Abstract
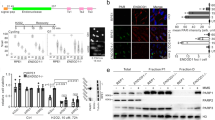
The p53 tumor suppressor plays a key role in the cell's response to genotoxic stress and loss of this ‘guardian of the genome’ is an important step in carcinogenesis. The ability of p53 to induce apoptosis through transactivation of its target genes is critical for its function as tumor suppressor. We have found that overexpression of p53 in human cancer cell lines resulted in apoptosis as measured by PARP cleavage. Furthermore we observed cleavage of both caspase 9 and caspase 8 after overexpression of p53 and found that p53-dependent apoptosis was inhibited by either cellular (c-Flip-s, Bcl-XL) or pharmacological inhibitors of caspase 8 or caspase 9 respectively. These results indicate that p53 is mediating apoptosis through both the mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. To elucidate the relevant p53 target genes and examine the caspase pathways utilized in vivo, we treated p53+/+ and age matched p53−/− mice with 5 Gy ionizing radiation or 0.5 mg/animal dexamethasone and harvested tissues at 0, 6 and 24 h. We examined the mRNA expression of p21, bax, KILLER/DR5, FAS/APO1 and EI24/PIG8 using TaqMan real time quantitative RT–PCR in the spleen, thymus and small intestine. Although the basal mRNA levels of these genes did not depend on the presence of p53, we observed a p53-dependent induction of all these targets in response to γ-irradiation and a p53-independent regulation for p21 and KILLER/DR5 in response to dexamethasone. Furthermore, we have demonstrated that the relative induction of these p53 target genes is tissue specific. Despite observing otherwise similar levels of death in these tissues, our findings suggest that in some cases apoptosis mediated through p53 occurs by redundant pathways or by a ‘group effect’ while in other tissues one or few targets may play a key role in p53-dependent apoptosis. Surprisingly, KILLER/DR5 is the dominantly induced transcript in both the spleen and small intestine suggesting a potentially important role for this p53 target gene in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S . 1998 Science 281: 322–325
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM . 1998 Science 281: 1305–1308
Bennett M, MacDonald K, Chan S-W, Luzio JP, Simari R, Weissberg P . 1998 Science 282: 290–293
Burns TF, El-Deiry WS . 1999 J. Cell. Physiol. 181: 231–239
Caelles C, Helmberg A, Karin M . 1994 Nature 370: 220–223
Chong MJ, Murray MR, Gosink EC, Russel HRC, Srinivasen A, Kapsetaki M, Korsmeyer SJ, McKinnon PJ . 2000 PNAS 97: 889–894
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Morris RG, Bird CC, Hooper ML, Wyllie AH . 1993 Nature 362: 849–852
Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, McArthur MJ, Montgomery Jr CA, Butel JS, Bradely A . 1992 Nature 356: 215–221
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825
El-Deiry WS, Harper JW, O'Connor PM, Velculescu VE, Canman CE, Jackman J, Pietenpol JA, Burrell M, Hill DE, Wang YS, Wiman KG, Mercer WE, Kastan MB, Kohn KW, Elledge SJ, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1994 Cancer Res 54: 1169–1174
Fouchier RAM, Meyer BE, Simon JHM, Fischer U, Malim M . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 4531–4539
Fuchs EJ, McKenna KA, Bedi A . 1997 Cancer Research 57: 2550–2554
Gu Z, Flemington C, Chittenden T, Zambetti GP . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 233–241
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, Potter J, Yoshida R, Kaufman SA, Lowe SW, Penninger JM, Mak TW . 1998 Cell 94: 339–352
Haupt Y, Rowan S, Shaulian E, Vousden K, Oren M . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 2170–2183
Haupt T, Barak Y, Oren M . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 1596–1606
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC . 1991 Science 253: 49–53
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer J-L, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J . 1997 Nature 388: 190–195
Kalejta RF, Shenk T, Beavis AJ . 1997 Cytometry 29: 286–291
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW . 1991 Cancer Res. 51: 6304–6311
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD . 1997 Science 275: 1132–1136
Knudson CM, Tung KSK, Tourtellotte WG, Brown GAJ, Korsmeyer SJ . 1995 Science 270: 96–99
Lee SH, Shin MS, Kim HS, Lee HK, Park WS, Kim SY, Lee JH, Han SY, Park JY, Oh RR, Jang JJ, Han JY, Lee JY, Yoo NJ . 1999 Cancer Res. 59: 5683–5686
Lehar SM, Nacht M, Jacks T, Vater CA, Chittenden T, Guild BC . 1996 Oncogene 20: 1181–1187
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J . 1998 Cell 94: 491–501
Lockhart DJ, Dong H, Byrne MC, Follettie MT, Gallo MV, Chee MS, Mittmann M, Wang C, Kobayashi M, Horton H, Brown EJ . 1996 Nature Biotechnol. 14: 1675–1680
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA, Jacks T . 1993 Nature 362: 847–852
