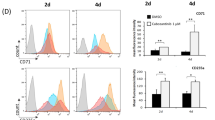
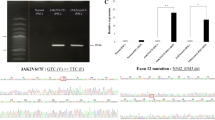
Abstract
HLA-G5 is secreted by erythroblasts in all hematopoietic organs, suggesting a role for this protein in erythropoiesis. To examine this, we analyzed whether HLA-G5 affects the proliferation of UT7/EPO and HEL erythroleukemia cells and characterized the mechanism by which HLA-G5 influences erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) signaling. We show that HLA-G5 inhibits the proliferation of UT7/EPO cells, the EPOR signaling of which is similar to that of normal erythroid progenitors. HLA-G5-mediated inhibition was associated with reduced phosphorylation of JAK2 kinase and that of the downstream signaling proteins STAT-5 and STAT-3. Involvement of JAK2 in erythroid cell proliferation has been highlighted by the role of JAK2 V617F mutation in polycythemia vera (PV), a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by erythroid lineage overproduction. We demonstrate that HLA-G5 downregulates EPOR constitutive signaling of JAK2 V617F-expressing HEL cells, leading to inhibition of cell proliferation through G1 cell cycle arrest. Combination of HLA-G5 with JAK inhibitor I further decreases HEL cell growth. Clinical relevance is provided by analysis of PV patients who carry JAK2 V617F mutation, showing that HLA-G5 inhibits the formation of erythropoietin-independent erythroid colonies. Such HLA-G5-mediated inhibition constitutes a new parameter to be considered in the design of future approaches aimed at treating JAK2 V617F-positive myeloproliferative disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carosella ED, Moreau P, Le Maoult J, Le Discorde M, Rouas-Freiss N . HLA-G molecules: from maternal–fetal tolerance to tissue acceptance. Adv Immunol 2003; 81: 199–252.
Menier C, Rabreau M, Challier JC, Le Discorde M, Carosella ED, Rouas-Freiss N . Erythroblasts secrete the nonclassical HLA-G molecule from primitive to definitive hematopoiesis. Blood 2004; 104: 3153–3160.
Wu H, Liu X, Jaenisch R, Lodish HF . Generation of committed erythroid BFU-E and CFU-E progenitors does not require erythropoietin or the erythropoietin receptor. Cell 1995; 83: 59–67.
Richmond TD, Chohan M, Barber DL . Turning cells red: signal transduction mediated by erythropoietin. Trends Cell Biol 2005; 15: 146–155.
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005; 365: 1054–1061.
James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005; 434: 1144–1148.
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 387–397.
Zhao R, Xing S, Li Z, Fu X, Li Q, Krantz SB et al. Identification of an acquired JAK2 mutation in polycythemia vera. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 22788–22792.
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1779–1790.
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD . The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2002; 100: 2292–2302.
Le Rond S, Azema C, Krawice-Radanne I, Durrbach A, Guettier C, Carosella ED et al. Evidence to support the role of HLA-G5 in allograft acceptance through induction of immunosuppressive/regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2006; 176: 3266–3276.
McMaster M, Zhou Y, Shorter S, Kapasi K, Geraghty D, Lim KH et al. HLA-G isoforms produced by placental cytotrophoblasts and found in amniotic fluid are due to unusual glycosylation. J Immunol 1998; 160: 5922–5928.
Menier C, Riteau B, Carosella ED, Rouas-Freiss N . MICA triggering signal for NK cell tumor lysis is counteracted by HLA-G1-mediated inhibitory signal. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 63–70.
Riteau B, Menier C, Khalil-Daher I, Sedlik C, Dausset J, Rouas-Freiss N et al. HLA-G inhibits the allogeneic proliferative response. J Reprod Immunol 1999; 43: 203–211.
Komatsu N, Yamamoto M, Fujita H, Miwa A, Hatake K, Endo T et al. Establishment and characterization of an erythropoietin-dependent subline, UT-7/Epo, derived from human leukemia cell line, UT-7. Blood 1993; 82: 456–464.
Bouscary D, Pene F, Claessens YE, Muller O, Chretien S, Fontenay-Roupie M et al. Critical role for PI 3-kinase in the control of erythropoietin-induced erythroid progenitor proliferation. Blood 2003; 101: 3436–3443.
Kirito K, Nakajima K, Watanabe T, Uchida M, Tanaka M, Ozawa K et al. Identification of the human erythropoietin receptor region required for Stat1 and Stat3 activation. Blood 2002; 99: 102–110.
Quentmeier H, MacLeod RA, Zaborski M, Drexler HG . JAK2 V617F tyrosine kinase mutation in cell lines derived from myeloproliferative disorders. Leukemia 2006; 20: 471–476.
Walz C, Crowley BJ, Hudon HE, Gramlich JL, Neuberg DS, Podar K et al. Activated Jak2 with the V617F point mutation promotes G1/S phase transition. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 18177–18183.
Pardanani A, Hood J, Lasho T, Levine RL, Martin MB, Noronha G et al. TG101209, a small molecule JAK2-selective kinase inhibitor potently inhibits myeloproliferative disorder-associated JAK2V617F and MPLW515L/K mutations. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1658–1668.
Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, Shahar M, Arpaia E, Lapidot Z et al. Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature 1996; 379: 645–648.
Waldmann TA . The biology of interleukin-2 and interleukin-15: implications for cancer therapy and vaccine design. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 595–601.
Murray PJ . The JAK–STAT signaling pathway: input and output integration. J Immunol 2007; 178: 2623–2629.
Lippert E, Boissinot M, Kralovics R, Girodon F, Dobo I, Praloran V et al. The JAK2-V617F mutation is frequently present at diagnosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 2006; 108: 1865–1867.
Dai C, Chung IJ, Krantz SB . Increased erythropoiesis in polycythemia vera is associated with increased erythroid progenitor proliferation and increased phosphorylation of Akt/PKB. Exp Hematol 2005; 33: 152–158.
Kiladjian JJ, Cassinat B, Turlure P, Cambier N, Roussel M, Bellucci S et al. High molecular response rate of polycythemia vera patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha-2a. Blood 2006; 108: 2037–2040.
Ugurel S, Rebmann V, Ferrone S, Tilgen W, Grosse-Wilde H, Reinhold U . Soluble human leukocyte antigen-G serum level is elevated in melanoma patients and is further increased by interferon-alpha immunotherapy. Cancer 2001; 92: 369–376.
Rebmann V, Regel J, Stolke D, Grosse-Wilde H . Secretion of sHLA-G molecules in malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol 2003; 13: 371–377.
Acknowledgements
We thank Marie-Laurence Menot for establishment of PV diagnosis, Thomas Domet for technical assistance and Abderrahim Naji for statistical analysis. We also thank Dr Bela Papp (Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris, France), Dr Patrick Mayeux (Institut Cochin, Paris, France) and Dr Michael Mac Master (University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA) for the HEL cell line, UT7/EPO cell line and the 4H84 antibody, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was done at the Service de Recherches en Hémato-Immunologie, CEA/DSV/I2BM—IUH, Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menier, C., Guillard, C., Cassinat, B. et al. HLA-G turns off erythropoietin receptor signaling through JAK2 and JAK2 V617F dephosphorylation: clinical relevance in polycythemia vera. Leukemia 22, 578–584 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2405050
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2405050
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neoplastic B-cell growth is impaired by HLA-G/ILT2 interaction
Leukemia (2012)
-
The role of HLA-G in immunity and hematopoiesis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)