Abstract
Objective:
Reduced serum adiponectin levels have been found in obesity and type 2 diabetes and variations in the adiponectin gene (APM1) have been associated with type 2 diabetes and features of the metabolic syndrome in different populations.
Study Design:
Here, we investigated the expression of APM1 in adipose tissue and studied the relationship between variation in APM1 expression, the APM1 G276T polymorphism, the common PPARG Pro12Ala polymorphism and clinical features of 36 morbidly obese (body mass index (BMI) 41.5±4.9 kg/m2) nondiabetic subjects.
Results:
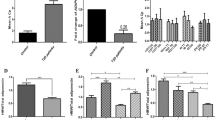
APM1 mRNA expression in visceral fat was correlated with serum adiponectin levels (r=0.54, P=0.012). In visceral, but not in subcutaneous, adipose tissue APM1 mRNA level was 38% higher among carriers of the APM1 G276T T allele (G/T and T/T) than among carriers of the G/G genotype (0.91±0.06 for G/T and T/T carriers vs 0.66±0.09 for G/G carriers, P=0.013). Carriers of the T allele also had significantly higher body fat percent compared to G/G carriers (65±6 vs 56±10%, P=0.011).
Conclusion:
Our results indicate that genetic variation in APM1 influences the expression of the gene in visceral adipose tissue and suggest a potential role for such variation in regulation of body fat accumulation in obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 2409–2415.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 409: 307–312.
Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Kotani K, Nakamura T et al. Enhanced expression of PAI-1 in visceral fat: possible contributor to vascular disease in obesity. Nat Med 1996; 2: 800–803.
Friedman JM, Halaas JL . Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998; 395: 763–770.
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 257: 79–83.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1930–1935.
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999; 100: 2473–2476.
Daimon M, Oizumi T, Saitoh T, Kameda W, Hirata A, Yamaguchi H et al. Decreased serum levels of adiponectin are a risk factor for the progression to type 2 diabetes in the Japanese Population: the Funagata study. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 2015–2020.
Tschritter O, Fritsche A, Thamer C, Haap M, Shirkavand F, Rahe S et al. Plasma adiponectin concentrations predict insulin sensitivity of both glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2003; 52: 239–243.
Hara K, Boutin P, Mori Y, Tobe K, Dina C, Yasuda K et al. Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 2002; 51: 536–540.
Kondo H, Shimomura I, Matsukawa Y, Kumada M, Takahashi M, Matsuda M et al. Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2325–2328.
Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Dina C, Lobbens S, Delannoy V, Gaget S et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 2607–2614.
Populaire C, Mori Y, Dina C, Vasseur F, Vaxillaire M, Kadowaki T et al. Does the -11377 promoter variant of APM1 gene contribute to the genetic risk for Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese families? Diabetologia 2003; 46: 443–445.
Hu FB, Doria A, Li T, Meigs JB, Liu S, Memisoglu A et al. Genetic variation at the adiponectin locus and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes 2004; 53: 209–213.
Gu HF, Abulaiti A, Ostenson CG, Humphreys K, Wahlestedt C, Brookes AJ et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the proximal promoter region of the adiponectin (APM1) gene are associated with type 2 diabetes in Swedish caucasians. Diabetes 2004; 53 (Suppl 1): S31–S35.
Fumeron F, Aubert R, Siddiq A, Betoulle D, Pean F, Hadjadj S et al. Adiponectin gene polymorphisms and adiponectin levels are independently associated with the development of hyperglycemia during a 3-year period: the epidemiologic data on the insulin resistance syndrome prospective study. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1150–1157.
Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Di Paola R, Berg AH, Warram JH, Scherer PE et al. A haplotype at the adiponectin locus is associated with obesity and other features of the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2306–2312.
Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Salvemini L, Coco A, Kim SH, Fini G et al. Multigenic control of serum adiponectin levels: evidence for a role of the APM1 gene and a locus on 14q13. Physiol Genomics 2004; 19: 170–174.
Filippi E, Sentinelli F, Trischitta V, Romeo S, Arca M, Leonetti F et al. Association of the human adiponectin gene and insulin resistance. Eur J Hum Genet 2004; 12: 199–205.
Bacci S, Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Ma X, Rauseo A, Salvemini L et al. The +276 G/T single nucleotide polymorphism of the adiponectin gene is associated with coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 2015–2020.
Lihn AS, Bruun JM, He G, Pedersen SB, Jensen PF, Richelsen B . Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2004; 219: 9–15.
Motoshima H, Wu X, Sinha MK, Hardy VE, Rosato EL, Barbot DJ et al. Differential regulation of adiponectin secretion from cultured human omental and subcutaneous adipocytes: effects of insulin and rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 5662–5667.
Ohashi K, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Sumitsuji S et al. Adiponectin I164T mutation is associated with the metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 43: 1195–1200.
Yang WS, Tsou PL, Lee WJ, Tseng DL, Chen CL, Peng CC et al. Allele-specific differential expression of a common adiponectin gene polymorphism related to obesity. J Mol Med 2003; 81: 428–434.
Arner P . Regional adipocity in man. J Endocrinol 1997; 155: 191–192.
Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K et al. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 2001; 50: 2094–2099.
