Abstract
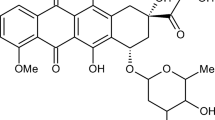
Two citric acid crosslinked γ-cyclodextrin oligomers (pγ-CyD) with a MW of 21-33 kDa and 10-15 γ-CyD units per molecule were prepared by following green chemistry methods and were fully characterized. The non-covalent association of doxorubicin (DOX) with these macromolecules was investigated in neutral aqueous medium by means of circular dichroism (CD), UV-vis absorption and fluorescence. Global analysis of multiwavelength spectroscopic CD and fluorescence titration data, taking into account the DOX monomer-dimer equilibrium, evidenced the formation of 1?:?1 and 1?:?2 pγ-CyD unit-DOX complexes. The binding constants are 1-2 orders of magnitude higher than those obtained for γ-CyD and depend on the characteristics of the oligomer batch used. The concentration profiles of the species in solution evidence the progressive monomerization of DOX with increasing oligomer concentration. Confocal fluorescence imaging and spectral imaging showed a similar drug distribution within the MCF-7 cell line incubated with either DOX complexed to pγ-CyD or free DOX. In both cases DOX is taken up into the cell nucleus without any degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Dal Ben, M. Palumbo, G. Zagotto, G. Capranico and S. Moro, DNA topoisomerase II structures and anthracycline activity: insights into ternary complex formation, Curr. Pharm. Des., 2007, 13, 2766–2780.
G. Minotti, P. Menna, E. Salvatorelli, G. Cairo and L. Gianni, Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity, Pharmacol. Rev., 2004, 56, 185–229
A. Gabizon, H. Shmeeda and Y. Barenholz, Pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin - Review of animal and human studies, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 2003, 42, 419–436
A. A. Gabizon, Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: Metamorphosis of an old drug into a new form of chemotherapy, Cancer Invest., 2001, 19, 424–436.
M. E. Davis and M. E. Brewster, Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2004, 3, 1023–1035
V. Villari, A. Mazzaglia, R. Darcy, C. M. O’Driscoll and N. Micali, Nanostructures of Cationic Amphiphilic Cyclodextrin Complexes with DNA, Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14, 811–817.
F. van de Manakker, T. Vermonden, C. F. van Nostrum and W. E. Hennink, Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Pharmaceutical/Biomedical Applications, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 3157–3175.
P. Y. Grosse, F. Bressolle and F. Pinguet, Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin in HL-60 parental and multidrug-resistant cancer cell lines: effect on the cytotoxic activity and intracellular accumulation of doxorubicin, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 1997, 40, 489–494
P. Y. Grosse, F. Bressolle and F. Pinguet, Antiproliferative effect of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin in vitro and in human tumour xenografted athymic nude mice, Br. J. Cancer, 1998, 78, 1165–1169.
P. Y. Grosse, F. Bressolle and F. Pinguet, In vitro modulation of doxorubicin and docetaxel antitumoral activity by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, Eur. J. Cancer, 1998, 34, 168–174
P. Y. Grosse, F. Bressolle, P. Vago, J. Simony-Lafontaine, M. Radal and F. Pinguet, Tumor cell membrane as a potential target for methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, Anticancer Res., 1998, 18, 379–384
A. Al-Omar, S. Abdou, L. De Robertis, A. Marsura and C. Finance, Complexation study and anticellular activity enhancement by doxorubicin-cyclodextrin complexes on a multidrug-resistant adenocarcinoma cell line, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 1999, 9, 1115–1120.
S. Tilloy, V. Monnaert, L. Fenart, H. Bricout, R. Cecchelli and E. Monflier, Methylated beta-cyclodextrin as P-gp modulators for deliverance of doxorubicin across an in vitro model of blood-brain barrier, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2006, 16, 2154–2157
V. Monnaert, D. Betbeder, L. Fenart, H. Bricout, A. M. Lenfant, C. Landry, R. Cecchelli, E. Monflier and S. Tilloy, Effects of gamma- and hydroxypropyl-gamma-cyclodextrins on the transport of doxorubicin across an in vitro model of blood-brain barrier, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 2004, 311, 1115–1120.
