Abstract
Objective:
To establish the accuracy of bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) for the assessment of total and appendicular body composition in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients.
Design:
Cross-sectional study.
Setting:
University Nephrology Clinic.
Subjects:
In all, 20 PD patients and 77 healthy controls matched for gender, age and body mass index.
Methods:
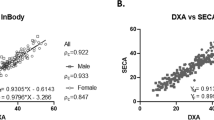
Whole-body fat-free mass (FFM) and appendicular lean tissue mass (LTM) were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Resistance (R) of arms, trunk and legs was measured by eight-polar BIA at frequencies of 5, 50, 250 and 500 kHz. Whole-body resistance was calculated as the sum of R of arms, trunk and legs. The resistance index (RI) was calculated as the ratio between squared height and whole-body or segmental R.
Results:
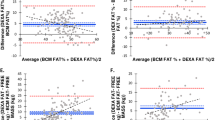
RI at 500 kHz was the best predictor of FFM, LTMarm and LTMleg in both PD patients and controls. Equations developed on controls overestimated FFM and LTMarm and underestimated LTMleg when applied to PD patients. Specific equations were thus developed for PD patients. Using these equations, the percent root mean-squared errors of the estimate for PD patients vs controls were 5 vs 6% for FFM, 8 vs 8% for LTMarm and 7 vs 8% for LTMleg.
Conclusion:
Eight-polar BIA offers accurate estimates of total and appendicular body composition in PD patients, provided that population-specific equations are used.
Sponsorship:
University of Modena and Reggio Emilia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedogni G, Malavolti M, Severi S, Poli M, Mussi C, Fantuzzi AL & Battistini N (2002): Accuracy of an eight-point tactile-electrode impedance method in the assessment of total body water. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 56, 1143–1148.
Bedogni G, Marra M, Bianchi L, Malavolti M, Nicolai E, De Filippo E & Scalfi L (2003): Comparison of bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of appendicular body composition in anorexic women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 1068–1072.
Bhatla B, Moore H, Emerson P, Keshaviah P, Prowant B, Nolph KD & Singh A (1995): Lean body mass estimation by creatinine kinetics, bioimpedance, and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Asaio J. 41, M442–M446.
Borovnicar DJ, Wong KC, Kerr PG, Stroud DB, Xiong DW, Strauss BJ & Atkins RC (1996): Total body protein status assessed by different estimates of fat-free mass in adult peritoneal dialysis patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50, 607–616.
Cano N (1999): Haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: metabolic alterations and nutritional status. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2, 329–333.
Guo S & Chumlea WC (1996): Statistical methods for the development and testing of predictive equations. In Human body composition, eds Roche AF, Heymsfield SB & Lohman TG. pp 191–202. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Konings CJ, Kooman JP, Schonck M, Cox-Reijven PL, van Kreel B, Gladziwa U, Wirtz J, Gerlag PG, Hoorntje SJ, Wolters J, Heidendal GA, van der Sande FM & Leunissen KM (2002): Assessment of fluid status in peritoneal dialysis patients. Periton. Dial. Int. 22, 683–692.
Konings CJ, Kooman JP, Schonck M, van Kreel B, Heidendal GA, Cheriex EC, van der Sande FM & Leunissen KM (2003): Influence of fluid status on techniques used to assess body composition in peritoneal dialysis patients. Periton. Dial. Int. 23, 184–190.
Kopple JD (1997): Nutritional status as a predictor of morbidity and mortality in maintenance dialysis patients. Asaio J. 43, 246–250.
Locatelli F, Fouque D, Heimburger O, Drueke TB, Cannata-Andia JB, Horl WH & Ritz E (2002): Nutritional status in dialysis patients: a European consensus. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17, 563–572.
Lohman TG, Roche AF & Martorell R (eds.) (1988): Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Human Champaign IL: Human Kinetics Books.
Malavolti M, Mussi C, Poli M, Fantuzzi AL, Salvioli G, Battistini N & Bedogni G (2003): Cross-calibration of eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis versus dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of total and appendicular body composition in healthy subjects aged 21–82 years. Ann. Hum. Biol. 30, 380–391.
Pietrobelli A, Morini P, Battistini N, Chiumello G, Nunez C & Heymsfield SB (1998): Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: prediction from multiple frequency segmental bioimpedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 507–511.
Pietrobelli A, Rubiano F, St-Onge MP & Heymsfield SB (2004): New bioimpedance analysis system: improved phenotyping with whole-body analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 58, 1479–1484.
Sartorio A, Malavolti M, Agosti F, Marinone P, Caiti O, Battistini N & Bedogni G (2005): Body water distribution in severe obesity and its assessment from eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 59, 155–160.
Wang W, Wang Z, Faith M, Kotler D, Shih R & Heymsfield S (1999): Regional skeletal muscle measurement: evaluation of new dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry model. J. Appl. Physiol. 87, 1163–1171.
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Turney JH, Davies PS, Day JM & Smith MA (1996a): Four-component model of body composition in chronic renal failure comprising dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and measurement of total body water by deuterium oxide dilution. Clin. Sci. 91, 763–769.
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Turney JH, Davies PS, Day JM & Smith MA (1997): Measurement of total body water and urea kinetic modelling in peritoneal dialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 47, 52–57.
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Turney JH, Tompkins L, Brownjohn AM & Smith MA (1996b): Whole body and regional body composition in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 11, 1613–1618.
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Wright A, Coward WA, Turney JH, Brownjohn AM, Smith MA & Truscott JG (2004): Abnormalities of body composition in peritoneal dialysis patients. Periton. Dial. Int. 24, 169–175.
Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Wright A, Coward WA, Turney JH, Brownjohn AM, Truscott JG & Smith MA (2001): The measurement of total body potassium in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Periton. Dial Int. 21 (Suppl 3), S163–S167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantors: G Medici and G Bedogni.
Contributions: GM performed the selection and clinical evaluation of patients. CM performed dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry of patients and controls and BIA measurements of patients. ALF performed the nutritional and anthropometric assessment of patients and controls. MM performed the selection and BIA measurements of controls. AA coordinated the study. GB analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medici, G., Mussi, C., Fantuzzi, A. et al. Accuracy of eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of total and appendicular body composition in peritoneal dialysis patients. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 932–937 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602165
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602165
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ratiometric Impedance Sensing of Fingers for Robust Identity Authentication
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Gender-specific associations of skeletal muscle mass and arterial stiffness among peritoneal dialysis patients
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Effects of procedure, upright equilibrium time, sex and BMI on the precision of body fluid measurements using bioelectrical impedance analysis
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2018)
-
Higher skeletal muscle mass may protect against ischemic stroke in community-dwelling adults without stroke and dementia: The PRESENT project
BMC Geriatrics (2017)
-
Contribution of branched-chain amino acids to purine nucleotide cycle: a pilot study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2017)