Ridderstrale M, Carlsson E, Klannemark M, Cederberg A, Kosters C, Tornqvist H et al. FOXC2 mRNA Expression and a 5′ untranslated region polymorphism of the gene are associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes 2002; 51: 3554–3560.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Engeli S, Feldpausch M, Gorzelniak K, Hartwig F, Heintze U, Janke J et al. Association between adiponectin and mediators of inflammation in obese women. Diabetes 2003; 52: 942–947.
Hoffstedt J, Arvidsson E, Sjolin E, Wahlen K, Arner P . Adipose tissue adiponectin production and adiponectin serum concentration in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1391–1396.
Statnick MA, Beavers LS, Conner LJ, Corominola H, Johnson D, Hammond CD et al. Decreased expression of apM1 in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans with type 2 diabetes. Int J Exp Diabetes Res 2000; 1: 81–88.
Yan H, Yuan W, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . Allelic variation in human gene expression. Science 2002; 297: 1143.
Qiao L, Maclean PS, Schaack J, Orlicky DJ, Darimont C, Pagliassotti M et al. C/EBPalpha regulates human adiponectin gene transcription through an intronic enhancer. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1744–1754.
Kershaw EE, Flier JS . Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2548–2556.
Vohl MC, Sladek R, Robitaille J, Gurd S, Marceau P, Richard D et al. A survey of genes differentially expressed in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in men. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1217–1222.
Giusti V, Suter M, Verdumo C, Gaillard RC, Burckhardt P, Pralong FP . Molecular determinants of human adipose tissue: differences between visceral and subcutaneous compartments in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1379–1384.
Swinburn BA, Nyomba BL, Saad MF, Zurlo F, Raz I, Knowler WC et al. Insulin resistance associated with lower rates of weight gain in Pima Indians. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 168–173.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 2001; 7: 941–946.
Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Matsuda M, Nagaretani H et al. Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat Med 2002; 8: 731–737.
Shand BI, Scott RS, Elder PA, George PM . Plasma adiponectin in overweight, nondiabetic individuals with or without insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes Metab 2003; 5: 349–353.
Liu YM, Lacorte JM, Viguerie N, Poitou C, Pelloux V, Guy-Grand B et al. Adiponectin gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women in response to short-term very low calorie diet and refeeding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 5881–5886.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, Ortmeyer HK, Arita Y, Hansen BC et al. Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1126–1133.
Lihn AS, Ostergard T, Nyholm B, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B, Schmitz O . Adiponectin expression in adipose tissue is reduced in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: E443–E448.
Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G . Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 2003; 52: 1779–1785.
Garaulet M, Viguerie N, Porubsky S, Klimcakova E, Clement K, Langin D et al. Adiponectin gene expression and plasma values in obese women during very-low-calorie diet. Relationship with cardiovascular risk factors and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 756–760.
Milan G, Granzotto M, Scarda A, Calcagno A, Pagano C, Federspil G et al. Resistin and adiponectin expression in visceral fat of obese rats: effect of weight loss. Obes Res 2002; 10: 1095–1103.
Iwaki M, Matsuda M, Maeda N, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Makishima M et al. Induction of adiponectin, a fat-derived antidiabetic and antiatherogenic factor, by nuclear receptors. Diabetes 2003; 52: 1655–1663.
Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M, Lindgren CM, Vohl MC, Nemesh J et al. The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 76–80.
Yamamoto Y, Hirose H, Miyashita K, Nishikai K, Saito I, Taniyama M et al. PPAR(gamma)2 gene Pro12Ala polymorphism may influence serum level of an adipocyte-derived protein, adiponectin, in the Japanese population. Metabolism 2002; 51: 1407–1409.
Thamer C, Machicao F, Fritsche A, Stumvoll M, Haring H . No influence of the PPARgamma2 Pro12Ala genotype on serum adiponectin concentrations in healthy Europeans. Metabolism 2003; 52: 798; author reply 98–99.
Kolehmainen M, Uusitupa MI, Alhava E, Laakso M, Vidal H . Effect of the Pro12Ala polymorphism in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma2 gene on the expression of PPARgamma target genes in adipose tissue of massively obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1717–1722.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the Foundation for Strategic Research through the National Network for Cardiovascular Research, the Swedish Foundation for the Study of Diabetes, the Albert Påhlssons Foundation, the Swedish Medical Research Council, Malmö University Hospital Foundation, the Ernhold Lundström Foundation, the Anna-Lisa and Sven-Eric Lundgren Foundation, the Crafoord Foundation, the Lundberg Foundation, the Magnus Bergvall Foundation, the Fredrik and Ingrid Thurings Foundation, the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (Sankyo Pharma).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fredriksson, J., Carlsson, E., Orho-Melander, M. et al. A polymorphism in the adiponectin gene influences adiponectin expression levels in visceral fat in obese subjects. Int J Obes 30, 226–232 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803138
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803138
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Contribution of ADIPOQ Variants to the Genetic Susceptibility of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Reproductive Sciences (2021)
-
The Relation of Light-to-Moderate Alcohol Consumption to Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in Nondiabetic Adults: the Moderating Effects of Depressive Symptom Severity, Adiposity, and Sex
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine (2017)
-
Adiponectin mRNA in adipose tissue and its association with metabolic risk factors in postmenopausal obese women
Hormones (2013)
-
A common variant in the adiponectin gene and polycystic ovary syndrome risk
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
Common genetic variation in adiponectin, leptin, and leptin receptor and association with breast cancer subtypes
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2011)