Abstract
The period homolog genes Per1, Per2 and Per3 are important components of the circadian clock system. In addition to their role in maintaining circadian rhythm, these genes have been linked to mood disorders, stress response and vulnerability to addiction and alcoholism. In this study, we combined high-resolution sequence analysis and quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping of gene expression and behavioral traits to identify Per3 as a compelling candidate for the interaction between circadian rhythm, alcohol and stress response. In the BXD family of mouse strains, sequence variants in Per3 have marked effects on steady-state mRNA and protein levels. As a result, the transcript maps as a cis-acting expression QTL (eQTL). We found that an insertion/deletion (indel) variant in a putative stress response element in the promoter region of Per3 causes local control of transcript abundance. This indel results in differences in protein binding affinities between the two alleles through the Nrf2 transcriptional activator. Variation in Per3 is also associated with downstream differences in the expression of genes involved in circadian rhythm, alcohol, stress response and schizophrenia. We found that the Per3 locus is linked to stress/anxiety traits, and that the basal expression of Per3 is also correlated with several anxiety and addiction-related phenotypes. Treatment with alcohol results in increased expression of Per3 in the hippocampus, and this effect interacts with acute restraint stress. Our data provide strong evidence that variation in the Per3 transcript is causally associated with and also responsive to stress and alcohol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Numerous physiological processes and behaviors in mammals exhibit an inherent circadian oscillation that is vital for normal function. Disruption in the diurnal cycle is a common feature of different types of psychiatric illnesses including stress and anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder and depression.1 The circadian rhythm is under the coordinated regulation of clock genes such as Arntl, Dbp and Csnk1d, and the period homologs Per1, Per2 and Per3.2, 3 There is now growing evidence that implicates allelic variants in these genes in the development of neuropsychiatric diseases.4, 5 Additionally, clock genes have also been linked to responses to neuropharmacological agents in model organisms, as well as alcoholism and addiction in humans.2, 6 In mice, inactivation of Per1 and Per2 leads to changes in sensitivity to cocaine and ethanol,7 and in humans, gene variants in PER2 have been linked to alcoholism.8
There are close ties between stressful life experiences, mood disorders, substance abuse and sleep disturbances. Stressors have often been found to precede depressive episodes in humans.9 Studies in animals also show that stress can lead to depression-like behavior and sleep disruption with correlated changes in neural activity.10, 11 There is also evidence that both chronic stress and exposure to ethanol can have a far reaching impact on expression of circadian genes.12, 13 We have recently shown that prolonged restraint stress significantly upregulates expression of Dbp, Per1, Per2 and Per3 in multiple brain regions of C57BL/6J (B6) and DBA/2J (D2) inbred mouse strains.13 An important question then is whether or not natural variation in the expression of these genes also has a causal impact on stress and ethanol response in these mice?
Studies using inbred mouse strains have already demonstrated the importance of heritable genetic factors in stress-response and stress-induced alterations in sleep pattern.14 Here we investigate a specific period gene, Per3, and evaluate how sequence variants in this gene alter transcription factor binding, gene expression and correlated behavior. In humans, variants in PER3 have been associated with differences in sleep homeostasis,15, 16 susceptibility and onset age of bipolar disorder, and different aspects of mood disorder including differences in novelty seeking.17, 18, 19, 20 In mice, expression of Per3 in the brain is highly variable in strains derived by crossing the B6 and D2 parental strains (the BXD family). We have exploited this normal endogenous variation in transcript abundance to explore the association between a circadian gene and complex stress and alcohol related behaviors.
The BXDs are a genetically highly divergent set of inbred strains that show significant variation in alcohol preference and stress sensitivity.21, 22 They have been extensively phenotyped for behavioral traits and are particularly suitable for systems genetics analysis of sequence variants, expression differences and linkage to behavioral traits. In this study, we identify an insertion/deletion (indel) mutation in a promoter motif located in the 5′ UTR of Per3 that may underlie this variation in transcript abundance. We also examine the functional consequence of this sequence variant on downstream gene expression in the brain and behavioral traits related to stress and alcohol. As the hippocampus is a site vulnerable to both stress and alcohol,23, 24, 25 we also examined the effects of stress and alcohol on Per3 expression in the hippocampus of the BXDs. We provide evidence that expression of Per3 is both causally associated with behavioral differences in stress response and is influenced by stress and ethanol treatment.
Materials and methods
Mouse strains
The BXD strains were derived by inbreeding the F2 progeny of B6 and D2 strains.26 Newer sets of BXDs were created by inbreeding advanced intercross progeny.27, 28 Animals were weaned at 25 days-of-age and housed in same-sex cages, 2–5 mice per cage at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center. Animals were maintained on a 12:12 light/dark cycle at room temperature that ranged from 20–24 °C and had free access to standard laboratory chow and water. All animal work was conducted according to an approved animal use protocol (UTHSC680) and in accordance with procedures approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Data sets for expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) mapping
We have previously generated large array data sets that survey gene expression in different brain regions of the BXD strains. These data sets profile up to 71 members of the BXD family and have been used extensively for eQTL mapping. In this study, we used the Hippocampus Consortium M430v2 (June06) RMA as the primary mapping data set.29 Additional data sets from the whole brain, prefrontal cortex and cerebellum were used to verify the strong cis-effect for Per3 (see Table 2 of Mozhui et al.30 for an overview of these data sets). A detailed description of strain, sex, tissue preparation and microarray method, normalization and correction procedures for each individual data set is available at www.genenetwork.org.
eQTL mapping
We used the average strain expression signal detected by each probe set as the quantitative trait. QTL mapping was done using QTL Reaper.31, 32 A set of 3795 informative markers were used for mapping,28, 33 and up to a million permutations were performed to calculate the genome-wide empirical P-values and the associated likelihood ratio statistic score.
