Abstract
The quantum anomaly that breaks the symmetry, for example the parity and the chirality, in the quantization leads to a physical quantity with a topological Chern invariant. We report the observation of a Chern structure in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms by employing electric transport. We observed the superconductor-to-insulator transition by reducing the thickness of Sr2RuO4 single crystals. The appearance of a gap structure in the insulating phase implies local superconductivity. Fractional quantized conductance was observed without an external magnetic field. We found an anomalous induced voltage with temperature and thickness dependence, and the induced voltage exhibited switching behavior when we applied a magnetic field. We suggest that there was fractional magnetic-field-induced electric polarization in the interlayer. These anomalous results are related to topological invariance. The fractional axion angle Θ = π/6 was determined by observing the topological magneto-electric effect in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The mathematical structure characterized by Chern numbers1 has yielded very important findings in both condensed-matter and high-energy physics2. The quantum Hall effect in graphene provides the quantized Hall conductance of  with p and q coprimes3. The quantization of the Hall current and anyonic particles with exotic mutual statistics can be explained by the Chern-Simons (CS) term in (2 + 1)-dimensional topological field theory, which is known as the parity anomaly4,5,6. In 3 + 1 dimensions, the neutral pion decay7,8 and the creation of excitation momentum by quantized vortices in the superfluid 3He9 are described by the chiral anomaly. However, as yet there has been no experimental evidence of quantum anomalies and Chern structures in superconductors. Recently, the magneto-electric effect in topological superconductors and insulators has been predicted theoretically from the Chern-Pontryagin term (topological Θ-term with Θ = ±π) in 3 + 1 dimensions10,11. The Chern structure in superconductivity is interesting in itself and may also have implications regarding the esoteric physics of quantum chromodynamics (axion electrodynamics)12,13 in condensed-matter experiments. In addition to the purely scientific interest that it arouses, the Chern structure may provide the basis for new applications to magneto-electric coupling devices and for the development of the topological quantum computation of non-Abelian statistics14.
with p and q coprimes3. The quantization of the Hall current and anyonic particles with exotic mutual statistics can be explained by the Chern-Simons (CS) term in (2 + 1)-dimensional topological field theory, which is known as the parity anomaly4,5,6. In 3 + 1 dimensions, the neutral pion decay7,8 and the creation of excitation momentum by quantized vortices in the superfluid 3He9 are described by the chiral anomaly. However, as yet there has been no experimental evidence of quantum anomalies and Chern structures in superconductors. Recently, the magneto-electric effect in topological superconductors and insulators has been predicted theoretically from the Chern-Pontryagin term (topological Θ-term with Θ = ±π) in 3 + 1 dimensions10,11. The Chern structure in superconductivity is interesting in itself and may also have implications regarding the esoteric physics of quantum chromodynamics (axion electrodynamics)12,13 in condensed-matter experiments. In addition to the purely scientific interest that it arouses, the Chern structure may provide the basis for new applications to magneto-electric coupling devices and for the development of the topological quantum computation of non-Abelian statistics14.
Layered perovskite Sr2RuO4 is a leading candidate for a spin-triplet and chiral p-wave superconductor in quasi-two-dimensional electron systems15, and is also known as a Chern superconductor with a non-zero Chern invariant. The spontaneously broken time-reversal and parity symmetry realize novel topological quantum phenomena such as zero-magnetic-field quantum Hall effects16,17,18, gapless Majorana excitations in an edge or the core of vortices19 and the non-Abelian statistics of half-quantum vortices20. However, the chiral-multi-domains in millimeter-scale Sr2RuO4 obscure these novel phenomena. We have reported that the current-voltage (I–V) curves in the microscale chiral single domain of Sr2RuO4 with submicron thickness violate parity due to the excitation of the Majorana-Wyle fermions along the one-dimensional chiral edge current21,22. To clarify the Chern structure through quantum transport in units of e2/h in two-(or quasi-two-) dimensional chiral superconducting layers, we have investigated electric transport properties by using chiral single domain size Sr2RuO4 with nanoscale thickness23. Specifically, in this paper, we report the fractionalized Chern structure (number) in the quantum critical region from the results of the anomalous properties, which are revealed by reducing the Sr2RuO4 thickness to the nanometer range.
One unsolved problem in Sr2RuO4 systems is the two superconducting phases with Tc ~ 1.5 and 3 K. Although pure Sr2RuO4 single crystals exhibit a Tc of about 1.5 K, enhancement to about 3 K has been reported in Sr2RuO4-Ru eutectic systems24. However, recent investigations have found that, even in pure Sr2RuO4 without Ru inclusions, an enhanced Tc of around 3 K is observed when measuring uniaxial pressure effects along the c axis25, strain effects26 and the properties near the lattice dislocations27. As regards this discrepancy, electric transport measurements in nanoscale thin films of Sr2RuO4 single crystals allow access to both topological quantum states and the pairing mechanism itself in chiral p-wave superconductors.
