Abstract
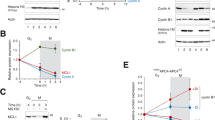
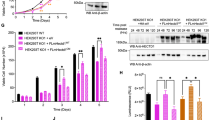
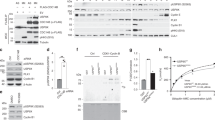
The serine protease Omi/HtrA2 was initially regarded as a proapoptotic molecule that proteolyses several proteins to induce cell death. Recent studies, however, indicate that loss of Omi protease activity increases susceptibility to stress-induced cell death. These complicated findings suggest that the protease activity of Omi is involved not only in apoptosis but also in cellular homeostasis. However, the targets which Omi uses to mediate this novel process are unknown. Previously, we showed that WARTS (WTS)/large tumor-suppressor 1 mitotic kinase interacts with the protein/discs-large protein/zonula (PDZ) domain of Omi and promotes its protease activity. We now report that WTS is a substrate for Omi protease activity, thus it is not only a regulator but also a downstream target of this protease. Interaction with Omi PDZ domain is required for WTS to be proteolysed. When caspase-9-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were treated with staurosporine, WTS was proteolysed by activated endogenous Omi without induction of cell death. Therefore, protease activity of Omi and proteolysis of WTS are not necessarily required for cell death. We found that depletion of Omi from HeLa cells results in accelerated cell proliferation despite no significant change in the duration of mitosis. The depletion of WTS showed the same effect on S phase progression. Therefore, WTS proteolytic fragment(s) generated by Omi may act as an inhibitor of G1/S progression. Our data reveal a role for Omi-mediated processing of WTS in negative regulation of cell cycle progression at interphase, suggesting a novel function of Omi other than apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LATS1:
-
large tumor-suppressor 1
- HtrA:
-
high temperature requirement
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- DMPK:
-
myotonic dystrophy protein kinase
- dlg:
-
discs large
- z-VAD-fmk:
-
benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-(OMe) fluoromethyl ketone
- BAF:
-
BOC-Asp-(OMe) fluoromethyl ketone
- STS:
-
staurosporine
References
Bardin AJ, Amon A . (2001). Men and sin: what's the difference? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 815–826.
Cilenti L, Soundarapandian MM, Kyriazis GA, Stratico V, Singh S, Gupta S et al. (2004). Regulation of HAX-1 anti-apoptotic protein by Omi/HtrA2 protease during cell death. J Biol Chem 279: 50295–50301.
Faccio L, Fusco C, Chen A, Martinotti S, Bonventre JV, Zervos AS . (2000). Characterization of a novel human serine protease that has extensive homology to bacterial heat shock endoprotease HtrA and is regulated by kidney ischemia. J Biol Chem 275: 2581–2588.
Gray CW, Ward RV, Karran E, Turconi S, Rowles A, Viglienghi D et al. (2000). Characterization of human HtrA2, a novel serine protease involved in the mammalian cellular stress response. Eur J Biochem 267: 5699–5710.
Harvey KF, Pfleger CM, Hariharan IK . (2003). The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 114: 457–467.
Hegde R, Srinivasula SM, Zhang Z, Wassell R, Mukattash R, Cilenti L et al. (2002). Identification of Omi/HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J Biol Chem 277: 432–438.
Hirota T, Morisaki T, Nishiyama Y, Marumoto T, Tada K, Hara T et al. (2000). Zyxin, a actin filament assembly, targets the mitotic apparatus by interacting with h-warts/LATS1 tumor suppressor. J Cell Biol 149: 1073–1086.
Hock B, Bohme B, Karn T, Yamamoto T, Kaibuchi K, Holtrich U et al. (1998). PDZ-domain-mediated interaction of the Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase EphB3 and the ras-binding protein AF6 depends on the kinase activity of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9779–9784.
Iida S, Hirota T, Morisaki T, Marumoto T, Hara T, Kuninaka S et al. (2004). Tumor suppressor WARTS ensures genomic integrity by regulating both mitotic progression and G1 tetraploidy checkpoint function. Oncogene 23: 5266–5274.
Jones JM, Datta P, Srinivasula SM, Ji W, Gupta S, Zhang Z et al. (2003). Loss of Omi mitochondrial protease activity causes the neuromuscular disorder of mnd2 mutant mice. Nature 425: 721–727.
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H et al. (1998). Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 94: 325–337.
Kuninaka S, Nomura M, Hirota T, Iida S, Hara T, Honda S et al. (2005). The tumor suppressor WARTS activates the Omi/HtrA2-dependent pathway of cell death. Oncogene 24: 5287–5298.
Li W, Srinivasula SM, Chai J, Li P, Wu JW, Zhang Z et al. (2002). Structural insights into the pro-apoptotic function of mitochondrial serine protease HtrA2/Omi. Nat Struct Biol 9: 436–441.
Martins LM, Iaccarino I, Tenev T, Gschmeissner S, Totty NF, Lemoine NR et al. (2002). The serine protease Omi/HtrA2 regulates apoptosis by binding XIAP through a reaper-like motif. J Biol Chem 277: 439–444.
Martins LM, Morrison A, Klupsch K, Fedele V, Moisoi N, Teismann P et al. (2004). Neuroprotective role of the reaper-related serine protease HtrA2/Omi revealed by targeted deletion in mice. Mol Cell Biol 24: 9848–9862.
McPherson JP, Tamblyn L, Elia A, Migon E, Shehabeldin A, Matysiak-Zablocki E et al. (2004). Lats2/Kpm is required for embryonic development, proliferation control and genomic integrity. EMBO J 23: 3677–3688.