Identification of transcripts that map to the Per3 locus
The following analytical steps were taken to identify transcripts that may be modulated by the variant in Per3 locus and are potential downstream targets of Per3: (1) We rank ordered all transcripts with expression levels >8 units that had significant point-wise linkage with the marker (rs4140148) closest to Per3. In all, 3880 transcripts were then selected that had trans QTLs near Per3 at a nominal linkage P-value <0.01. (2) Pearson's product correlation was then computed between Per3 and these potential downstream transcripts. Only transcripts that had significant expression correlations with Per3 (P<0.01) were selected for further analysis. (3) We performed partial correlation analysis controlling for the Per3 transcript and removed the transcripts that mapped back to the marker near Per3. (4) Finally, we used prior literature based information on these genes to nominate those transcripts most plausibly linked to Per3 function.
Correlation analysis
We correlated the first principal component (PC1) of Per3 with 2837 published phenotypes in GeneNetwork, which include numerous behavioral traits related to stress and alcohol response. To evaluate the false discovery rate, the adjusted P-value was computed by Westfall and Young's multiple testing procedure.34 Briefly, we randomly permuted the PC1 data 1000 times. For each permutation, we computed the adjusted P-value of Pearson's correlation between randomized PC1 and 2837 phenotypes. The adjusted P-value was determined by ranking the correlation coefficient.
Analysis of allele specific expression difference
To evaluate expression differences between the B6 and D2 alleles (B and D, respectively), we measured allelic expression in F1 hybrids using a combination of RT-PCR and a single-base primer extension technique (SNaPshot, Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com). Primer 335 was used to design a pair of PCR primers that target sequences on the same exon and flanking an informative single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
Four pools of RNA from the hippocampus and four pools of genomic DNA from the spleen of F1 hybrids (male and female B6 × D2 F1 and D2 × B6 F1 hybrids) were prepared. To avoid contamination by genomic DNA, RNA pools were treated with Turbo DNase (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA), and then first strand cDNA was synthesized (GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, USA). The genomic DNA samples were used as controls, and both cDNA and genomic DNA samples were tested concurrently using the same assay to compare expression from the B and D alleles of Per3. We amplified the cDNA and genomic DNA using GoTaq Flexi DNA polymerase (Promega Corporation, www.promega.com). PCR products were purified using ExoSap-IT (USB Corporation, www.usbweb.com) followed by SNaPshot to extend primers by a single fluorescently labeled ddNTPs. Fluorescently labeled products were purified using calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP, New England BioLabs, Beverly, MA, USA) and separated by capillary electrophoresis on ABI3130 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Quantification was done using GeneMapper v4.0 software (Applied Biosystems), and transcript abundance was measured by peak intensities associated with each allele. Ratios of B and D allele expression in both cDNA and genomic DNA pools were computed, and a t-test was done to validate expression differences and polarity of parental alleles.
Identification of potential binding sites in Per3 sequence
The transcriptional start site of Per3 was determined using the Database of Transcriptional Start Sites (DBTSS; http://dbtss.hgc.jp).36 Potential transcription factor-binding sites were then identified using the TRANSFAC database and P-Match software37 by screening the 2-kb upstream region of the Per3 sequence. All binding sites were found using default parameters in P-Match.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and supershift assay
Two oligonucleotides with 5′-biotin modification representing both the B and D alleles of the Per3 promoter indel were synthesized by MWG Operon (Supplementary Table S1). These oligonucleotides were annealed to form double-stranded probes. Nuclear proteins were isolated from the hippocampus of B6 and D2 mice. EMSA was performed using the Lightshift Chemiluminescent EMSA Kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). Each 20 μl binding reaction contained 50 fmol of biotin end-labeled target DNA, 1 × binding buffer, 1 μg of Poly(dI.dC) and 25 μg of nuclear protein extract. These reactions were incubated for 20 min at room temperature. In the supershift experiments, 3 μl ATF3 or NRF2 antibody were added, and samples were electrophoresed for 90 min at 100 volts in a 6% polyacrylamide gel (0.5% TBE running buffer). They were then transferred to a Biodyne B membrane (Pierce) and crosslinked in a Stratagene CrossLinker (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA). The Protein–DNA complexes were detected by the ThermoShift Luminescent Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (Pierce). The membranes were exposed with X-ray film.
Western blotting
Fresh hippocampus was dissected from the following strains at 2 months-of-age: BXD2, BXD22, BXD28 and BXD42. Extraction of nuclear and soluble protein was performed following a standard protocol (see Supplementary Methods and Li et al.38). Immunoblotting was performed using the WesternDot 625 Goat Anti-Mouse Western Blot Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 25 μg of total protein (nuclear and soluble fractions combined) was loaded into each well of a 4–12% NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen). Anti-Per3 primary antibody was used at a concentration of 0.2 μg ml−1 and immunopositive bands were visualized using SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Pierce) and the HRP-conjugated secondary antibody provided with the WesternDot kit. Blots were scanned using AlphaImager HP, and the intensity of each immunopositive band was quantified using AlphaView Imaging Software (version 3.0.3.0, AlphaInnotech Corp, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Unpaired t-tests were performed to determine if significant differences in protein levels were present between low (BXD2 and BXD22) and high (BXD28 and BXD42) strains.
Sequencing
The genome of DBA/2J strain has recently been sequenced by our group with 100 × average coverage using Illumina GAII and ABI SOLiD technologies.39 Reads with 25 and 50 bp from SOLiD and reads with 100 bp from Illumina GAII and HiSeq 2000 were mapped to the C57BL/6J reference genome using Corona-Lite v 4.0.2 (http://solidsoftwaretools.com/gf/) and the MAQ program v0.7.1,40 respectively. A threshold of three or more supporting reads and a consensus quality score >30 (Illumina) or a confidence value >0.5 (SOLiD) was used to declare SNPs. A complete compendium of new polymorphisms between the D2 and B6 (the source of the reference mouse genome) parental strains are freely available at GeneNetwork (www.genenetwork.org), and original sequence data are available at www.ncbi.nih.gov/sra.