In this paper, we report the emergence of a Chern structure in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 single crystal nanofilms based on the anomalous transport properties observed for the in-plane and interlayer directions. By reducing the Sr2RuO4 thickness to the nanometer range, we found that a fractional quantum Hall resistance of h/4e2 − h/2e2 occurred as a consequence of the spontaneous Hall current without an external magnetic field. The gap structure below 3 K shows localized superconducting islands connected by tunnel junctions. The anomalous induced voltage and the switching behavior were observed as a function of temperature and thickness under zero bias current for an applied magnetic field parallel to the c axis. The applied magnetic field induced electric polarization in the interlayer of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms. In Sr2RuO4 with a nanoscale thickness, we suggested that the fractional topological magneto-electric effect occurs in three (quasi-two) dimensions, which is characterized by the fractional axion angle (coefficient) Θ = π/6 of the E · B term in the chiral anomaly.
Results
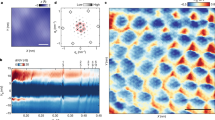
Figure 1(a) shows the temperature dependence of the longitudinal resistivity ρxx for various thicknesses of exfoliated Sr2RuO4 films.  is resistance per square per RuO2. In general, bulk (thick) superconductors exhibit zero longitudinal resistivity below Tc. We have observed zero resistivity below Tc = 1.59 K for microscale Sr2RuO4 with a thickness of 340 nm, which is consistent with the Tc of bulk Sr2RuO4 crystals15,24. Samples with a thickness of 147 and 470 nm exhibited a slight drop in resistivity around 1.5 ~ 3 K, and showed non-zero resistivity below Tc. The result shows that the flow of vortices can be caused by quantum fluctuations of the superconducting phase28,29. Interestingly, the insulating behavior was observed in samples A and B with nanoscale thickness. It has been reported that the effect of a negative pressure acts on thin films as the thickness of the exfoliated films decreases to the nanometer range30. The pressure plays a key role in modifying the electric properties of the family of ruthenium oxides31. Thus we presume that the transition from superconductor to insulator appeared in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms as a result of reducing sample thickness to the nanometer range.
is resistance per square per RuO2. In general, bulk (thick) superconductors exhibit zero longitudinal resistivity below Tc. We have observed zero resistivity below Tc = 1.59 K for microscale Sr2RuO4 with a thickness of 340 nm, which is consistent with the Tc of bulk Sr2RuO4 crystals15,24. Samples with a thickness of 147 and 470 nm exhibited a slight drop in resistivity around 1.5 ~ 3 K, and showed non-zero resistivity below Tc. The result shows that the flow of vortices can be caused by quantum fluctuations of the superconducting phase28,29. Interestingly, the insulating behavior was observed in samples A and B with nanoscale thickness. It has been reported that the effect of a negative pressure acts on thin films as the thickness of the exfoliated films decreases to the nanometer range30. The pressure plays a key role in modifying the electric properties of the family of ruthenium oxides31. Thus we presume that the transition from superconductor to insulator appeared in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms as a result of reducing sample thickness to the nanometer range.
(a) Temperature dependence of the resistivity ρxx for different thicknesses of Sr2RuO4 single crystals.  is resistance per square per RuO2 layer. The dotted horizontal line represents (h/4e2) = 6.45 kΩ. (b) Scanning electron micrographs of the top and side views of sample A. Temperature dependence of Rxy and Rxx. The dotted horizontal lines are a guide for the eye. (c) Vxy − I characteristics for sample A at temperatures in a zero magnetic field. dI/dVxy as a function of Vxy. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the superconducting gap Δ. (d) Tunneling spectra dI/dVxy for sample A in various magnetic fields. (e) Schematic of local superconducting islands weakly coupled by tunneling junctions, where θ is the superconducting phase. This may be similar to small Josephson junction arrays.
is resistance per square per RuO2 layer. The dotted horizontal line represents (h/4e2) = 6.45 kΩ. (b) Scanning electron micrographs of the top and side views of sample A. Temperature dependence of Rxy and Rxx. The dotted horizontal lines are a guide for the eye. (c) Vxy − I characteristics for sample A at temperatures in a zero magnetic field. dI/dVxy as a function of Vxy. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the superconducting gap Δ. (d) Tunneling spectra dI/dVxy for sample A in various magnetic fields. (e) Schematic of local superconducting islands weakly coupled by tunneling junctions, where θ is the superconducting phase. This may be similar to small Josephson junction arrays.
