Abstract
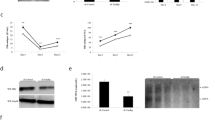
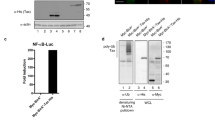
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) has many cellular functions and is a major factor in hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma caused by HBV infection. A proteomic approach was used to search for HBx-interacting proteins in order to elucidate the molecular mechanism of hepatocarcinogenesis. HBx was attached to myc and flag tags (MEF tags) and expressed in 293T cells; the protein complex formed within the cells was purified and characterized by mass spectrometry. COP9 signalosome (CSN) subunits 3 and 4 were subsequently identified as HBx-interacting proteins. In addition, CSN subunit 5, Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 (Jab1), was shown to be a novel cellular target of HBx. In vivo and in vitro interactions between HBx and Jab1 were confirmed by standard immunoprecipitation and GST pull-down assays. An analysis of HBx deletion constructs showed that amino acids 30–125 of HBx were responsible for binding to Jab1. Confocal laser microscopy demonstrated that HBx was mainly localized in the cytoplasm, while Jab1 was found mainly in the nucleus and partially in the cytoplasm, and that the two proteins colocalized in the cytoplasm. The cotransfection of HBx and Jab1 resulted in substantial activator protein 1 (AP-1) activation and knockdown of endogenous Jab1 attenuated AP-1 activation caused by HBx. In addition, the coexpression of HBx and Jab1 potentiated phosphorylation of JNK, leading to the subsequent phosphorylation of c-Jun, whereas the level of c-Jun and JNK phosphorylation induced by HBx was decreased in Jab1 knockdown cells. These results suggest that the interaction between HBx and Jab1 enhances HBx-mediated AP-1 activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae MK, Ahn MY, Jeong JW, Bae MH, Lee YM, Bae SK et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 9–12.
Bech-Otschir D, Kraft R, Huang X, Henklein P, Kapelari B, Pollmann C et al. (2001). EMBO J 20: 1630–1639.
Bech-Otschir D, Seeger M, Dubiel W . (2002). J Cell Sci 115: 467–473.
Benn J, Schneider RJ . (1994). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 10350–10354.
Benn J, Su F, Doria M, Schneider RJ . (1996). J Virol 70: 4978–4985.
Bouchard MJ, Wang LH, Schneider RJ . (2001). Science 294: 2376–2378.
Chamovitz DA, Segal D . (2001). EMBO Rep 2: 96–101.
Cheong JH, Yi M, Lin Y, Murakami S . (1995). EMBO J 14: 143–150.
Chopra S, Fernandez De Mattos S, Lam EW, Mann DJ . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 32413–32416.
Claret FX, Hibi M, Dhut S, Toda T, Karin M . (1996). Nature 383: 453–457.
Cope GA, Suh GS, Aravind L, Schwarz SE, Zipursky SL, Koonin EV et al. (2002). Science 298: 608–611.
Doria M, Klein N, Lucito R, Schneider RJ . (1995). EMBO J 14: 4747–4757.
Eferl R, Ricci R, Kenner L, Zenz R, David JP, Rath M et al. (2003). Cell 112: 181–192.
Eferl R, Wagner EF . (2003). Nat Rev Cancer 3: 859–868.
Ganem D, Varmus HE . (1987). Annu Rev Biochem 56: 651–693.
Henkler F, Hoare J, Waseem N, Goldin RD, McGarvey MJ, Koshy R et al. (2001). J Gen Virol 82: 871–882.
Henkler F, Lopes AR, Jones M, Koshy R . (1998). J Gen Virol 79 (Part 11): 2737–2742.
Ichimura T, Yamamura H, Sasamoto K, Tominaga Y, Taoka M, Kakiuchi K et al. (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 13187–13194.
Imamura T, Kanai F, Kawakami T, Amarsanaa J, Ijichi H, Hoshida Y et al. (2004). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318: 289–296.
Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S, Tanaka Y, Kasahara A et al. (1998). Hepatology 27: 951–958.
Jazag A, Ijichi H, Kanai F, Imamura T, Guleng B, Ohta M et al. (2005). Oncogene 24: 662–671.
Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi R, Hall RA, Donowitz M et al. (2000). EMBO J 19: 6778–6791.
Kato N, Yoshida H, Kioko Ono-Nita S, Kato J, Goto T, Otsuka M et al. (2000). Hepatology 32: 405–412.
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T, Jay G . (1991). Nature 351: 317–320.
Kleemann R, Hausser A, Geiger G, Mischke R, Burger-Kentischer A, Flieger O et al. (2000). Nature 408: 211–216.