Predicting the effects of non-coding and coding SNPs and indels
To predict the potential functional impact of amino-acid substitutions we used two different methods—Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant (SIFT)41 and Polymorphism Phenotyping (PolyPhen).42 SIFT uses sequence homology to predict whether a substitution is likely to affect protein function, and PolyPhen predicts protein function on the basis of 3D structure and multiple alignments of homologous sequences.
The non-coding SNPs (ncSNPs) impact score is the product of the functional element and mutation effect scores. The functional element score reflects how likely it is that the SNP is located in a functional region of the genome. The mutation score reflects the likelihood that the SNP affects the function of an overlapping element based on the evolutionary conservation of the position in alignments with other placental mammals. Thus, all ncSNPs and indels with non-zero impact scores have some evidence of functional relevance.
Stress and ethanol treatments
Forty-three BXD strains were subjected to acute restraint stress (15 min) followed by alcohol (1.8 g kg−1 i.p.) or saline injection according to the standard operating procedure for Integrative Neuroscience Initiative on Alcoholism (INIA) (https://www.iniastress.org/sop.html). Mice were allocated into five groups: RSE (restraint stress followed by ethanol), RSS (restraint stress followed by saline), NOE (no stress followed by ethanol), NOS (no stress followed by saline) and NON (no stress and no injections, baseline control). For the RSE and RSS groups, mice were placed in an immobilization tube for 15 min and then injected with either ethanol or saline (12.5% v/v, 1.8 g kg−1), and returned to home cages. For the NOE and NOS groups, mice were injected with ethanol or saline control without restraint treatment. Four hours after treatment, mice were killed and tissues were processed as described below.
Tissue dissection and RNA isolation
Mice from the normative naive set (NON) and restraint/ethanol treatment sets (NOS, NOE, RSE and RSS) were killed at ∼2–3 months-of-age by cervical dislocation. Details on the strain, sex and age of each animal can be accessed from http://www.genenetwork.org/dbdoc/UT_ILM_BXD_hipp_NON_0909.html. Brains were removed quickly and stored in RNAlater (Ambion) overnight at 4 °C, then kept at −80 °C until use. The hippocampus was removed as described in Lu et al.,43 and left and right hippocampi were pooled and stored at −80 °C. RNA was isolated from these tissues using RNA STAT-60 (Tel-Test, www.tel-test.com) as per the manufacturer's instructions. RNA purity and concentration were evaluated with a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Rockland, DE, USA), and RNA integrity was assessed on the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Palo Alto, CA, USA). We required an RNA integrity number of >8. This RNA integrity number value is based on the intensity ratio and amplitude of 18s and 28s rRNA signals.
Microarray analysis of stress and ethanol treatment groups
Hippocampal gene expression was assayed using Illumina Sentrix Mouse-6 v1.1 arrays according to manufacturer's protocols (http://www.illumina.com/). Microarray runs for the five groups (RSE, RSS, NOE, NOS and NON) were carried out in a counterbalanced manner to avoid batch effects. Raw microarray data were normalized using the rank invariant method and background subtraction protocols provided by Illumina as part of the BeadStation software suite. We log-transformed the expression values and stabilized the variance of each array to a mean of 8 and a s.d. of 2 per array. A single unit on this scale (log2) corresponds to a twofold difference in expression.
Restraint and ethanol-treated data sets were used to evaluate the effect of these treatments on Per3. We used a linear nested-ANOVA model to evaluate the effect of Per3 genotype, sex and treatment (RSE, RSS, NOE, NOS and NON) on expression. The ANOVA model was analyzed using the R software (http://www.R-project.org). Differences were considered significant when P<0.05.
Per3 knockout (KO) mice and gene expression
Two Per3 KO female mice (C57BL/6J background) were obtained from Vanderbilt University. Creation of the KOs is described in Pendergast et al.44 The original Per3 KOs were created on a 129/Sv background.45 The KOs were then backcrossed to the C57BL/6J strain.
We measured gene expression in the hippocampus of these KOs and wildtype using Illumina Sentrix Mouse-6 v1.1 arrays according to the manufacturer's protocols. Array data were normalized using the rank invariant method. Probes were then filtered by expression and only probe sets with above background expression were retained. Differential expression was then assessed by unpaired Student's t-test. Differences are considered significant when a P-value is <0.05.
Results
Expression variation of Per3 in the hippocampus of BXD strains
The expression of Per3 varies widely among the BXD family with differences that range from approximately twofold to fivefold depending on the specific probe set (Supplementary Table S2). Higher expression is invariably associated with the D allele; an effect seen most prominently in the 3′ UTR (1460662_at and 1421087_at), and the 3′ UTR and last three exons of Per3 (1421086_at) (Figure 1a). None of the probe sets overlap SNPs between D and B genotypes (SNPs will tend to increase the apparent expression of the B genotype; see ref. 46) Additional probe sets targeting introns are either not abundantly expressed (1442243_at) or overlap SNPs (1458176_at and 1441445_at) and were excluded from analysis (Figure 1a).