The two-dimensional superconductor-insulator transition allows a quantum resistance near the quantum critical point due to superconducting phase fluctuations32,33,34. Figure 1(b) shows the temperature dependence of the Hall resistance Rxy and longitudinal resistance Rxx in sample A with a thickness of 17 nm. With decreasing temperature, the Hall resistance increased with a log T dependence, and reached about 12.1 kΩ below 0.8 K. Interestingly, in the absence of an external magnetic field, we measured a Hall resistance of 12.1 kΩ, which is close to the quantum resistance of h/2e2. A Hall resistance of Rxy = 6.8 kΩ ~ h/4e2 was also observed in sample B (see Supplementary Fig. S1). The quantum Hall resistance was reproduced in other Hall electrodes and samples in the order of 1 ~ 20 kΩ. We note that the Rxx values of samples A and B were 5.3 kΩ ~ h/5e2 and 6.1 kΩ ~ h/4e2, respectively, at lower temperature. These values are very close to the universal resistances of  in a two-dimensional superconductor-insulator transition35,36. The universal resistance requires the existence of both localized Cooper pairs and moving vortices on the insulating side of the quantum phase transition, which is known as a Bose insulator. Thus we think that the Hall and longitudinal quantum resistance in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms is related to the dynamics of Cooper pairs and vortices in the Bose-insulating phase of two dimensions. The Rxy and Rxx values in the thick samples with thicknesses of a few hundred nanometers exhibited much smaller values of 0.1 ~ 1Ω than the quantum resistance in the thin film samples. We need to determine exact thickness dependence of quantized values of two dimensional samples and thick samples in future works.
in a two-dimensional superconductor-insulator transition35,36. The universal resistance requires the existence of both localized Cooper pairs and moving vortices on the insulating side of the quantum phase transition, which is known as a Bose insulator. Thus we think that the Hall and longitudinal quantum resistance in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms is related to the dynamics of Cooper pairs and vortices in the Bose-insulating phase of two dimensions. The Rxy and Rxx values in the thick samples with thicknesses of a few hundred nanometers exhibited much smaller values of 0.1 ~ 1Ω than the quantum resistance in the thin film samples. We need to determine exact thickness dependence of quantized values of two dimensional samples and thick samples in future works.
We investigated the superconducting properties in the insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms at low temperature. Figure 1(c) shows the I–Vxy characteristics of the Hall bar geometry, and dI/dVxy as a function of the Hall voltage Vxy in a zero magnetic field at several temperatures, which is vertically shifted for clarity (see Supplementary Fig. S2 for dI/dVxx − Vxx). Surprisingly, below 3 K, clear gap structures were observed in both the Hall and the longitudinal conductance spectra. The temperature dependence of the superconducting gap extracted from the coherence peak width in the tunneling spectra is shown in the inset of Fig. 1(c). The result is comparable to the superconducting gap size found in previous reports on tunneling spectroscopy in Sr2RuO4 systems37,38,39,40,41. The appearance of the gap structure above Tc = 1.5 K reminds us of the pseudo-gap state in cuprate superconductors and the 3 K phase in Sr2RuO4 systems24,25,26,27. The result shows that the local superconducting islands connected by small Josephson junctions can emerge even in the insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms below 3 K due to the quantum fluctuation of the superconducting phase θ as shown in Fig. 1(e). Thus, Vxy as well as Vxx is dependent on the current. The field dependence of the tunneling spectra for sample A at 0.46 K is shown in Fig. 1(d). The observation of the gap behavior at 4 T provides evidence for local superconductivity surviving up to high fields. Here a 400-nm-thick Sr2RuO4 single crystal (sample C) shows neither the suppression of Tc nor an enhancement to 3 K (see Supplementary Fig. S3).