Mendez J, Stillman B . (2000). Chromatin association of human origin recognition complex, cdc6, and minichromosome maintenance proteins during the cell cycle: assembly of prereplication complexes in late mitosis. Mol Cell Biol 20: 8602–8612.
Morita S, Kojima T, Kitamura T . (2000). Plat-E: an efficient and stable system for transient packaging of retroviruses. Gene Therapy 7: 1063–1066.
Nishiyama Y, Hirota T, Morisaki T, Hara T, Marumoto T, Iida S et al. (1999). A human homolog of Drosophila warts tumor suppressor, h-warts, localized to mitotic apparatus and specifically phosphorylated during mitosis. FEBS Lett 459: 159–165.
Nitta M, Kobayashi O, Honda S, Hirota T, Kuninaka S, Marumoto T et al. (2004). Spindle checkpoint function is required for mitotic catastrophe induced by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 23: 6548–6558.
Pallen MJ, Wren BW . (1997). The HtrA family of serine proteases. Mol Microbiol 26: 209–221.
Songyang Z, Fanning AS, Fu C, Xu J, Marfatia SM, Chishti AH et al. (1997). Recognition of unique carboxyl-terminal motifs by distinct PDZ domains. Science 275: 73–77.
St John MA, Tao W, Fei X, Fukumoto R, Carcangiu ML, Brownstein DG et al. (1999). Mice deficient of Lats1 develop soft-tissue sarcomas, ovarian tumours and pituitary dysfunction. Nat Genet 21: 182–186.
Sudo T, Ota Y, Kotani S, Nakao M, Takami Y, Takeda S et al. (2001). Activation of Cdh1-dependent APC is required for G1 cell cycle arrest and DNA damage-induced G2 checkpoint in vertebrate cells. EMBO J 20: 6499–6508.
Suzuki Y, Imai Y, Nakayama H, Takahashi K, Takio K, Takahashi R . (2001). A serine protease, HtrA2, is released from the mitochondria and interacts with XIAP, inducing cell death. Mol Cell 8: 613–621.
Tao W, Zhang S, Turenchalk GS, Stewart RA, St John MA, Chen W et al. (1999). Human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster lats tumour suppressor modulates CDC2 activity. Nat Genet 21: 177–181.
Tapon N, Harvey KF, Bell DW, Wahrer DC, Schiripo TA, Haber DA et al. (2002). Salvador Promotes both cell cycle exit and apoptosis in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Cell 110: 467–478.
Trencia A, Fiory F, Maitan MA, Vito P, Barbagallo AP, Perfetti A et al. (2004). Omi/HtrA2 promotes cell death by binding and degrading the anti-apoptotic protein ped/pea-15. J Biol Chem 279: 46566–46572.
Udan RS, Kango-Singh M, Nolo R, Tao C, Halder G . (2003). Hippo promotes proliferation arrest and apoptosis in the Salvador/Warts pathway. Nat Cell Biol 5: 914–920.
van Loo G, van Gurp M, Depuydt B, Srinivasula SM, Rodriguez I, Alnemri ES et al. (2002). The serine protease Omi/HtrA2 is released from mitochondria during apoptosis. Omi interacts with caspase-inhibitor XIAP and induces enhanced caspase activity. Cell Death Differ 9: 20–26.
Vercammen D, Beyaert R, Denecker G, Goossens V, Van Loo G, Declercq W et al. (1998). Inhibition of caspases increases the sensitivity of L929 cells to necrosis mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 187: 1477–1485.
Verhagen AM, Silke J, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Kaufmann H, Connolly LM et al. (2002). HtrA2 promotes cell death through its serine protease activity and its ability to antagonize inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. J Biol Chem 277: 445–454.
Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D . (2003). Hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 114: 445–456.
Yang QH, Church-Hajduk R, Ren J, Newton ML, Du C . (2003). Omi/HtrA2 catalytic cleavage of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) irreversibly inactivates IAPs and facilitates caspase activity in apoptosis. Genes Dev 17: 1487–1496.
Yang X, Yu K, Hao Y, Li DM, Stewart R, Insogna KL et al. (2004). LATS1 tumour suppressor affects cytokinesis by inhibiting LIMK1. Nat Cell Biol 6: 609–617.
Acknowledgements
We thank T Kitamura for supplying PLAT-E cells and pMX vector, T Yamamoto for LATS2 expression vectors and a specific antibody; Y Nishimura for L929 cells; J Moon for editorial assistance; Y Fukushima for help in preparing the manuscript; members of the Saya lab for valuable suggestions; and members of the Gene Technology Center at Kumamoto University for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Research for the Future Program of the Japan Society for the promotion of Science and by a grant for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (to HS) and by a grant for Cancer Research from Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (to SK). HS is also supported by a grant from the Tokyo Biochemical Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuninaka, S., Iida, SI., Hara, T. et al. Serine protease Omi/HtrA2 targets WARTS kinase to control cell proliferation. Oncogene 26, 2395–2406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210042
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210042
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protease-independent control of parthanatos by HtrA2/Omi
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Apoptotic proteins with non-apoptotic activity: expression and function in cancer
Apoptosis (2023)
-
Molecular complexity and gene expression controlling cell turnover during a digestive cycle of carnivorous sponge Lycopodina hypogea
Cell and Tissue Research (2022)
-
Mitochondrial Proteome Changes Correlating with β-Amyloid Accumulation
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
The Role of Parl and HtrA2 in Striatal Neuronal Injury After Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2013)