Cis-modulation of Per3 expression by B and D alleles in the hippocampus. (a) Expression of Per3 was measured by six Affymetrix M430v2 probe sets. Probe sets 1421087_at and 1460662_at target different portions of the 3′ UTR and probe set 1421086_at targets the 3′ UTR and the last coding exons of Per3. Approximate positions of these probe sets and the Per3 isoforms are shown. The reference gene model is based on RefSeq gene NM_016831 (UCSC genome Browser mm9, build 37). (b) Expression QTLs for the three probe sets (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at) show significant cis-regulation of Per3 expression. The y axis denotes likelihood ratio statistic (LRS) scores and the x axis denotes physical position (Mb) on chromosome 4. The peak LRS is near the location of the Per3 gene (gray triangle). The horizontal lines indicate the genome-wide suggestive (gray) and significant (red) thresholds.
To generate a single consensus estimate of expression across the panel of BXD strains, we computed the PC1 of three probe sets (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at). We used this consensus Per3 eigengene to identify BXD strains with the lowest and highest expression. In the hippocampus, BXD2 and BXD22 have the lowest, and BXD28 and BXD42 have the highest expression of Per3 (Figure 2a). This genetic difference in transcript levels between the extreme strains was confirmed at the protein level by western blot analysis that showed lower PER3 level in BXD2 and BXD22 compared with BXD28 and BXD42 (Figure 2b,c).
Analysis of PER3 protein level in mouse hippocampus. (a) Per3 has significant expression variation in the BXDs. The wide expression range is shown by the PC1 of the Per3 probe sets (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at). The extreme strains (red bars) are BXD2 and BXD22 with the lowest transcript level, and BXD28 and BXD42 with the highest transcript level. Strains are indicated along the x axis. (b) PER3 protein level in the hippocampus of the two high and two low strains was analyzed by western blot. PER3 protein bands are detected as doublets ranging from 131 to 150 kDa. (c) Densitometric analysis shows a significant expression difference between the strains that is consistent with transcript level. The difference was determined using Student's t test (*=P<0.01).
eQTL analysis of Per3
All three Per3 probe sets (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at) are associated with a significant QTL on distal chromosome 4, close to the location of the Per3 gene itself (150.38 Mb). The maximum likelihood ratio statistic is 162 at SNP marker rs6358921 (149.929 Mb). The D allele is associated with a positive-additive effect and a 1.66-fold (20.735) increase in expression per allele (Figure 1b). This cis-eQTL for Per3 was confirmed in five other brain regions (Supplementary Figure S1). This highly significant and robust cis-QTL is strong evidence that sequence variants in or near Per3 cause differences in transcript expression levels.
To validate the cis-regulation of Per3, we measured allele specific expression in B6D2F1 and D2B6F1 hybrids.46, 47 Three SNPs in the 3′ UTR and a SNP in exon 15 of Per3 were used to capture expression differences between the D and B alleles. The allele-specific expression analysis confirms that the D allele has approximately twofold higher expression than the B allele (Table 1) and that the effect is almost entirely due to one or more local polymorphisms.
Sequence variation in Per3
To identify cis-acting polymorphisms in Per3 that cause expression variation between B and D alleles, we examined Per3 sequence differences using the recently sequenced genome of DBA/2J.39 There are a total of 163 SNPs and 30 indels in Per3 between the B6 and D2 genomes. Of these, four are non-synonymous mutations in exons 1 (Pro10Leu), 9 (Arg372Gln), 13 (Phe500Leu) and 15 (Glu590Gly) (Table 2). We used the SIFT and PolyPhen algorithms to predict the impact of these four non-synonymous mutations on protein function. The mutations Pro10Leu in exon 1 and Phe500Leu in exon 9 are predicted to be damaging and deleterious by SIFT and PolyPhen 2, respectively. The mutations Phe500Leu in exon 13 and Glu590Gly in exon 15 are predicted to be deleterious by PolyPhen 2 only. These amino-acid changes can potentially affect the structure and/or function of Per3 and have an influence on the expression of downstream genes.
To determine the potential impact of non-coding SNPs on Per3 transcription, we predicted impact scores for these SNPs based on overlap with conserved functional elements. There are 159 SNPs and 18 indels (Supplementary Table S3) within 5 kb upstream or downstream of the transcription start site of Per3. Although the majority of these sequence variants have low-impact scores, two SNPs—rs32260283 and rs32042445—and an indel at 150.418813 Mb are all within 1 kb of the Per3 transcription start site and are located in conserved regulatory elements (Open Regulatory Annotation Database ID: OREG0048389 and OREG0033366). We searched the TRANSFAC database for DNA motifs in the upstream region of Per3 that may be disrupted by these variants.37 We found that an indel (-/T) disrupts a putative stress response core element (STRE: CCCCT/AGGGG) in BXD strains that inherit the B allele. This site is a potential candidate for the cis-QTL underlying the expression difference and the massive cis-eQTL associated with Per3.
Effect of indel on protein binding
To determine whether the indel in the STRE motif alters transcription factor binding, we performed EMSA using oligonucleotides from B6 (49 bp) and D2 (50 bp). The EMSA detected two DNA-protein complexes that were unique to the D2 promoter sequence and absent in B6 (Figure 3a). Super-shift assay with the PER3 antibody revealed no difference and no evidence of autoregulation (data not shown). The EMSA result supports the hypothesis that the -/T polymorphism in STRE affects binding of transcription factors.
Functional characterization of the indel in the STRE promoter element. (a) The protein binding properties of the core STRE element in B6 and D2 was evaluated by EMSA. Double-stranded probe sequences were designed for the B6 (49-mer oligonucleotide on the left; lanes 1–6) and D2 (50-mer oligonucleotide on the right; lanes 7–12) alleles. In all, 100 fmol and 40 fmol of these probes were used to assay protein extracted from the brain tissue of B6 and D2. DNA–protein complexes are indicated by arrows. The B allele, which has the deletion, does not show DNA–protein complexes, whereas the D allele formed two DNA–protein complexes with protein from both B6 and D2 when 100 fmol of probes was used (lane 7 and 9). Control lanes 5 and 11 have 0 fmol probes. Lanes 6 and 12 are free oligonucleotides without protein. The upper three bands in lanes 1–5 and 7–11 are non-specific DNA–protein complexes. (b) Supershift assay using antibody against ATF3 shows no binding of the STRE-protein complex by ATF3. The arrowhead indicates the location of the STRE-protein complex. (c) Supershift assay with antibody against NRF3 reveal a slow migrating STRE-protein complex that contains NRF2. The arrowhead (complex) indicates the location of the STRE-DNA complex, and the arrow indicates the location of the NRF2 supershifted complex.