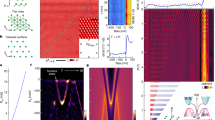
Quantum fluctuations near a quantum critical region bring out the topological properties of systems. To examine the topological magneto-electric coupling in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms, we measured the voltage V with Hall-bar geometry and the longitudinal voltage V′ at zero bias current. Figure 2(a) shows the magnetic field dependence of the voltage V when a magnetic field is applied parallel to the c axis from a zero magnetic field up to ±7 T for sample A. Interestingly, we found an anomalous induced voltage of about |ΔV| = 62 V in a zero magnetic field at 0.43 K. In the longitudinal geometry, there was an induced voltage V′ of |ΔV′| = 40 μV. The spontaneous voltage was reproduced in different terminals. In the Bose-insulating (local superconducting) state below 3 K, the anomalous voltage appeared as shown in the inset of Fig. 2(b), which is consistent with the V − B characteristics in Fig. 2(a). Figure 2(b) shows the thickness dependence of the induced voltage at lower temperature. As the sample thickness t was reduced, the induced voltage increased, which is fitted well by the relation V = 1/t. Since spontaneous voltage is related to sample thickness, we can eliminate the contribution of the thermoelectric voltage and a junction at the Au/Sr2RuO4 interface or at a microcrack. Furthermore, the switching behavior of an induced voltage was observed in the region between ±1.0 and ±5.8 T. The solid red line in Fig. 2(a) is the average result for the B − V characteristics. Figure 3(a) shows the magnetic field dependence of the induced voltage and the switching voltage at various temperatures. With increasing temperature, the anomalous induced voltage and the switching voltage were gradually suppressed, and vanished above 3 K. In sample C with a thickness of 400 nm, we also observed an induced voltage of 1 μV and switching behavior under an applied magnetic field as shown in Fig. 2(d). The anomalies became smaller than the results observed for sample A. Table 1 summarizes the properties obtained by varying the thickness.
(a) Dependence of induced voltage on magnetic field at 0.43 and 4.3 K with zero bias current. Arrows represent the magnetic sweep direction from zero magnetic field to ±7 T. The solid red curve represents the average result for the measured data. (b) Thickness dependence of induced voltage at lower temperature. The dotted line represents the fitting result, which is described well by V = 1/t. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the induced voltage. (c) The anomalous switching voltage VSW extracted from the B − V curves in (a). (d) Magnetic field dependence of V and VSW for sample C.
(a) Magnetic field dependence of the anomalous voltage at various temperatures with zero bias current from zero magnetic field to 7 T. The E · B value in a low magnetic field (the blue region  ) is equivalent to that in the red region
) is equivalent to that in the red region  caused by voltage switching at temperatures below 2 K. (b) Temperature dependence of VSW. (c) Temperature dependence of the E · B integral value. The data were fitted by an exponential curve.
caused by voltage switching at temperatures below 2 K. (b) Temperature dependence of VSW. (c) Temperature dependence of the E · B integral value. The data were fitted by an exponential curve.
Discussions
To analyze the switching phenomena in more detail, we subtract the average B − V curves from the measured B − V characteristics. The results for sample A are shown in Figs 2(c) and 3(b). Here the voltage VSW represents the switching voltage component of the induced voltage. As the magnetic field increases, the anomalous switching voltage VSW increases above ~±1 T. The VSW for the applied magnetic field reaches its maximum value near ±3.5 T, and then decreases. Intriguingly, the switching voltage was clearly observed below 1.5 K. We think that the observation of this anomalous switching voltage is related to the intrinsic properties of the chiral p-wave superconductor Sr2RuO4, because the feature appears below a Tc of about 1.5 K in bulk Sr2RuO4.
We discuss the enhancement of the critical magnetic field in relation to the existence of localized superconducting islands of Sr2RuO4. In sample C as shown in Fig. 2(d), the magnetic field of 0.04 T caused the anomalous V and VSW to vanish, which is consistent with μ0Hc2 in bulk Sr2RuO4. On the other hand, in Figs 2(a) and 3(a), the anomalous voltage is induced even in a magnetic field beyond μ0Hc2 reported for pure bulk Sr2RuO4. To reveal whether or not this anomalous behavior is an intrinsic characteristic of Sr2RuO4, we need to consider the physical properties of the 3 K phase. The 3 K superconductivity in Sr2RuO4-Ru systems induces the enhancement of the upper critical field to  and
and  15. In general, the critical magnetic field in mesoscopic superconductors becomes larger than that in bulk superconductors. We estimated
15. In general, the critical magnetic field in mesoscopic superconductors becomes larger than that in bulk superconductors. We estimated  and
and  using Hc3 = 1.7 Hc242. This may be comparable to the result for the B − V characteristics in our nanofilms because we observed the gap structure in a high field of 4 T as shown in Fig. 1(d).
using Hc3 = 1.7 Hc242. This may be comparable to the result for the B − V characteristics in our nanofilms because we observed the gap structure in a high field of 4 T as shown in Fig. 1(d).
Now let us consider the switching behavior of the resistivity (voltage) in superconducting systems. The Hall resistivity at very low temperature exhibited erratic switching in the vicinity of the quantum superconductor-to-insulator transition in La2−xSrxCuO4, which is considered an indication of the charge-cluster glass state43. In the superconducting state of Sr2RuO4, the dynamics of the chiral domains generates switching behaviors as a function of magnetic field or time44. Our anomalous switching may resemble these results because the domains in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 fluctuate in space and time. At present, some possible explanations for the results are conceivable. Below, we discuss in detail a topological interpretation in terms of our results as an interesting possibility.
