Abstract
BACKGROUND: Obesity results from a chronic imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure. However, experimental evidence of the relative contribution of interindividual differences in energy intake and expenditure (resting or due to physical activity) to weight gain is limited.
OBJECTIVE: To assess prospectively the association between baseline measurements of daily energy metabolism and weight changes by studying free-living adult Pima Indians, one of the most obese populations in the world.
DESIGN: A study of the pathogenesis of obesity in the Pima Indians living in Southwestern Arizona. The participants were 92 nondiabetic Pima Indians (64M/28F, 35±12 y, 35±9% body fat; mean±s.d.). At baseline, free-living daily energy metabolism was assessed by doubly labeled water and resting metabolic rate (RMR) by indirect calorimetry. Data on changes in body weight (5.8±6.5 kg) over a follow-up period of 4±3 y were available in 74 (49M/25F) of the 92 subjects.
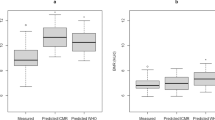
RESULTS: The baseline calculated total energy intake (r=0.25, P=0.028) and RMR (r=−0.28, P=0.016) were significantly associated with changes in body weight. The baseline energy expenditure due to physical activity was not associated with changes in body weight.
CONCLUSION: Using state-of-the-art methods to assess energy intake and expenditure in free-living conditions, we show for the first time that the baseline calculated total energy intake is a determinant of changes in body weight in Pima Indians. These data also confirm that a low RMR is a risk factor for weight gain in this population.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH-NHLBI Obesity Initiative Task Force. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults–the evidence report. Obes Res 1998; 6: 1–209.
Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Saad MF, Charles MA, Nelson RG, Howard BV, Bogardus C, Bennett PH . Obesity in the Pima Indians: its magnitude and relationship with diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 1991; 53: 1543S–1551S.
Bogardus C, Lillioja S, Ravussin E . The pathogenesis of obesity in man: results of studies on Pima Indians. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1990; 14 (Suppl): 5–13.
Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Knowler WC, Christin L, Freymond D, Abbott WG, Boyce V, Howard BV, Bogardus C . Reduced rate of energy expenditure as a risk factor for body-weight gain. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 467–472.
Ravussin E, Bogardus C . Energy balance and weight regulation: genetics versus environment. Br J Nutr 2000; 83 (Suppl 1): S17–S20.
Schoeller DA, Ravussin E, Schutz Y, Acheson KJ, Baertschi P, Jequier E . Energy expenditure by doubly labeled water: validation in humans and proposed calculation. Am J Physiol 1986; 250: R823–R830.
Schutz Y, Weinsier RL, Hunter GR . Assessment of free-living physical activity in humans: an overview of currently available and proposed new measures. Obes Res 2001; 9: 368–379.
Schulz LO, Alger S, Harper I, Wilmore JH, Ravussin E . Energy expenditure of elite female runners measured by respiratory chamber and doubly labeled water. J Appl Physiol 1992; 72: 23–28.
Black AE, Coward WA, Cole TJ, Prentice AM . Human energy expenditure in affluent societies: an analysis of 574 doubly-labelled water measurements. Eur J Clin Nutr 1996; 50: 72–92.
Ravussin E, Harper IT, Rising R, Bogardus C . Energy expenditure by doubly labeled water: validation in lean and obese subjects. Am J Physiol 1991; 261: E402–E409.
Prentice AM, Black AE, Coward WA, Cole TJ . Energy expenditure in overweight and obese adults in affluent societies: an analysis of 319 doubly-labelled water measurements. Eur J Clin Nutr 1996; 50: 93–97.
Rising R, Harper IT, Fontvielle AM, Ferraro RT, Spraul M, Ravussin E . Determinants of total daily energy expenditure: variability in physical activity. Am J Clin Nutr 1994; 59: 800–804.
Ravussin E, Gautier JF . Metabolic predictors of weight gain. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23 (Suppl 1): 37–41.
WHO Study Group. Diabetes mellitus. WHO Tech Rep Ser 1985; 727: 11.
Goldman RF, Buskirk ER . A method for underwater weighing and the determination of body density. In: Brozek J, Hershel A (eds). Techniques for measuring body composition. National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC; 1961. pp 78–106.
Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, Hanson J . Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for total-body and regional bone-mineral and soft-tissue composition. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 51: 1106–1112.
Siri WE . Body composition from fluid spaces and density: analysis of methods. In: Brozek J, Hershel A (eds). Techniques for measuring body composition. National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC; 1961. pp 223–244.
Tataranni PA, Ravussin E . Use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in obese individuals. Am J Clin Nutr 1995; 62: 730–734.
Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Anderson TE, Christin L, Bogardus C . Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. Methods and results using a respiratory chamber. J Clin Invest 1986; 78: 1568–1578.
Tataranni PA, Larson DE, Snitker S, Ravussin E . Thermic effect of food in humans: methods and results from use of a respiratory chamber. Am J Clin Nutr 1995; 61: 1013–1019.
Ravussin E, Rising R . Daily energy expenditure in humans: measurements in a respiratory chamber and by doubly labeled water. In: Kinney JM, Tucker HN (eds). Energy metabolism: tissue determinants and cellular corollaries. Raven Press, Ltd: New York; 1992. pp 81–96.