The STRE motif is known to regulate gene expression in response to cellular stress, possibly by affecting the binding of transcription factors such as NRF2 and ATF3.48, 49 We examined whether NRF2 or ATF3 binds to the STRE site by performing a super-shift assay using antibodies against these two transcription factors. A new slow migrating complex containing NRF2 was present in both B6 and D2 protein extracts but was absent when ATF3 antibody was used (Figure 3b,c). This result suggests that NRF2 mediates the expression of Per3 through the STRE element and is likely to be involved in the differential expression of Per3 in the BXD family.
Correlation between Per3 expression and behavioral traits
We next examined whether the marked variation in Per3 expression has an impact on putative downstream phenotypes. We carried out covariance analyses of PC1 of the three probe sets (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at) with an extensive database of BXD phenotypes to identify traits that are strongly linked with variation in Per3 transcript abundance. The first component of Per3 expression is significantly correlated with five anxiety-related behaviors and five ethanol-responsive traits (P<0.05; Figure 4; Supplementary Table S4). Each of these 10 behavioral traits was assayed by different research groups using independent BXD cohorts and highlights a robust correlation between Per3 and anxiety- and alcohol-related traits.
Correlation network graph of Per3 with behavioral phenotypes. The PC1 of Per3 expression (1421087_at, 1460662_at and 1421086_at) is highly correlated with ethanol-related and stress-related traits (P<0.05). The correlation coefficient, P-value and GeneNetwork's Trait IDs are shown in Supplementary Table S4. The thickness of line denotes the absolute correlation coefficient.
Impact of Per3 on downstream gene expression and function
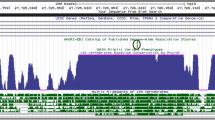
To extract and evaluate intermediate molecular and genetic networks interposed between the Per3 polymorphism and higher order phenotypes, we extracted transcripts with trans QTLs that map to the Per3 locus in the neocortex (Figure 5). We found a set of 48 transcripts with likelihood ratio statistic scores above 10 that map near Per3 (nominal P<0.01). This set includes genes associated with RNA processing (Pabpc1, Rbm14, Rps11, Sfrs1 and Sfrs12), ion channel activity (Cacna1c, Trpm2 and Fxyd6) and synaptic function (Anks1b and Doc2a). We next asked if any of these 48 genes that are putatively trans-regulated by Per3 have functional associations with (1) circadian rhythm, (2) stress or (3) alcoholism. For this, we mined the literature for such associations using the Chilibot web resource (http://www.chilibot.net/).50 Four genes (Rbm14, Pabpc1, Irak2 and Il2rb) are associated with circadian rhythm, six genes (Trpm2, Erp29, Sepp1, Cacna1c, Smpd2 and Trim29) are associated with responses to physiological and cellular stress, two genes (Pdlim5 and Fxyd6) are associated with schizophrenia and one gene (Cast) is associated with alcoholism.
Downstream genes regulated by Per3. 48 transcripts map as trans-QTLs to Per3 (chromosome 4, 150–151 Mb) at likelihood ratio statistic >10 (P<0.01) in the neocortex dataset. These include genes associated with circadian rhythm (highlighted yellow), stress response (green), alcoholism (blue), schizophrenia (gray) and synaptic functions (turquoise). Seven of these genes are differentially expressed between Per3 KO and wildtype (red). Nodes highlighted in two colors are genes that are differentially expressed between Per3 KO and wildtype as well as associated with stress, alcoholism or schizophrenia.
To confirm potential Per3 downstream targets, we compared expression levels between wild type and homozygous Per3 KO mice. We found 2217 differentially expressed genes (P<0.05), seven of which (Cast, Trpm2, Anks1b, Gpr81, Hsbp1, Pdlim5 and 4930528J18Rik) are also among the 48 transcripts with trans QTLs near Per3.
Effect of stress and ethanol on Per3 expression
Given the associations between Per3 and stress- and alcohol-related traits, we evaluated the expression of Per3 under five different conditions: (1) RSE, (2) RSS, (3) NOS, (4) NOE and (5) NON. Four-way nested ANOVA revealed significant effects of strain and an interaction between stress and ethanol on Per3 expression (P<0.05; Figure 6a). Post hoc analysis showed significantly higher Per3 expression (P<0.05) in the ethanol and the stress with ethanol groups (NOE and RSE) compared with the naive (NON) and saline controls (NOS). However, there was no significant effect of restraint alone—that is, no difference between RSS and NON/NOS groups on Per3 expression (P<0.08) (Figure 6b).
Effects of stress and ethanol on the Per3 expression. (a) Nested ANOVA found significant stress × ethanol effect on Per3 expression in the BXDs. Solid line denotes expression of Per3 under ethanol followed by stress treatments; dotted line denotes expression of Per3 under saline followed by stress treatments. (b) Expression of Per3 in 146 BXD strains under stress and non-stress treatments are depicted as box plots. The horizontal lines indicate the median values, the boxes represent the inter-quartile range between 25th and 75th percentiles; the upper line extending from the box indicates the largest value between the 75th percentiles and 1.5 times the inter-quartile range. The lower line extending from the box indicates the smallest point between the 25th percentiles and 1.5 times the inter-quartile range. The open circle represents values that lie outside these ranges.