To understand the origin of the anomalous behaviors, we address (I) the fractional quantum Hall conductance in the conducting layer without a magnetic field, (II) the fractional magnetic-induced electric polarization in the interlayer, and (III) the integral value of E · B in the topological term. First, let us discuss the fractional quantum Hall conductance in a zero magnetic field in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms. From Rxy = 12.1 kΩ and Rxx = 5.3 kΩ for sample A, the sheet Hall conductance  per RuO2 layer was determined by using the relation
per RuO2 layer was determined by using the relation  ,
,  , d = 6 Å (=c/2). By considering the number of sheets ns, we represent the Hall conductance as
, d = 6 Å (=c/2). By considering the number of sheets ns, we represent the Hall conductance as  . Why do Sr2RuO4 nanofilms exhibit Hall conductance quantized in the unit of conductance quantum
. Why do Sr2RuO4 nanofilms exhibit Hall conductance quantized in the unit of conductance quantum  ? The concept of chiral p-wave superconductivity can be developed by the induced CS-term of the effective Lagrangian in topological field theory16,17. The CS-term induces the existence of a spontaneous Hall current in a zero magnetic field perpendicular to the bias current direction. However, the quantum Hall effect in Sr2RuO4 has yet to be observed experimentally for the following reasons. The Hall resistance in a thick sample becomes smaller than that in a thin film sample, and the observation of the ensemble averaging of the Hall current in multi-chiral domains is complicated. With respect to these issues, an important solution is for the sample to consist of nanoscale thin films of ~10 layers2,18 and for the chiral single domain size to be ~1 μm21. Our samples satisfy these conditions. Thus, by using Sr2RuO4 nanofilms, we can observe the fractional quantum Hall conductance near the quantum critical region.
? The concept of chiral p-wave superconductivity can be developed by the induced CS-term of the effective Lagrangian in topological field theory16,17. The CS-term induces the existence of a spontaneous Hall current in a zero magnetic field perpendicular to the bias current direction. However, the quantum Hall effect in Sr2RuO4 has yet to be observed experimentally for the following reasons. The Hall resistance in a thick sample becomes smaller than that in a thin film sample, and the observation of the ensemble averaging of the Hall current in multi-chiral domains is complicated. With respect to these issues, an important solution is for the sample to consist of nanoscale thin films of ~10 layers2,18 and for the chiral single domain size to be ~1 μm21. Our samples satisfy these conditions. Thus, by using Sr2RuO4 nanofilms, we can observe the fractional quantum Hall conductance near the quantum critical region.
Using the result shown by the fitted slope of |ΔV|/ΔB in Fig. 2(a), we discuss the contribution of the electric polarization under a magnetic field in the Sr2RuO4 interlayer. We assume that our layered sample is a superconducting bilayer system in order to discuss the possibility of magneto-electric polarization. The capacitance C = εIA/d = 10 fF of the interlayer is estimated, where εI/ε0 ~ 10 is the interlayer dielectric constant, d (=6 Å) is the interlayer distance in Sr2RuO2, and A is the area 0.14 μm2 between the electrodes. We determined the effective electric charge Q∗ ~ 8 e from the induced voltage of |ΔV| = 63 μV. Moreover, we obtained the effective magnetic flux  from the relation
from the relation  , where
, where  is the magnetic flux quantum. We found the fractional magneto-electric polarization
is the magnetic flux quantum. We found the fractional magneto-electric polarization  from the slope in the positive (negative) magnetic field. Surprisingly, the fractional coefficient of the magnetic-field-induced electric polarization is equivalent to that of the Hall conductance in the bilayer film.
from the slope in the positive (negative) magnetic field. Surprisingly, the fractional coefficient of the magnetic-field-induced electric polarization is equivalent to that of the Hall conductance in the bilayer film.
