Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association between a healthy diet indicator and the prevalence of cognitive impairment in the elderly.
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Setting: Population based.
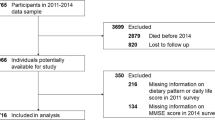
Subjects: A total of 1651 subjects (560 men and 1091 women) including everybody aged 70 y or more, and a random sample of people (about 40%) aged 65–69 y resident in four rural towns in the province of Pavia, Italy in 1992–1993.
Interventions: The healthy diet indicator based on the WHO guidelines for the prevention of chronic diseases was calculated as reported by Huijbregts et al (1998; Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 826–831). Food intake was estimated by means of a 180-item food-frequency questionnaire and nutrient intake was calculated using the food composition database compiled for epidemiologic studies in Italy. The cognitive function was categorized into four levels—normal cognition, mild, moderate and severe cognitive deficit—according to the neuropsychological test score. The relationship beween the dietary and the ordinal cognitive function variables was studied using the proportional-odds model.
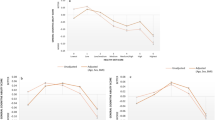
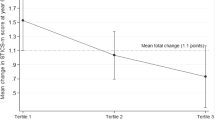
Results: After adjustment for age, sex, education, total energy intake, cigarrette smoking, alcohol consumption and physical activity, a better healthy diet score was associated with a lower prevalence of cognitive deficit. The cumulative odds ratio was 0.85 (95% CI 0.77–0.93).
Conclusions: Our results suggest an association beween a globally satisfactory diet and better cognitive performance in the elderly. However, the specific aspects of a ‘healthy diet’ for the elderly should be clarified.
Sponsorship: National Research Council (Italy), ‘Invecchiamento’ Project no. 95.01048.PF40.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2001) 55, 1053–1058
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A (1990) Categorical Data Analysis New York: John Wiley
Behl C (1999) Vitamin E and other antioxidants in neuroprotection Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 69 213–219
Cattin L, Bordin P, Fonda M, Adamo C, Barbone F, Bovenzi M, Manto A, Pedone C & Pahor M (1997) Factors associated with cognitive impairment among older Italian inpatients. Gruppo Italiano di Farmacovigilanza nell' Anziano (G.I.F.A.) J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 45 1324–1330
Chan AD (1998) Vitamin E and atherosclerosis J. Nutr. 128 1593–1596
Corti MC, Guralnik JM, Salive ME, Harris T, Ferruci L, Glyn RJ & Havlik RJ (1997) Clarifying the direct relation between total cholesterol levels and death from coronary heart disease in older persons Ann. Intern. Med. 126 753–760
Coulston AM (1999) The role of dietary fats in plant-based diets Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 70 512S–515S
Elias PK, Elias MF, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H & Wolf PA (1999) Alcohol consumption and cognitive performance in the Framingham Heart Study Am. J. Epidemiol. 150 580–589
Folstein MF, Folstein SE & McHugh PR (1975) ‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician J. Psychiatr. Res. 12 89–198
Foy CJ, Passmore AP, Vahidassr MD, Young IS & Lawson JT (1999) Plama chain-breaking antioxidants in Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson's disease Q. J. Med. 92 39–45
Gale CR, Martyn CN & Cooper C (1996) Cognitive impairment and mortality in a cohort of elderly people Br. Med. J. 312 608–611
Gillman MW, Cupples LA, Gagnon D, Posner BM, Ellison RC, Castelli WP & Wolf PA (1995) Protective effect of fruits and vegetables on development of stroke in men J.A.M.A. 273 1113–1117
Gillman MW, Cupples LA, Millen BE, Ellison RC & Wolf PA (1997) Inverse association of dietary fat with development of ischemic stroke in men J.A.M.A. 278 2145–2150
Hendrie HC (1998) Epidemiology of dementia and Alzheimer's disease Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiat. 6 S3–S18
Hendrie HC, Gao S, Hall KS, Hui SL & Unverzagt FW (1996) The relationship between alcohol consumption, cognitive performance and daily functioning in an urban sample of older black Americans J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 44 1158–1165
Hillbom M & Numminen H (1998) Alcohol and stroke: pathophysiologic mechanisms Neuroepidemiology 17 281–287
Huijbregts P, Feskens E, Rasanen L, Fidanza F, Nissinen A, Menotti A & Kromhout D (1997) Dietary pattern and 20 y mortality in elderly men in Finland, Italy and The Netherlands: longitudinal cohort study Br. Med. J. 315 13–17
Huijbregts PPCW, Feskens EJM, Rasanen L, Fidanza F, Alberti-Fidenza A, Nissinen A, Giampaoli S & Kromhout D (1998) Dietary patterns and cognitive function in elderly men in Finland, Italy and The Netherlands Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52 826–831
Jama JW, Launer LJ, Witterman JCM, den Breeijen JH, Breleter MMB, Grobbee DE & Hofman A (1996) Dietary antioxidants and cognitive function in a population-based sample of older persons Am. J. Epidemiol. 144 275–280