Klein NP, Bouchard MJ, Wang LH, Kobarg C, Schneider RJ . (1999). EMBO J 18: 5019–5027.
Klein NP, Schneider RJ . (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 6427–6436.
Liu P, Kimmoun E, Legrand A, Sauvanet A, Degott C, Lardeux B et al. (2002). J Hepatol 37: 63–71.
Maguire HF, Hoeffler JP, Siddiqui A . (1991). Science 252: 842–844.
Miyagishi M, Taira K . (2002). Nat Biotechnol 20: 497–500.
Mizushima S, Nagata S . (1990). Nucleic Acids Res 18: 5322.
Murakami S, Cheong JH, Kaneko S . (1994). J Biol Chem 269: 15118–15123.
Natoli G, Avantaggiati ML, Chirillo P, Costanzo A, Artini M, Balsano C et al. (1994). Mol Cell Biol 14: 989–998.
Natsume T, Yamauchi Y, Nakayama H, Shinkawa T, Yanagida M, Takahashi N et al. (2002). Anal Chem 74: 4725–4733.
Naumann M, Bech-Otschir D, Huang X, Ferrell K, Dubiel W . (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 35297–35300.
Nijhara R, Jana SS, Goswami SK, Kumar V, Sarkar DP . (2001a). FEBS Lett 504: 59–64.
Nijhara R, Jana SS, Goswami SK, Rana A, Majumdar SS, Kumar V et al. (2001b). J Virol 75: 10348–10358.
Omata M . (1998). N Engl J Med 339: 114–115.
Oron E, Mannervik M, Rencus S, Harari-Steinberg O, Neuman-Silberberg S, Segal D et al. (2002). Development 129: 4399–4409.
Qadri I, Maguire HF, Siddiqui A . (1995). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1003–1007.
Rigaut G, Shevchenko A, Rutz B, Wilm M, Mann M, Seraphin B . (1999). Nat Biotechnol 17: 1030–1032.
Shaulian E, Karin M . (2002). Nat Cell Biol 4: E131–6.
Shirakata Y, Kawada M, Fujiki Y, Sano H, Oda M, Yaginuma K et al. (1989). Jpn J Cancer Res 80: 617–621.
Shirakata Y, Koike K . (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 22071–22078.
Sitterlin D, Lee TH, Prigent S, Tiollais P, Butel JS, Transy C . (1997). J Virol 71: 6194–6199.
Tanaka Y, Kanai F, Kawakami T, Tateishi K, Ijichi H, Kawabe T et al. (2004). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318: 461–469.
Tateishi K, Omata M, Tanaka K, Chiba T . (2001). J Cell Biol 155: 571–579.
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Arata Y, Mori S, Maeda M, Tanaka T et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 2302–2310.
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Kato J . (1999). Nature 398: 160–165.
Uhle S, Medalia O, Waldron R, Dumdey R, Henklein P, Bech-Otschir D et al. (2003). EMBO J 22: 1302–1312.
Wan M, Cao X, Wu Y, Bai S, Wu L, Shi X et al. (2002). EMBO Rep 3: 171–176.
Wei N, Deng XW . (1999). Trends Genet 15: 98–103.
Zhang SM, Sun DC, Lou S, Bo XC, Lu Z, Qian XH et al. (2005). Arch Virol 150: 1579–1590.
Zoulim F, Saputelli J, Seeger C . (1994). J Virol 68: 2026–2030.
Acknowledgements
We thank David J Mann, Michael Karin, Katsuro Koike, Makoto Miyagishi, and Kazunari Taira for providing the plasmids; Tomoki Chiba (Laboratory of Frontier Science, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science, Tokyo, Japan) and the members of the Omata lab for helpful discussions; and Mitsuko Tsubouchi for technical assistance. This work was supported in part by the Health Science Research Grants for Medical Frontier Strategy Research from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan, and grants-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan. YT is a research fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, Y., Kanai, F., Ichimura, T. et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein enhances AP-1 activation through interaction with Jab1. Oncogene 25, 633–642 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209093
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209093
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of JAB1 in neurological development and disorders
Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Screening of the HBx transactivation domain interacting proteins and the function of interactor Pin1 in HBV replication
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Tumor suppressive role of mitochondrial sirtuin 4 in induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
TGF-β1 accelerates the hepatitis B virus X-induced malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor cells by upregulating miR-199a-3p
Oncogene (2020)
-
ER stress regulating protein phosphatase 2A-B56γ, targeted by hepatitis B virus X protein, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of hepatocytes
Cell Death & Disease (2018)