K. Hattori, A. Kenmoku, T. Mizuguchi, D. Ikeda, M. Mizuno and T. Inazu, Saccharide-branched cyclodextrins as targeting drug carriers, J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem., 2006, 56, 9–16
Y. Oda, N. Kobayashi, T. Yamanoi, K. Katsuraya, K. Takahashi and K. Hattori, Beta-cyclodextrin conjugates with glucose moieties designed as drug carriers: Their syntheses, evaluations using concanavalin A and doxorubicin, and structural analyses by NMR spectroscopy, Med. Chem., 2008, 4, 244–255
Y. Oda, H. Yanagisawa, M. Maruyama, K. Hattori and T. Yamanoi, Design, synthesis and evaluation ofd-galactose-beta-cyclodextrin conjugates as drug-carrying molecules, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 8830–8840
G. J. L. Bernardes, R. Kikkeri, M. Maglinao, P. Laurino, M. Collot, S. Y. Hong, B. Lepenies and P. H. Seeberger, Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of carbohydrate-functionalized cyclodextrins and liposomes for hepatocyte-specific targeting, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 4987–4996.
W. Zhu, Y. Li, L. Liu, Y. Chen and F. Xi, Supramolecular hydrogels as a universal scaffold for stepwise delivering Dox and Dox/cisplatin loaded block copolymer micelles, Int. J. Pharm., 2012, 437, 11–19
Q.-D. Hu, H. Fan, Y. Ping, W.-Q. Liang, G.-P. Tang and J. Li, Cationic supramolecular nanoparticles for co-delivery of gene and anticancer drug, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 5572–5574
L. Y. Qiu, R. J. Wang, C. Zheng, Y. Jin and L. Q. Jin, Beta-cyclodextrin-centered star-shaped amphiphilic polymers for doxorubicin delivery, Nanomedicine, 2010, 5, 193–208
H. Kim, S. Kim, C. Park, H. Lee, H. J. Park and C. Kim, Glutathione-Induced Intracellular Release of Guests from Mesoporous Silica Nanocontainers with Cyclodextrin Gatekeepers, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4280–4283
E. S. Gil, J. S. Li, H. N. Xiao and T. L. Lowe, Quaternary Ammonium beta-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles for Enhancing Doxorubicin Permeability across the In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 505–516
Y. Hagiwara, H. Arima, F. Hirayama and K. Uekama, Prolonged retention of doxorubicin in tumor cells by encapsulation of gamma-cyclodextrin complex in pegylated liposomes, J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem., 2006, 56, 65–68
H. Arima, Y. Hagiwara, F. Hirayama and K. Uekama, Enhancement of antitumor effect of doxorubicin by its complexation with gamma-cyclodextrin in pegylated liposomes, J. Drug Targeting, 2006, 14, 225–232
T. Liu, X. J. Li, Y. F. Qian, X. L. Hu and S. Y. Liu, Multifunctional pH-Disintegrable micellar nanoparticles of asymmetrically functionalized beta-cyclodextrin-Based star copolymer covalently conjugated with doxorubicin and DOTA-Gd moieties, Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 2521–2531
N. Lin and A. Dufresne, Supramolecular Hydrogels from In Situ Host-Guest Inclusion between Chemically Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cyclodextrin, Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14, 871–880.
S. Daoud-Mahammed, P. Couvreur, K. Bouchemal, M. Cheron, G. Lebas, C. Amiel and R. Gref, Cyclodextrin and Polysaccharide-Based Nanogels: Entrapment of Two Hydrophobic Molecules, Benzophenone and Tamoxifen, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 547–554
S. Daoud-Mahammed, J. L. Grossiord, T. Bergua, C. Amiel, P. Couvreur and R. Gref, Self-assembling cyclodextrin based hydrogels for the sustained delivery of hydrophobic drugs, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2008, 86A, 736–748
S. Daoud-Mahammed, P. Couvreur, C. Amiel, M. Besnard, M. Appel and R. Gref, Original tamoxifen-loaded gels containing cyclodextrins: in situ self-assembling systems for cancer treatment, J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol., 2004, 14, 51–55
S. Daoud-Mahammed, C. Ringard-Lefebvre, N. Razzouq, V. Rosilio, B. Gillet, P. Couvreur, C. Amiel and R. Gref, Spontaneous association of hydrophobized dextran and poly-beta-cyclodextrin into nanoassemblies. Formation and interaction with a hydrophobic drug, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 307, 83–93
S. Daoud-Mahammed, P. Couvreur and R. Gref, Novel self-assembling nanogels: stability and lyophilisation studies, Int. J. Pharm., 2007, 332, 185–191.