Discussion
Our work suggests that Per3, a circadian regulator, has a pleiotropic influence on response to alcohol and stress, and provides a potential causal link between stress, sleep disruption and addiction. Expression of Per3 varies up to fivefold among strains of mice and is under strong cis-acting control in the BXD family. In addition to these prominent genotypic effects on expression, there are also effects caused by alcohol and an interaction with restraint-induced stress. Our study is the first to attempt to systematically investigate the association between Per3 and behavioral phenotypes. The implication of our study is that Per3 serves as a new candidate gene for alcohol- and stress-responsive behavior, and supports a role for Per3 in circadian clock function.45
We have identified an indel in the stress response promoter motif that alters DNA–protein complexes formed by Nrf2, a transcriptional activator. This indel is an excellent candidate contributing to strain differences in Per3 expression and is also likely a molecular locus regulating interaction between stress and alcohol responses. The indel in the STRE promoter element is an especially strong candidate for the cis-QTL. EMSA showed two DNA–protein complexes that were unique to the D allele promoter variant associated with higher gene expression. In contrast, low expression of Per3 is linked to the B allele promoter variant. Interestingly, STREs modulate transcription of stress-responsive genes under various cellular challenges, including oxidative stress.49, 51 Because alcohol is known to induce oxidative stress in the brain,52, 53 the STRE variant may be an important regulator of basal and alcohol/stress-responsive expression of Per3.
The transcriptome and allele-specific expression analyses consistently detected higher expression for the D allele of Per3 relative to the B allele. This difference is accompanied by a large number of sequence differences between strains that inherit these alternative B and D alleles and haplotypes. By resequencing the Per3 gene we detected 163 SNPs that differentiated the B and D genotypes. The majority of these SNPs—142 of 163—are in introns. However, we detected four missense mutations, two of which are predicted by both SIFT and PolyPhen 2 to produce significant functional changes in the PER3 protein.
The set of mutations we have detected in both the promoter and untranslated regions are of significant relevance in explaining the high level of variation in Per3 mRNA levels. Complex transcription regulatory loops and posttranscriptional decay mechanisms are known to modulate the normal diurnal dynamics of Per3 expression.54, 55, 56 The sequence of the 3′ UTR is important in decay kinetics of Per3 mRNA, and mutations in a U-rich stretch can radically alter message stability.54 However, none of the 3′ UTR SNPs between B and D alleles overlap this crucial U-rich region. Per3 also has long and short 3′ UTR isoforms. We therefore cannot dismiss differences in 3′ UTR structure and mRNA decay rates as a possible source of variation in Per3 message levels.
The hippocampus is a key region that helps mediate response to stressors. A hallmark is feedback inhibition of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Chronic stress leads to changes in both neuronal activity and neuronal morphology.25 The hippocampus is also particularly vulnerable to the effects of alcohol. Both human and rodent studies have shown that prolonged exposure to both stress and alcohol leads to hippocampal atrophy.23, 24 The hippocampus is an especially suitable site to study the interaction of stressors and alcohol. In this study, we found a significant interaction of stress and ethanol on Per3 expression, which suggests that ethanol and stress affect the expression of Per3 in an opposing manner. The interaction of ethanol and stress could be mediated via the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal system.
We were initially motivated to study Per3 because chronic restraint upregulates the expression of this gene in both B6 and D2 parental strains,13 and because the expression of Per3 is associated with a highly significant cis-QTL in the BXD family. Per1 and Per2 were also upregulated by the same restraint stress protocol, but unlike Per3, expression of these two genes is not self regulated. The very strong cis-regulation of Per3 with a likelihood ratio statistic of ∼160 (LOD ∼35) in some brain regions made this gene a prime candidate for an analysis of downstream consequences of expression differences using reverse complex trait analysis.45, 56 We found that variation in expression of Per3 has downstream effects on stress response, anxiety-associated traits and addiction-related behavior (Figure 4). The Per3 downstream network also modulates 48 transcripts associated with circadian rhythm, stress response, alcoholism and schizophrenia. Of seven downstream genes that are also differentially expressed between KO and wildtype, three genes (Cast, Trpm2 and Pdlim5) are associated with stress response, alcoholism and schizophrenia. Cast was identified as the susceptibility gene for alcohol dependence through genome-wide association study in humans.57 Trpm2 is highly expressed in the brain and is involved in response to stress and in the genetic etiology of bipolar disorder.58 Pdlim5 has been identified as a potential susceptibility gene for schizophrenia in humans.59 These results not only demonstrate a link between sequence differences, variation in transcript abundance and phenotypes, but also imply that Per3 is an excellent candidate gene for alcohol and stress responses.
In this study, we used an integrative approach to relate gene expression variation of Per3 with systems level phenotypes. We found that a local sequence variant contributes to significant differences in the mRNA and protein level of Per3 among the BXD family as well as the parental B6 and D2 strains. Such quantitative differences in mRNA were correlated with physiological and behavioral traits related to stress and addiction, suggesting that natural variations in Per3 may be causally associated with these traits. Treatments with alcohol and acute restraint in turn had significant effects on Per3 expression. The combined analysis of downstream genes and differential expression between KO and wildtype showed that Per3 has functional implications in alcohol and stress response.
References
Lauterbach D, Behnke C, McSweeney LB . Sleep problems among persons with a lifetime history of posttraumatic stress disorder alone and in combination with a lifetime history of other psychiatric disorders: a replication and extension. Compr Psychiatry 2011; 52: 580–586.
McClung CA . Circadian rhythms, the mesolimbic dopaminergic circuit, and drug addiction. ScientificWorldJournal 2007; 7: 194–202.
Yagita K, Okamura H . Forskolin induces circadian gene expression of rPer1, rPer2 and dbp in mammalian rat-1 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 2000; 465: 79–82.