Below, we consider the topological magneto-electric effect in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms to understand the relationship between fractional Hall conductance and electric polarization. The chiral anomaly7,8 in the (3 + 1)-dimensional topological field theory can introduce an additional Θ-term  10,11. This topological term denotes the existence of the magneto-electric effects. Namely, an applied electric field generates a magnetic polarization
10,11. This topological term denotes the existence of the magneto-electric effects. Namely, an applied electric field generates a magnetic polarization  , and an applied magnetic field generates an electric polarization
, and an applied magnetic field generates an electric polarization  . The quantum Hall current
. The quantum Hall current  flows as the contribution of the topological surface state in the (3 + 1)-dimensional magneto-electric effect. For strongly correlated electron systems, the fractional parameter Θ = p/q with p, q odd integers is predicted by analogy with fractional quantum Hall effects45,46. This model of fractionalization in the chiral anomaly appears to be beneficial in terms of understanding our anomalous results.
flows as the contribution of the topological surface state in the (3 + 1)-dimensional magneto-electric effect. For strongly correlated electron systems, the fractional parameter Θ = p/q with p, q odd integers is predicted by analogy with fractional quantum Hall effects45,46. This model of fractionalization in the chiral anomaly appears to be beneficial in terms of understanding our anomalous results.
Furthermore, we discuss the possibility of the fractionalization of the topological Θ-parameter. Using the experimental results, we discuss the integral value  in the topological Θ-term. We found that the value of E (=ΔV/d) · B represented by the blue square region
in the topological Θ-term. We found that the value of E (=ΔV/d) · B represented by the blue square region  in Fig. 3(a) is equivalent to that of E · B represented by the red rhombic region
in Fig. 3(a) is equivalent to that of E · B represented by the red rhombic region  in Fig. 3(a,b). An important point is that the obtained value of E · B is 6(h/e2) at 0.43 K. Similarly, at temperatures below 2.0 K, we estimated the value of E · B in both the square region in a low magnetic field and the rhombic region provided by the voltage switching. We confirmed that the E · B values are the same in the blue and red regions at each temperature. The correspondence of the E · B value is also reproduced in sample C in Fig. 2(d). This means that the induced voltage in a low magnetic field is closely related to the occurrence of the switching voltage under a magnetic field, and these are connected to the topological invariant. Figure 3(c) shows the temperature dependence of the E · B value. The data points are fitted by an exponential curve. We believe that the E · B value exists in the
in Fig. 3(a,b). An important point is that the obtained value of E · B is 6(h/e2) at 0.43 K. Similarly, at temperatures below 2.0 K, we estimated the value of E · B in both the square region in a low magnetic field and the rhombic region provided by the voltage switching. We confirmed that the E · B values are the same in the blue and red regions at each temperature. The correspondence of the E · B value is also reproduced in sample C in Fig. 2(d). This means that the induced voltage in a low magnetic field is closely related to the occurrence of the switching voltage under a magnetic field, and these are connected to the topological invariant. Figure 3(c) shows the temperature dependence of the E · B value. The data points are fitted by an exponential curve. We believe that the E · B value exists in the  region. According to the fitting curve, at T = 0, (III) the E · B value is about 12 h/e2, which is comparable to (I) the zero-magnetic-field quantum Hall conductance
region. According to the fitting curve, at T = 0, (III) the E · B value is about 12 h/e2, which is comparable to (I) the zero-magnetic-field quantum Hall conductance  and (II) the magnetic-field-induced electro-polarization
and (II) the magnetic-field-induced electro-polarization  . By substituting
. By substituting  into the topological term SΘ, we obtained the fractional angle
into the topological term SΘ, we obtained the fractional angle  , where N is an integer multiple. For the fractional angle Θ = π/6, the quantum Hall conductance
, where N is an integer multiple. For the fractional angle Θ = π/6, the quantum Hall conductance  , and electric polarization
, and electric polarization  are discussed theoretically10,46. This is consistent with our experimental observations. Thus, we suggested the presence of the fractional topological magneto-electric effect in Sr2RuO4 layers using the results of both the fractional Hall conductance and the fractional magneto-electric polarization in the fractional axion angle. Namely, these observations correspond to the fractional Chern structure caused by the quantum anomaly in Sr2RuO4.
are discussed theoretically10,46. This is consistent with our experimental observations. Thus, we suggested the presence of the fractional topological magneto-electric effect in Sr2RuO4 layers using the results of both the fractional Hall conductance and the fractional magneto-electric polarization in the fractional axion angle. Namely, these observations correspond to the fractional Chern structure caused by the quantum anomaly in Sr2RuO4.
In conclusion, we have detected the emergence of the Chern structure in Bose-insulating Sr2RuO4 nanofilms by observing the fractional Hall conductance on the surface and the fractional electric polarization in the interlayer. In a zero magnetic field, a quantized fractional Hall resistance was observed in the local superconducting state below 3 K. Under zero bias current, we found the anomalous induced voltage and the switching behavior of the induced voltage for an applied magnetic field parallel to the c axis. The applied magnetic field generated electric polarization in the interlayer of Sr2RuO4. The results suggest the presence of the fractional topological magneto-electric effect in Sr2RuO4 nanofilms. The fractional axion angle Θ = π/6 in the topological Θ-term was also determined.