E. Renard, A. Deratani, G. Volet and B. Sebille, Preparation and characterization of water soluble high molecular weight beta-cyclodextrin-epichlorohydrin polymers, Eur. Polym. J., 1997, 33, 49–57
R. Gref, C. Amiel, K. Molinard, S. Daoud-Mahammed, B. Sebille, B. Gillet, J. C. Beloeil, C. Ringard, V. Rosilio, J. Poupaert and P. Couvreur, New self-assembled nanogels based on host-guest interactions: Characterization and drug loading, J. Controlled Release, 2006, 111, 316–324.
R. Anand, F. Manoli, I. Manet, S. Daoud-Mahammed, V. Agostoni, R. Gref and S. Monti, Beta-cyclodextrin polymer nanoparticles as carriers for doxorubicin and artemisinin: a spectroscopic and photophysical study, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2012, 11, 1285–1292.
T. Nakanishi, S. Fukushima, K. Okamoto, M. Suzuki, Y. Matsumura, M. Yokoyama, T. Okano, Y. Sakurai and K. Kataoka, Development of the polymer micelle carrier system for doxorubicin, J. Controlled Release, 2001, 74, 295–302.
R. Anand, S. Ottani, F. Manoli, I. Manet and S. Monti, A close-up on doxorubicin binding to gamma-cyclodextrin: an elucidating spectroscopic, photophysical and conformational study, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 2346–2357.
O. Bekers, J. H. Beijnen, M. Otagiri, A. Bult and W. J. M. Underberg, Inclusion complexation of Doxorubicin and Daunorubicin with Cyclodextrins, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 1990, 8, 671–674
O. Bekers, J. H. Beijnen, B. J. Vis, A. Suenaga, M. Otagiri, A. Bult and W. J. M. Underberg, Effect of Cyclodextrin Complexation on the Chemical-Stability of Doxorubicin and Daunorubicin in Aqueous-Solutions, Int. J. Pharm., 1991, 72, 123–130
O. Bekers, J. J. Kettenesvandenbosch, S. P. Vanhelden, D. Seijkens, J. H. Beijnen, A. Bult and W. J. M. Underberg, Inclusion Complex-Formation of Anthracycline Antibiotics with Cyclodextrins - a Proton Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance and Molecular Modeling Study, J. Inclusion Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem., 1991, 11, 185–193.
N. Husain, T. T. Ndou, A. M. Delapena and I. M. Warner, Complexation of Doxorubicin with Beta-Cyclodextrins and Gamma-Cyclodextrins, Appl. Spectrosc., 1992, 46, 652–658.
B. Martel, M. Weltrowski, D. Ruffin and M. Morcellet, Polycarboxylic acids as crosslinking agents for grafting cyclodextrins onto cotton and wool fabrics: Study of the process parameters, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 83, 1449–1456.
T. H. H. Thi, F. Chai, S. Lepretre, N. Blanchemain, B. Martel, F. Siepmann, H. F. Hildebrand, J. Siepmann and M. P. Flament, Bone implants modified with cyclodextrin: Study of drug release in bulk fluid and into agarose gel, Int. J. Pharm., 2010, 400, 74–85
N. Blanchemain, Y. Karrout, N. Tabary, C. Neut, M. Bria, J. Siepmann, H. F. Hildebrand and B. Martel, Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin modified vascular prosthesis: Influence of the modification level on the drug delivery properties in different media, Acta Biomater., 2011, 7, 304–314.
S. Joudieh, P. Bon, B. Martel, M. Skiba, M. Lahiani-Skiba, Cyclodextrin Polymers as Efficient Solubilizers of Albendazole: Complexation and Physico-Chemical Characterization, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2009, 9, 132–140
Y. Bakkour, G. Vermeersch, M. Morcellet, F. Boschin, B. Martel and N. Azaroual, Formation of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with doxycyclin-hyclate: NMR investigation of their characterisation and stability, J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem., 2006, 54, 109–114.