Kalmijn S, Feskens EJM, Launer LJ, Kromhout D (1997) Polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, and cognitive function in very old men Am. J. Epidemiol. 145 33–41
Katan MB, Grundy SM & Willet WC (1997) Beyond low-fat diets New Engl. J. Med. 337 563–567
Klipstein-Grobusch K, Geleijnse JM, den Breeijen JH, Boeing H, Hofman A, Grobbee DE & Witteman JCM (1999) Dietary antioxidants and risk of myocardial infarction in the elderly: the Rotterdam Study Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 69 261–266
Kretchmer N, Beard JL & Carlson S (1996) The role of nutrition in the development of normal cognition Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63 997S–1001S
La Rue A, Koehler KM, Wayne SJ, Chiulli SJ, Haaland KY & Garry PJ (1997) Nutritional status and cognitive functioning in a normally aging sample: a 6-y reassessment Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65 20–29
Launer LJ & Kalmijn S (1998) Anti-oxidant and cognitive function: a review of clinical and epidemiologic studies J. Neural Transm. 53 (Suppl), 1–8
Lichtenstein AH & Van Horn L (1998) Very low fat diets Circulation 98 935–939
Mendelsohn AB, Belle SH, Stoehr GP & Ganguli M (1998) Use of antioxidant supplements and its association with cognitive function in a rural elderly cohort Am. J. Epidemiol. 148 38–44
Oliver MF (1997) It is more important to increase the intake of unsaturated fats than to decrease the intake of saturated fats: evidence from clinical trials relating to ischemic heart disease Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66 980S–986S
Ortega RM, Requejo AM, Andrés P, Lopez-Sobaler AM, Quintas ME, Redondo MR, Navia B & Rivas T (1997) Dietary intake and cognitive function in a group of elderly people Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66 803–809
Paleologos M, Cumming RG & Lazarus R (1998) Cohort study of vitamin C intake and cognitive impairment Am. J. Epidemiol. 148 45–50
Perkins AJ, Hendrie HC, Callahan CM, Gao S, Unverzagt FW, Xu Y, Hall KS & Hui SL (1999) Association of antioxidants with memory in a multiethnic elderly sample using the third national health and nutrition examination survey Am. J. Epidemiol. 150 37–44
Perrig WJ, Perrig P & Stahelin HB (1997) The relation between antioxidants and memory performance in the old and very old J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 45 718–724
Ranieri P, Rozzini R, Franzoni S, Barbisoni P & Trabucchi M (1998) Serum cholesterol levels as a measure of frailty in elderly patients Exp. Aging Res. 24 169–179
Riggs KM, Spiro A III, Tucker K & Rush D (1996) Relations of vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, folate, and homocysteine to cognitive performance in the Normative Aging Study Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63 306–314
Salvini S, Parpinel M, Gnagnarella P, Maisonneuve P & Turrini A (1998) Banca dati di composizione degli alimenti per studi epidemiologici in Italia Milano: Istituto Europeo di Oncologia
SAS Institue Inc (1996) SAS/STAT Software Changes and Enhancements through Release 6.11 Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc
Seino F, Date C, Nakayama T, Yoshiike N, Yokoyama T, Yamaguchi M, Tanaka H (1997) Dietary lipids and incidence of cerebral infarction in a Japanese rural community J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 43 83–99
SENECA Investigators (1996) Mental health: Mini-Mental State Examination and geriatric depression scores of elderly Europeans in the SENECA study of 1993 Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50 (Suppl 2), S112–S116
WHO (1990) Diet, nutrition, and the prevention of chronic diseases Report of a WHO Study Group. Technical Report Series no. 797 Geneva: WHO
Willett W (1998) Nutritional Epidemiology 95–97 New York: Oxford University Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corrêa Leite, M., Nicolosi, A., Cristina, S. et al. Nutrition and cognitive deficit in the elderly: a population study. Eur J Clin Nutr 55, 1053–1058 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601270
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601270
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between erythrocyte membrane fatty acids and gut bacteria in obesity-related cognitive dysfunction
AMB Express (2023)
-
Nutrition, Immigration and Health Determinants are Linked to Verbal Fluency among Anglophone Adults in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA)
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2020)
-
Effect of monosodium l-glutamate (umami substance) on cognitive function in people with dementia
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2019)
-
Predictive Effect of Malnutrition on Long-Term Clinical Outcomes among Older Men: A Prospectively Observational Cohort Study
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2019)
-
Trajectories of nutritional status and cognitive impairment among older Taiwanese with hip fracture
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging (2017)