C. López-Alarcón, L. García-Río, M. Martín-Pastor, H. Speisky, Redox-changes associated with the glutathione-dependent ability of the Cu(II)–GSSG complex to generate superoxide, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2012, 20, 2869–2876.
D. K. Johnson, M. J. Stevenson, Z. A. Almadidy, S. E. Jenkins, D. E. Wilcox, N. E. Grossoehme, Stabilization of Cu(I) for binding and calorimetric measurements in aqueous solution, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 16494–11650.
P. Bagchi, M. T. Morgan, J. Bacsa, C. J. Fahrni, Robust affinity standards for Cu(I) biochemistry, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 18549–18559.
M. Tian, F. Guo, Y. Sun, W. Zhang, F. Miao, Y. Liu, G. Song, C. Ho, X. Yu, J. Z. Sun, W. Wong, A fluorescent probe for intracellular cysteine overcoming the interference by glutathione, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 6128–6133.
Acknowledgments
RGS thanks the Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India for providing a fellowship under the BARC-SPPU collaborative research programme. The authors are thankful to Ms Vishwa V. Gandhi for helping in the cell culture experiments. The authors are also thankful to Head, RPCD, BARC and Head, Chemistry Department, SPPU for their constant encouragement and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinde, R.G., Khan, A.A., Kunwar, A. et al. Fluorescence “off” and “on” signalling of esculetin in the presence of copper and thiol: a possible implication in cellular thiol sensing. Photochem Photobiol Sci 17, 1197–1205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00157j
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00157j