Abstract
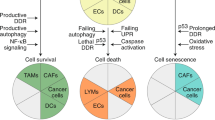
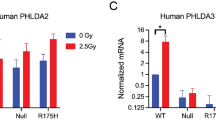
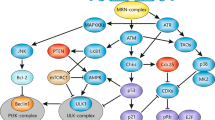
Activation of the tumor suppressor p53 after genotoxic insults may result in two different responses: growth arrest or apoptosis. In this study, we analysed how mitogenic stimulation of primary mouse lymphocytes influences p53 signaling upon γ-irradiation. We found that G0 lymphocytes rapidly went into p53-dependent apoptosis, whereas stimulated lymphocytes went into a p53-dependent, p21-mediated growth arrest. The switch in p53 response upon stimulation did neither result from a switch in transcriptional activation of major p53 target genes, nor from the high level of p21 expressed in stimulated, irradiated cells. Growth stimulation, however, led to the upregulation of the antiapoptotic factors Bcl-xL and Bfl-1. In resting cells, p53 induced apoptosis after γ-irradiation was accompanied by a breakdown of the mitochondrial membrane potential (Ψm) that was counteracted by growth stimulation. We propose that growth stimulation intercepted p53 proapoptotic signaling at the level of mitochondrial integrity, most likely by upregulating the antiapoptotic factors Bcl-xL and Bfl-1. Upregulation of Bcl-xL and of Bfl-1 upon growth stimulation was mediated by the PKC-dependent activation of NF-κB. Consequently, blocking PKC activity restored apoptosis in stimulated, irradiated splenocytes. The inherent coupling of growth stimulation with antiapoptotic signaling in primary lymphocytes might provide hints as to how precancerous lymphocytes bypass the need for mutational inactivation of p53. Thus, our findings might explain the relatively low frequency of p53 mutations in lymphomas in comparison to other tumor entities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ConA:
-
Concanavalin A
- EMSA:
-
electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor κB
- PE:
-
phycoerythrin
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PMA:
-
phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene difluoride
References
Abrahamson JLA, Lee JM and Bernstein A . (1995). Mol. Cell. Biol., 15, 6953–6960.
Adams JM and Cory S . (2001). Trends Biochem. Sci., 26, 61–66.
Amundson SA, Myers TG and Fornace Jr AJ . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 3287–3299.
Asada M, Yamada T, Ichijo H, Delia D, Miyazono K, Fukumuro K and Mizutani S . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1223–1234.
Bissonnette N and Hunting DJ . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 3461–3469.
Boise LH, Minn AJ, Noel PJ, June CH, Accavitti MA, Lindsten T and Thompson CB . (1995). Immunity, 3, 87–98.
Broome HE, Dargan CM, Krajewski S and Reed JC . (1995). J. Immunol., 155, 2311–2317.
Canman CE, Gilmer TM, Coutts SB and Kastan MB . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 600–611.
Castedo M, Hirsch T, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Macho A and Kroemer G . (1996). J. Immunol., 157, 512–521.
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS and Jove R . (1999). Immunity, 10, 105–115.
Chattopadhyay D, Ghosh MK, Mal A and Harter ML . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 9844–9856.
Chen C, Edelstein LC and Gelinas C . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 2687–2695.
Chiou SK, Rao L and White E . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 2556–2563.
Choi MS, Boise LH, Gottschalk AR, Quintans J, Thompson CB and Klaus GG . (1995). Eur. J. Immunol., 25, 1352–1357.
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N . (1987). Anal. Biochem., 162, 156–159.
Coudronniere N, Villalba M, Englund N and Altman A . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 3394–3399.
Dosch HM, Schuurman RK and Gelfand EW . (1980). J. Immunol., 125, 827–832.
Drexler HG, Fomhinee S, Matsue Y, Hu ZB, Hamaguchi H and Uphoff CC . (2000). Leukemia, 14, 198–206.
Dumon S, Santos SC, Debierre-Grockiego F, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Cocault L, Boucheron C, Mollat P, Gisselbrecht S and Gouilleux F . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 4191–4199.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1993). Cell, 75, 817–825.
Ferri KF and Kroemer G . (2001). Bioessays, 23, 111–1115.
Gorospe M, Cirielli C, Wang XT, Seth P, Capogrossi MC and Holbrook NJ . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 929–935.
Grillot DA, Merino R, Pena JC, Fanslow WC, Finkelman FD, Thompson CB and Nunez G . (1996). J. Exp. Med., 183, 381–391.
Grumont RJ, Rourke IJ and Gerondakis S . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 400–411.
Han J, Sabbatini P, Perez D, Rao L, Modha D and White E . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 461–477.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei M, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ . (1993). Cell, 75, 805–816.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M . (1997). Nature, 387, 296–299.
Hawrylowicz CM and Klaus GG . (1984). Immunology, 53, 703–711.
Henry H, Thomas A, Shen Y and White E . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 748–760.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Harris CC . (1991). Science, 253, 49–53.
Huang DC and Strasser A . (2000). Cell, 103, 839–842.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 301–310.
Karin M and Lin A . (2002). Nat. Immunol., 3, 221–227.