Coplen TB, Harper IT . An improved technique for the 2H/1H analysis of urines from diabetic volunteers. Biol Mass Spectrom 1994; 23: 437–439.
Forbes GB . Influence of nutrition. Human body composition. Growth, aging, nutrition, and activity. Springer-Verlag: New York; 1987. pp 209–247.
Pullar JD, Webster AJ . The energy cost of fat and protein deposition in the rat. Br J Nutr 1977; 37: 355–363.
Spady DW, Payne PR, Picou D, Waterlow JC . Energy balance during recovery from malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 1976; 29: 1073–1088.
Forbes GB, Brown MR, Welle SL, Lipinski BA . Deliberate overfeeding in women and men: energy cost and composition of the weight gain. Br J Nutr 1986; 56: 1–9.
Blundell JE . What foods do people habitually eat? A dilemma for nutrition, an enigma for psychology. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 71: 3–5.
Smith CJ, Nelson RG, Hardy SA, Manahan EM, Bennett PH, Knowler WC . Survey of the diet of Pima Indians using quantitative food frequency assessment and 24-hour recall. Diabetic Renal Disease Study. J Am Diet Assoc 1996; 96: 778–784.
Williams DE, Knowler WC, Smith CJ, Hanson RL, Roumain J, Saremi A, Kriska AM, Bennett PH, Nelson RG . The effect of Indian or Anglo dietary preference on the incidence of diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 811–816.
Stunkard AJ, Berkowitz RI, Stallings VA, Schoeller DA . Energy intake, not energy output, is a determinant of body size in infants. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 69: 524–530.
Weinsier RL, Nelson KM, Hensrud DD, Darnell BE, Hunter GR, Schutz Y . Metabolic predictors of obesity. Contribution of resting energy expenditure, thermic effect of food, and fuel utilization to four-year weight gain of post-obese and never-obese women. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 980–985.
Luke A, Rotimi CN, Adeyemo AA, Durazo-Arvizu RA, Prewitt TE, Moragne-Kayser L, Harders R, Cooper RS . Comparability of resting energy expenditure in Nigerians and US blacks. Obes Res 2000; 8: 351–359.
Prentice AM, Jebb SA . Obesity in Britain: gluttony or sloth? BMJ 1995; 311: 437–439.
Weinsier RL, Hunter GR, Heini AF, Goran MI, Sell SM . The etiology of obesity: relative contribution of metabolic factors, diet, and physical activity. Am J Med 1998; 105: 145–150.
DiPietro L . Physical activity in the prevention of obesity: current evidence and research issues. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999; 31: S542–S546.
Jebb SA, Moore MS . Contribution of a sedentary lifestyle and inactivity to the etiology of overweight and obesity: current evidence and research issues. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999; 31: S534–S541.
Wareham NJ, Hennings SJ, Prentice AM, Day NE . Feasibility of heart-rate monitoring to estimate total level and pattern of energy expenditure in a population-based epidemiological study: the Ely Young Cohort Feasibility Study 1994–5. Br J Nutr 1997; 78: 889–900.
Zurlo F, Ferraro RT, Fontvielle AM, Rising R, Bogardus C, Ravussin E . Spontaneous physical activity and obesity: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies in Pima Indians. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: E296–E300.
Goran MI, Shewchuk R, Gower BA, Nagy TR, Carpenter WH, Johnson RK . Longitudinal changes in fatness in white children: no effect of childhood energy expenditure. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 67: 309–316.
Schoeller DA, Shay K, Kushner RF . How much physical activity is needed to minimize weight gain in previously obese women? Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 66: 551–556.
Obesity: preventing and managing the global pandemic. WHO/NUT/NCD/98.1 1997.
Westerterp KR . Energy requirements assessed using the doubly-labelled water method. Br J Nutr 1998; 80: 217–218.
Leibel RL, Rosenbaum M, Hirsch J . Changes in energy expenditure resulting from altered body weight. N Engl J Med 1995; 332: 621–628.
Weyer C, Pratley RE, Salbe AD, Bogardus C, Ravussin E, Tataranni PA . Energy expenditure, fat oxidation, and body weight regulation: a study of metabolic adaptation to long-term weight change. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 1087–1094.
Acknowledgements
We thank the nursing staff for professional care of the volunteers and residents and leaders of the Gila River Community for their cooperation and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tataranni, P., Harper, I., Snitker, S. et al. Body weight gain in free-living Pima Indians: effect of energy intake vs expenditure. Int J Obes 27, 1578–1583 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802469
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802469
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification and characterization of the long non-coding RNA NFIA-AS2 as a novel locus for body mass index in American Indians
International Journal of Obesity (2023)
-
Longitudinal analysis of resting energy expenditure and body mass composition in physically active children and adolescents
BMC Pediatrics (2022)
-
The role of leptin and low testosterone in obesity
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Total energy expenditure is repeatable in adults but not associated with short-term changes in body composition
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Effects of underfeeding and oral vancomycin on gut microbiome and nutrient absorption in humans
Nature Medicine (2020)