C. Danel, N. Azaroual, C. Chavaria, P. Odou, B. Martel and C. Vaccher, Comparative study of the complex forming ability and enantioselectivity of cyclodextrin polymers by CE and H-1 NMR, Carbohydr. Polym., 2013, 92, 2282–2292.
J. R. E. Fraser, T. C. Laurent, H. Pertoft and E. Baxter, Plasma-Clearance, Tissue Distribution and Metabolism of Hyaluronic-Acid Injected Intravenously in the Rabbit, Biochem. J., 1981, 200, 415–424
M. I. ul-Haq, B. F. L. Lai, R. Chapanian and J. N. Kizhakkedathu, Influence of architecture of high molecular weight linear and branched polyglycerols on their biocompatibility and biodistribution, Biomaterials, 2013, 33, 9135–9147
T. Etrych, V. Subr, J. Strohalm, M. Sirova, B. Rihova and K. Ulbrich, HPMA copolymer-doxorubicin conjugates: The effects of molecular weight and architecture on biodistribution and in vivo activity, J. Controlled Release, 2012, 164, 346–354
M. E. Fox, F. C. Szoka and J. M. J. Frèchet, Soluble Polymer Carriers for the Treatment of Cancer: The Importance of Molecular Architecture, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 1141–1151.
B. Martel, D. Ruffin, M. Weltrowski, Y. Lekchiri and M. Morcellet, Water-soluble polvmers and gels from the polycondensation between cyclodextrins and poly(carboxylic acid)s: A study of the preparation parameters, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2005, 97, 433–442.
M. M. L. Fiallo, H. Tayeb, A. Suarato, A. Garnier-Suillerot, Circular dichroism studies on anthracycline antitumor compounds. Relationship between the molecular structure and the spectroscopic data, J. Pharm. Sci., 1998, 87, 967–975.
B. Samori, A. Rossi, I. D. Pellerano, G. Marconi, L. Valentini, B. Gioia and A. Vigevani, Interactions between Drugs and Nucleic-Acids 0.1. Dichroic Studies of Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, and Their Basic Chromophore, Quinizarin, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1987, 1419–1426.
P. Agrawal, S. K. Barthwal and R. Barthwal, Studies on self-aggregation of anthracycline drugs by restrained molecular dynamics approach using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy supported by absorption, fluorescence, diffusion ordered spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2009, 44, 1437–1451.
P. Changenet-Barret, T. Gustavsson, D. Markovitsi, I. Manet and S. Monti, Unravelling molecular mechanisms in the fluorescence spectra of Doxorubicin in aqueous solution by femtosecond fluorescence spectroscopy, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 2937–2944.
L. Angeloni, G. Smulevich and M. P. Marzocchi, Absorption, Fluorescence and Resonance Raman-Spectra of Adriamycin and Its Complex with DNA, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 1982, 38, 213–217.
K. K. Karukstis, E. H. Z. Thompson, J. A. Whiles and R. J. Rosenfeld, Deciphering the fluorescence signature of daunomycin and doxorubicin, Biophys. Chem., 1998, 73, 249–263.
A. H. J. Wang, G. Ughetto, G. J. Quigley and A. Rich, Interactions between an Anthracycline Antibiotic and DNA - Molecular-Structure of Daunomycin Complexed to D(Cpgptpapcpg) at 1.2-a Resolution, Biochemistry, 1987, 26, 1152–1163.
V. Rizzo, C. Battistini, A. Vigevani, N. Sacchi, G. Razzano, F. Arcamone, A. Garbesi, F. Colonna, M. L. Capobianco and L. Tondelli, Association of anthracyclines and synthetic hexanucleotides. Structural factors influencing sequence specificity, J. Mol. Recognit., 1989, 2, 132–141.
X. G. Qu, C. Z. Wan, H. C. Becker, D. P. Zhong and A. H. Zewail, The anticancer drug-DNA complex: Femtosecond primary dynamics for anthracycline antibiotics function, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2001, 98, 14212–14217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, R., Malanga, M., Manet, I. et al. Citric acid-γ-cyclodextrin crosslinked oligomers as carriers for doxorubicin delivery. Photochem Photobiol Sci 12, 1841–1854 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3pp50169h
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c3pp50169h