Roybal K, Theobold D, Graham A, DiNieri JA, Russo SJ, Krishnan V et al. Mania-like behavior induced by disruption of CLOCK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 6406–6411.
Shi J, Wittke-Thompson JK, Badner JA, Hattori E, Potash JB, Willour VL et al. Clock genes may influence bipolar disorder susceptibility and dysfunctional circadian rhythm. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008; 147B: 1047–1055.
Falcon E, McClung CA . A role for the circadian genes in drug addiction. Neuropharmacology 2009; 56 (Suppl 1): 91–96.
Abarca C, Albrecht U, Spanagel R . Cocaine sensitization and reward are under the influence of circadian genes and rhythm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 9026–9030.
Spanagel R, Pendyala G, Abarca C, Zghoul T, Sanchis-Segura C, Magnone MC et al. The clock gene Per2 influences the glutamatergic system and modulates alcohol consumption. Nat Med 2005; 11: 35–42.
Swaab DF, Bao AM, Lucassen PJ . The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev 2005; 4: 141–194.
Cano G, Mochizuki T, Saper CB . Neural circuitry of stress-induced insomnia in rats. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 10167–10184.
Sterlemann V, Ganea K, Liebl C, Harbich D, Alam S, Holsboer F et al. Long-term behavioral and neuroendocrine alterations following chronic social stress in mice: implications for stress-related disorders. Horm Behav 2008; 53: 386–394.
Chen CP, Kuhn P, Advis JP, Sarkar DK . Chronic ethanol consumption impairs the circadian rhythm of pro-opiomelanocortin and period genes mRNA expression in the hypothalamus of the male rat. J Neurochem 2004; 88: 1547–1554.
Mozhui K, Karlsson RM, Kash TL, Ihne J, Norcross M, Patel S et al. Strain differences in stress responsivity are associated with divergent amygdala gene expression and glutamate-mediated neuronal excitability. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 5357–5367.
Meerlo P, de Bruin EA, Strijkstra AM, Daan S . A social conflict increases EEG slow-wave activity during subsequent sleep. Physiol Behav 2001; 73: 331–335.
Archer SN, Robilliard DL, Skene DJ, Smits M, Williams A, Arendt J et al. A length polymorphism in the circadian clock gene Per3 is linked to delayed sleep phase syndrome and extreme diurnal preference. Sleep 2003; 26: 413–415.
Viola AU, Archer SN, James LM, Groeger JA, Lo JC, Skene DJ et al. PER3 polymorphism predicts sleep structure and waking performance. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 613–618.
Artioli P, Lorenzi C, Pirovano A, Serretti A, Benedetti F, Catalano M et al. How do genes exert their role? Period 3 gene variants and possible influences on mood disorder phenotypes. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2007; 17: 587–594.
Benedetti F, Dallaspezia S, Colombo C, Pirovano A, Marino E, Smeraldi E . A length polymorphism in the circadian clock gene Per3 influences age at onset of bipolar disorder. Neurosci Lett 2008; 445: 184–187.
Kripke DF, Nievergelt CM, Joo E, Shekhtman T, Kelsoe JR . Circadian polymorphisms associated with affective disorders. J Circadian Rhythms 2009; 7: 2.
Nievergelt CM, Kripke DF, Barrett TB, Burg E, Remick RA, Sadovnick AD et al. Suggestive evidence for association of the circadian genes PERIOD3 and ARNTL with bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2006; 141B: 234–241.
Cunningham CL . Localization of genes influencing ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in BXD recombinant inbred mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995; 120: 28–41.
Yang RJ, Mozhui K, Karlsson RM, Cameron HA, Williams RW, Holmes A . Variation in mouse basolateral amygdala volume is associated with differences in stress reactivity and fear learning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008; 33: 2595–2604.
Heinz A, Beck A, Grusser SM, Grace AA, Wrase J . Identifying the neural circuitry of alcohol craving and relapse vulnerability. Addict Biol 2009; 14: 108–118.
Redila VA, Olson AK, Swann SE, Mohades G, Webber AJ, Weinberg J et al. Hippocampal cell proliferation is reduced following prenatal ethanol exposure but can be rescued with voluntary exercise. Hippocampus 2006; 16: 305–311.
Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Chattarji S . Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6810–6818.
Taylor BA, Wnek C, Kotlus BS, Roemer N, MacTaggart T, Phillips SJ . Genotyping new BXD recombinant inbred mouse strains and comparison of BXD and consensus maps. Mamm Genome 1999; 10: 335–348.
Peirce JL, Lu L, Gu J, Silver LM, Williams RW . A new set of BXD recombinant inbred lines from advanced intercross populations in mice. BMC Genet 2004; 5: 7.
Williams RW, Gu J, Qi S, Lu L . The genetic structure of recombinant inbred mice: high-resolution consensus maps for complex trait analysis. Genome Biol 2001; 2, RESEARCH0046.
Overall R, Kempermann G, Peirce J, Lu L, Goldowitz D, Gage F et al. Genetics of the hippocampal transcriptome in mouse: a systematic survey and online neurogenomics resource. Front Neurogen 2009; 1: 55.
Mozhui K, Ciobanu DC, Schikorski T, Wang X, Lu L, Williams RW . Dissection of a QTL hotspot on mouse distal chromosome 1 that modulates neurobehavioral phenotypes and gene expression. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000260.
Chesler EJ, Lu L, Shou S, Qu Y, Gu J, Wang J et al. Complex trait analysis of gene expression uncovers polygenic and pleiotropic networks that modulate nervous system function. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 233–242.
Peirce JL, Li H, Wang J, Manly KF, Hitzemann RJ, Belknap JK et al. How replicable are mRNA expression QTL? Mamm Genome 2006; 17: 643–656.