Malkin D, Li FP, Strong FC, Fraumeni JFJ, Nelson CE, Kim DH, Kassel J, Gryka MA, Bischoff FZ, Tainsky MA . 1990 Science 250: 1233–1238
McCurrach ME, Connor TMF, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Lowe SW . 1997 PNAS 94: 2345–2349
Meng RD, Shih H, Prabhu NS, George DL, El-Deiry WS . 1998 Clin. Cancer Res. 4: 251–259
Meng RD, McDonald ER, Sheikh MS, Fornace Jr AJ, El-Deiry WS . 2000 Mol. Ther. 1: 130–144
Meng RD, El-Deiry WS . 2001 Exp. Cell Res. 262: 154–169
Midgley CA, Owens B, Briscoe CV, Thomas DB, Lane DP, Hall PA . 1995 J. Cell. Sci. 108: 1843–1848
Miyashita T, Reed JC . 1995 Cell 80: 293–299
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T, Tanaka N . 2000 Science 288: 1053–1057
Owen-Schaub LB, Zhang W, Cusack JC, Angel LS, Santee SM, Fujiwara T, Roth JA, Deisseroth AB, Zhang W-W, Kruzel E, Radinsky R . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 3032–3040
Ozoren N, Kunhong K, Burns TF, Dicker DT, Moscioni D, El-Deiry WS . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 6259–6265
Pai SI, Wu GS, Ozoren N, Wu L, Jen J, Sidransky D, El-Deiry WS . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 3513–3518
Pritchard DM, Potten CS, Korsmeyer SJ, Roberts S, Hickman JA . 1999 Oncogene 18: 7287–7293
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1997 Nature 389: 300–305
Sheikh MS, Huang Y, Fernandez-Salas EA, El-Deiry WS, Friess H, Amundson S, Yin J, Meltzer SJ, Holbrook NJ, Fornace Jr AJ . 1999 Oncogene 18: 4153–4159
Soengas MS, Alarcon RM, Yoshida H, Giaccia AJ, Hakem R, Mak TW, Lowe SW . 1999 Science 284: 156–159
Takimoto R, El-Deiry WS . 2000 Oncogene 19: 1735–1743
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y . 1998 Science 281: 312–316
Tschopp J, Irmeler M, Thome M . 1998 Curr. Opin. Immumol. 10: 552–558
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V, Chiannikulchai N, Beckmann JS, Mett IL, Rebrikov D, Brodianski VM, Kemper OC, Kollet O, Lapidot T, Soffer D, Sobe T, Avraham KB, Goncharov T, Holtmann H, Lonai P, Wallach D . 1998 Immunity 9: 267–276
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . 1992 Cell 70: 523–526
Wodicka L, Dong H, Mittmann M, Ho M-H, Lockhart DJ . 1997 Nature Biotechnol. 15: 1359–1367
Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald III ER, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID, Kao G, Gan D-D, Zhou J-Y, Muschel R, Hamilton SR, Spinner NB, Markowitz S, Wu G, El-Deiry WS . 1997 Nature Genet. 17: 141–143
Wu GS, Burns TF, Zhan Y, Alnemri ES, El-Deiry WS . 1999 Cancer Res. 59: 2770–2775
Yamada H, Tada-Oikawa S, Uchida A, Kawanishi S . 1999 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 265: 130–133
Yin XM, Wang K, Gross A, Zhao Y, Zinkel S, Klocke B, Roth KA, Korsmeyer SJ . 1999 Nature 400: 886–891
Zhao R, Gish K, Murphy M, Yin Y, Notterman D, Hoffman WH, Tom E, Mack DH, Levine AJ . 2000 Genes Development 14: 981–993
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Luschg A, Wang X . 1997 Cell 90: 405–413
Acknowledgements
This work was presented at the 91st Annual American Association for Cancer Research meeting in San Francisco, CA, USA on April 2nd, 2000, and at the 10th International p53 Workshop in Monterey, CA, USA on April 8th, 2000. The authors thank David T Dicker for excellent technical assistance with flow cytometry. We thank the MIT Biopolymers facility for hybridization of our Affymetix gene chips. TF Burns was supported in part by an NIH-MSTP training grant to the University of Pennsylvania. This work was supported by NIH grants CA 75454 (WS El-Deiry) and CA 75138 (EJ Bernhard and WS El-Deiry). WS El-Deiry is an Assistant Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burns, T., Bernhard, E. & El-Deiry, W. Tissue specific expression of p53 target genes suggests a key role for KILLER/DR5 in p53-dependent apoptosis in vivo. Oncogene 20, 4601–4612 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204484
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204484
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evidence for a radiation-responsive ‘p53 gateway’ contributing significantly to the radioresistance of lepidopteran insect cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
p600/UBR4 in the central nervous system
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Role of caspase-8 in thymus function
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)
-
Indomethacin Sensitizes TRAIL-Resistant Melanoma Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis through ROS-Mediated Upregulation of Death Receptor 5 and Downregulation of Survivin
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2014)
-
The fermented non-digestible fraction of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) triggers cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma cells
Genes & Nutrition (2014)