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Craig RW . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 6304–6311.
Klaus GG, O'Garra A, Bijsterbosch MK and Holman M . (1986). Eur. J. Immunol., 16, 92–97.
Krappmann D, Patke A, Heissmeyer V and Scheidereit C . (2001). Mol. Cell Biol., 21, 6640–6650.
Kubbutat MHG, Jones SN and Vousden KH . (1997). Nature, 387, 299–303.
Lee HH, Dadgostar H, Cheng Q, Shu J and Cheng G . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 9136–9141.
Lee JM . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 1653–1662.
Li YS, Kouassi E and Revillard JP . (1989). Eur. J. Immunol., 19, 1721–1725.
Lin X, O'Mahony A, Mu Y, Geleziunas R and Greene WC . (2000). Mol. Cell Biol., 20, 2933–2940.
Lin YP and Benchimol S . (1995). Mol. Cell Biol., 15, 6045–6054.
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA and Jacks T . (1993). Nature, 362263, 847–849.
Mahyar-Roemer M and Roemer K . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 3387–3398.
Marchetti P, Castedo M, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Hirsch T, Macho A, Haeffner A, Hirsch F, Geuskens M and Kroemer G . (1996). J. Exp. Med., 184, 1155–1160.
May P and May E . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7621–7636.
Meyuhas O . (2000). Eur. J. Biochem., 267, 6321–6330.
Miyashita T and Reed JC . (1995). Cell, 80, 293–299.
Mosner J, Mummenbrauer T, Bauer C, Szakiel G, Grosse F and Deppert W . (1995). EMBO J., 14, 4442–4449.
Muller M, Strand S, Hug H, Heinemann EM, Walczak H, Hofmann WJ, Stremmel W, Krammer PH and Galle PR . (1997). J. Clin. Invest., 99, 403–413.
Novogrodsky A and Katchalski E . (1971). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 228, 579–583.
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N . (2000). Science, 288, 1053–1058.
Oppenheim JJ and Rosenstreich DL . (1976). Prog. Allergy, 20, 65–194.
Samuel T, Weber HO, Rauch P, Verdoodt B, Eppel JT, McShea A, Hermeking H and Funk JO . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 45201–45206.
Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Lowe SW . (2002). Cancer Cell, 1, 289–298.
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Muller MM and Schaffner W . (1989). Nucleic Acids Res., 17, 6419.
Schuler M, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC, Fitzgerald P and Green DR . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 7337–7342.
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1501–1512.
Silva M, Benito A, Sanz C, Prosper F, Ekhterae D, Nunez G and Fernandez-Luna JL . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 22165–22169.
Sionov RV and Haupt Y . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6145–6157.
Su F, Overholtzer M, Besser D and Levine AJ . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 46–57.
Sun Z, Arendt CW, Ellmeier W, Schaeffer EM, Sunshine MJ, Gandhi L, Annes J, Petrzilka D, Kupfer A, Schwartzberg PL and Littman DR . (2000). Nature, 404, 402–407.
Thornborrow EC, Patel S, Mastropietro AE, Schwartzfarb EM and Manfredi JJ . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 990–999.
Tian H, Wittmack EK and Jorgensen TJ . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 679–684.
Truneh A, Albert F, Golstein P and Schmitt-Verhulst AM . (1985). Nature, 313, 318–320.
Tymms MJ . (1995). Methods Mol. Biol., 37, 31–46.
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT and Thompson CB . (1997). Cell, 91, 627–637.
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ . (2000). Nature, 408, 307–310.
Vousden KH . (2000). Cell, 103, 691–694.
Wedner HJ and Parker CW . (1976). Prog. Allergy, 20, 195–300.
Werner AB, De Vries E, Tait SW, Bontjer I and Borst J . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 22781–22788.
Yonish-Rouach E, Resnitzky D, Lotem J, Sachs L, Kimchi A and Oren M . (1991). Nature, 352, 345–347.
Zong WX, Edelstein LC, Chen C, Bash J and Gelinas C . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 382–387.
Acknowledgements
We thank Phil Leder (Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA) for kindly providing FvB/n p21−/− mice. This work was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (Mildred Scheel Stiftung), grant 10-1457-De 5 (‘Apoptosedefizienz und ihre Modulation bei malignen Erkrankungen’) and the Fonds des Chemisohen Industrie. The Heinrich-Pette-Institute is financially supported by Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg and Bundesministerium für Gesundheit. Many data are part of the PhD thesis of Stefan Heinrichs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinrichs, S., Deppert, W. Apoptosis or growth arrest: modulation of the cellular response to p53 by proliferative signals. Oncogene 22, 555–571 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206138
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206138
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NF-κB1 p50 promotes p53 protein translation through miR-190 downregulation of PHLPP1
Oncogene (2014)
-
Dissecting microregulation of a master regulatory network
BMC Genomics (2008)
-
Gadd45β is a pro-survival factor associated with stress-resistant tumors
Oncogene (2008)
-
Epigenetic mechanisms affect mutant p53 transgene expression in WAP-mutp53 transgenic mice
Oncogene (2005)
-
Oxidative stress attenuates Fas-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T cell line through Bfl-1 induction
Oncogene (2005)