Shifman S, Bell JT, Copley RR, Taylor MS, Williams RW, Mott R et al. A high-resolution single nucleotide polymorphism genetic map of the mouse genome. PLoS Biol 2006; 4: e395.
Westfall P, Young S . Resampling-Based Multiple Testing: Examples and Methods for P-Value Adjustment. John Wiley and Sons: New York, 1993.
Rozen S, Skaletsky H . Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 2000; 132: 365–386.
Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Sugano S, Nakai K . DBTSS, DataBase of Transcriptional Start Sites: progress report 2004. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32 (Database issue): D78–D81.
Chekmenev DS, Haid C, Kel AE . P-Match: transcription factor binding site search by combining patterns and weight matrices. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33 (Web Server issue): W432–W437.
Li Z, Mulligan MK, Wang X, Miles MF, Lu L, Williams RW . A transposon in comt generates mRNA variants and causes widespread expression and behavioral differences among mice. PLoS One 2010; 5: e12181.
Wang X, Agarwala R, Capra J, Chen Z, Church D, Ciobanu D et al. High-throughput sequencing of the DBA/2J mouse genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11 (Suppl 4): O7.
Li H, Ruan J, Durbin R . Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores. Genome Res 2008; 18: 1851–1858.
Ng PC, Henikoff S . Accounting for human polymorphisms predicted to affect protein function. Genome Res 2002; 12: 436–446.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 248–249.
Lu L, Airey DC, Williams RW . Complex trait analysis of the hippocampus: mapping and biometric analysis of two novel gene loci with specific effects on hippocampal structure in mice. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 3503–3514.
Pendergast JS, Friday RC, Yamazaki S . Distinct functions of Period2 and Period3 in the mouse circadian system revealed by in vitro analysis. PLoS One 2010; 5: e8552.
Shearman LP, Jin X, Lee C, Reppert SM, Weaver DR . Targeted disruption of the mPer3 gene: subtle effects on circadian clock function. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 6269–6275.
Ciobanu DC, Lu L, Mozhui K, Wang X, Jagalur M, Morris JA et al. Detection, validation, and downstream analysis of allelic variation in gene expression. Genetics 2010; 184: 119–128.
Cowles CR, Hirschhorn JN, Altshuler D, Lander ES . Detection of regulatory variation in mouse genes. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 432–437.
Alam J, Cook JL . Transcriptional regulation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene via the stress response element pathway. Curr Pharm Des 2003; 9: 2499–2511.
Gong P, Stewart D, Hu B, Vinson C, Alam J . Multiple basic-leucine zipper proteins regulate induction of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene by arsenite. Arch Biochem Biophys 2002; 405: 265–274.
Chen H, Sharp BM . Content-rich biological network constructed by mining PubMed abstracts. BMC Bioinformatics 2004; 5: 147.
Cohen B, Addadi Y, Sapoznik S, Meir G, Kalchenko V, Harmelin A et al. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor C by oxidative and thermal stress is mediated by lens epithelium-derived growth factor/p75. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 921–933.
Nordmann R . Oxidative stress from alcohol in the brain. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl 1987; 1: 75–82.
Renis M, Calabrese V, Russo A, Calderone A, Barcellona ML, Rizza V . Nuclear DNA strand breaks during ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. FEBS Lett 1996; 390: 153–156.
Kwak E, Kim TD, Kim KT . Essential role of 3′-untranslated region-mediated mRNA decay in circadian oscillations of mouse Period3 mRNA. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 19100–19106.
Maywood ES, O’Neill JS, Reddy AB, Chesham JE, Prosser HM, Kyriacou CP et al. Genetic and molecular analysis of the central and peripheral circadian clockwork of mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2007; 72: 85–94.
Ueda HR, Hayashi S, Chen W, Sano M, Machida M, Shigeyoshi Y et al. System-level identification of transcriptional circuits underlying mammalian circadian clocks. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 187–192.
Treutlein J, Cichon S, Ridinger M, Wodarz N, Soyka M, Zill P et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2009; 66: 773–784.
McQuillin A, Bass NJ, Kalsi G, Lawrence J, Puri V, Choudhury K et al. Fine mapping of a susceptibility locus for bipolar and genetically related unipolar affective disorders, to a region containing the C21ORF29 and TRPM2 genes on chromosome 21q22.3. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 134–142.
Li C, Tao R, Qin W, Zheng Y, He G, Shi Y et al. Positive association between PDLIM5 and schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2008; 11: 27–34.
Gaglani SM, Lu L, Williams RW, Rosen GD . The genetic control of neocortex volume and covariation with patterns of gene expression in mice. BMC Neuroscience 2009; 10: 44.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and Integrative Neuroscience Initiative on Alcoholism (INIA) (U01AA13499, U01AA017590 and U01AA014425), and supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30771200, 30971591 and 30770666). This work was also supported by the UTHSC Center for Integrative and Translational Genomics. We thank the CHDI Foundation and Dr Glenn D. Rosen for providing access to neocortical gene expression data for the BXD strains of mice.60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Translational Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Mozhui, K., Li, Z. et al. A promoter polymorphism in the Per3 gene is associated with alcohol and stress response. Transl Psychiatry 2, e73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2011.71
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2011.71
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of Per3, a circadian clock gene, in embryonic development of mouse cerebral cortex
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
A novel heat shock protein alpha 8 (Hspa8) molecular network mediating responses to stress- and ethanol-related behaviors
neurogenetics (2016)
-
Joint mouse–human phenome-wide association to test gene function and disease risk
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Adenosinergic Regulation of Striatal Clock Gene Expression and Ethanol Intake During Constant Light
Neuropsychopharmacology (2014)
-
Sleep and Substance Use Disorders: An Update
Current Psychiatry Reports (2014)