Methods
To obtain nanoscale Sr2RuO4 thin films, we synthesized Sr2RuO4 single crystals with a solid phase reaction, and selected single crystals with no embedded Ru metal and with homogeneity by observing optical microscope images, chemical composition and crystal orientation47. Sr2RuO4 single crystal nanofilms were exfoliated on a SiO2(300 nm)/Si substrate. We then fabricated gold electrodes using standard electron beam lithography methods. Scanning electron micrographs of the Sr2RuO4 nanofilms (samples A and B) are shown in Fig. 1(b) and Fig. S1(a). The sample thickness was determined from scanning electron micrographs obtained with a sample holder tilted at 70-degrees. The electric transport properties of several samples with thicknesses of 17–470 nm were measured by the four-terminal method using a homemade 3He refrigerator. All leads were equipped with RC filters (R = 1 kΩ and C = 22 nF). The longitudinal and Hall voltages and the differential conductance were measured with a nanovoltmeter (2182, Keithley) and a lock-in-amplifier (5210, Princeton Applied Research), respectively. The up and down magnetic field sweep rate was 0.102 mT/sec.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Nobukane, H. et al. Chern structure in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms. Sci. Rep. 7, 41291; doi: 10.1038/srep41291 (2017).
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Chern, S. S. Complex Manifolds without Potential Theory, 2nd Ed. (Springer-Verlag, 1979).
Volovik, G. E. The Universe in a Helium Droplet (Clarendon, Oxford, 2003).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197–200 (2005).
Semenoff, G. W. Condensed-matter simulation of a three-dimensional anomaly. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 2449 (1984).
Matsuyama, T. Quantization of conductivity induced by topological structure of energy momentum space in generalized QED3 . Prog. Theo. Phys. 77, 711–730 (1987).
Haldane, F. D. M. Model for a quantum Hall effect without Landau levels: condensed-matter realization of the “parity anomaly”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2015 (1988).
Adler, S. L. Axial-vector vertex in spinor electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 177, 2426 (1969).
Bell, J. S. & Jackiew, R. A PCAC puzzle: π0 → γγ in the σ-model. Nuovo Cimento A 60, 47 (1969).
Bevan, T. D. C. et al. Momentum creation by vortices in superfluid 3He as a model of primordial baryogenesis. Nature 386, 689–692 (1997).
Qi, X. L., Hughes, T. & Zhang, S. C. Topological field theory of time-reversal invariant insulators. Phys. Rev. B 78, 195424 (2008).
Qi, X. L., Witten, E. & Zhang, S. C. Axion topological field theory of topological superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 87, 134519 (2013).
Witten, E. Dyons of charge eθ/2π . Physics Lett. B 86, 283 (1979).
Wilczek, F. Two applications of axion electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1799 (1987).
Nayak, C., Simon, S. H., Stern, A., Freedman, M. & Sarma, S. D. Non-Abelian anyons and topological quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1083 (2008).
Mackenzie, A. P. & Maeno, Y. The superconductivity of Sr2RuO4 and the physics of spin-triplet pairing. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 657 (2003).
Goryo, J. & Ishikawa, K. Observation of induced Chern-Simons term in P- and T- violating superconductors. Phys. Lett. A 260, 294 (1999).
Volovik, G. E. An analog of the quantum Hall effect in a superfluid 3He film. Sov. Phys. JETP 67, 1804–1811 (1988).
Volovik, G. E. & Yakovenko, V. M. Fractional charge, spin statistics of solitons in superfluid 3He film. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1, 5263 (1989).
Read, N. & Green, D. Paired states of fermions in two dimensions with breaking of parity and time-reversal symmetries and the fractional quantum Hall effect. Phys. Rev. B 61, 10267 (2000).
Ivanov, D. A. Non-Abelian statistics of half-quantum vortices in p-wave superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 268 (2001)
Nobukane, H., Tokuno, A., Matsuyama, T. & Tanda, S. Majorana-Weyl fermions in the chiral superconductor Sr2RuO4 . Phys. Rev. B 83, 144502 (2011).
Nobukane, H. et al. Parity violation in a single domain of spin-triplet Sr2RuO4 superconductors. Solid State Commun. 149, 1212–1215 (2009).
Nobukane, H., Matsuyama, T. & Tanda, S. Topological electromagnetic response in the chiral superconductor Sr2RuO4 . Physica B 460, 160 (2015).
Maeno, Y., Kittaka, S., Nomura, T., Yonezawa, S. & Ishida, K. Evaluation of spin-triplet superconductivity in Sr2RuO4 . J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 011009 (2012).
Kittaka, S., Taniguchi, H., Yonezawa, S., Yaguchi, H. & Maeno, Y. Higher-T c superconducting phase in Sr2RuO4 induced by uniaxial pressure. Phys. Rev. B 81, 180510(R) (2010).
Hicks, C. W. et al. Strong increase of T c of Sr2RuO4 under both tensile and compressive strain. Science 344, 283–285 (2014).
Ying, Y. A. et al. Enhanced spin-triplet superconductivity near dislocations in Sr2RuO4 . Nature Communications 4, 2596 (2013).
Jaeger, H. M., Haviland, D. B., Orr, B. G. & Goldman, A. M. Onset of superconductivity in ultrathin granular metal films. Phys. Rev. B 40, 182 (1989).
van der Zant, H. S. J., Elion, W. J., Geerligs, L. J. & Mooij, J. E. Quantum phase transition in two dimensions: Experiments in Josephson-junction arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 10081 (1996).
Goli, P., Khan, J., Wickramaratne, D., Lake, R. K. & Balandin, A. A. Charge density waves in exfoliated films of van der Waals Materials: Evolution of Raman spectrum in TiSe2 . Nano Lett. 12, 5941 (2012).
Nakamura, F. et al. From Mott insulator to ferromagnetic metal: A pressure study of Ca2RuO4 . Phys. Rev. B 65, 220402(R) (2002).
Haviland, D. B., Liu, Y. & Goldman, A. M. Onset of superconductivity in the two-dimensional limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2180 (1989).
Tanda, S., Ohzeki, S. & Nakayama, T. Bose glass-vortex-glass phase transition and dynamics scaling for high-T c Nd2−x Ce x CuO4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 530 (1992).
Bollinger, A. T. et al. Superconductor-insulator transition in La2−x Sr x CuO4 at the pair quantum resistance Nature 472, 458 (2011).
Fisher, M. P. A., Grinstein, G. & Girvin, S. M. Presence of quantum diffusion in two dimensions: Universal resistance at the superconductor-insulator transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 587 (1990).
Fisher, M. P. A. Quantum phase transitions in disordered two-dimensional superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 923 (1990).
Laube, F., Goll, G., Löhneysen, H. v., Fogelström, M. & Lichtenberg, F. Spin-triplet superconductivity in Sr2RuO4 probed by Andreev reflection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1595 (2000).
Mao, Z. Q., Nelson, K. D., Jin, R., Liu, Y. & Maeno, Y. Observation of Andreev surface bound states in the 3-K phase region of Sr2RuO4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 037003 (2001).
Suderow, H. et al. A nodeless superconducting gap in Sr2RuO4 from tunneling spectroscopy. New J. Phys. 11 093004 (2009).
Kashiwaya, S. et al. Edge states of Sr2RuO4 detected by in-plane tunneling spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 077003 (2011).
Firmo, I. A. et al. Evidence from tunneling spectroscopy for a quasi-one-dimensional origin of superconductivity in Sr2RuO4 . Phys. Rev. B 88, 134521 (2013).
de Gennes, P. G. Superconductivity of metals and alloys (Benjamin, New York, 1969).
Wu, J., Bollinger, A. T., Sun, Y. & Bozovic, I. Hall effect in quantum critical charge-cluster glass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 4284 (2016).
Kidwingira, F., Sterand, J. D., Harlingen, D. J. V. & Maeno, Y. Dynamical superconducting order parameter domains in Sr2RuO4 . Science 314, 1267 (2006).
Swingle, B., Barkeshli, M., McGreevy, J. & Senthil, T. Correlated topological insulators and the fractional magnetoelectric effect. Phys. Rev. B 83, 195139 (2011).
Maciejko, J., Qi, X. L., Karch, A. & Zhang, S. C. Fractional topological insulators in three dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 246809 (2010).
Nobukane, H. et al. Transport properties in a single domain of microscale Sr2RuO4 single crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 020209 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Asano, K. Inagaki, T. Honma, K. Ichimura, S. Takayanagi, K. Yamaya, N. Matsunaga, and K. Nomura for experimental help and useful discussions. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (No. 25800183 and No. 26287069) and Takayanagi Memorial Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.N. performed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. T.M. and S.T. contributed to the interpretation of the results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Nobukane, H., Matsuyama, T. & Tanda, S. Chern structure in the Bose-insulating phase of Sr2RuO4 nanofilms. Sci Rep 7, 41291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41291
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41291
This article is cited by
-
Co-appearance of superconductivity and ferromagnetism in a Ca2RuO4 nanofilm crystal
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.