Abstract
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) reportedly has a low performance for distinguishing infection from non-infection. We explored the distribution of the patients diagnosed by SIRS (SIRS patients) or a quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) (qSOFA patients) and confirmed the performance of the both for predicting ultimate infection after hospital admission. We retrospectively analyzed the data from a multicenter prospective study. When emergency physicians suspected infection, SIRS or the qSOFA were applied. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC) was used to assess the performance of the SIRS and qSOFA for predicting established infection. A total of 1,045 patients were eligible for this study. The SIRS patients accounted for 91.6% of qSOFA patients and they showed a higher rate of final infection than that of non-SIRS patients irrespective of the qSOFA diagnosis. The AUCs for predicting infection with SIRS and a qSOFA were 0.647 and 0.582, respectively. The SIRS significantly predicted an ultimate infection (AUC, 0.675; p = 0.018) in patients who met the SIRS and qSOFA simultaneously. In conclusion, the SIRS patients included almost all qSOFA patients. SIRS showed a better performance for predicting infection for qSOFA in those who met both definitions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Since the announcement of the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3), much debate has been had on the accuracy of the quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) score for predicting mortality due to sepsis compared with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria1,2,3. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses in various settings, e.g. emergency departments, intensive-care units (ICUs), and general wards have consistently demonstrated a high sensitivity and low specificity with SIRS criteria but a low sensitivity and high specificity with the qSOFA score for predicting hospital mortality in patients suspected of or with an infection4,5,6,7,8,9,10. Herwanto et al.11 robustly confirmed these results presenting the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) and noted that neither score is perfect, each having its own limitations.
One reasons the Sepsis-3 criteria were proposed was under the definition of SIRS, systemic inflammation due to infectious and non-infectious insults such as pancreatitis and trauma, it is difficult to differentiate sepsis from noninfectious insults1,3. No difference in the accuracy for diagnosing sepsis defined by the Sepsis-3 criteria has been reported between SIRS criteria and qSOFA scores10; however, another systematic review and meta-analysis reported the significantly superior performance of the SIRS criteria to the qSOFA score for diagnosing sepsis in patients outside the ICU12. One unresolved issue is the performance of the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score for predicting established infection as distinguished from noninfectious insults in patients with suspected infection. A previous report found that infectious patients who met the SIRS criteria included almost all of those who met qSOFA definition in the emergency department13. Another issue to be resolved is the degree of overlap between the patients who met the SIRS criteria (SIRS patients) and those who met qSOFA definition (qSOFA patients) in patients with suspected infection.
The objectives of this study conducted in an emergency department were exploring the distribution of the patients with suspected infection diagnosed based on the SIRS criteria or qSOFA score and to confirm the performance of the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score for predicting an ultimate infection diagnosis after hospital admission as distinguished from noninfectious insults.
Methods
Study design, setting, and ethical approval
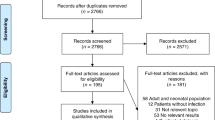
This is a retrospective prognostic study used the data of the Emergency Room (ER) cohort from the prospective, multicenter study of the Japanese Association for Acute Medicine (JAAM) Sepsis Prognostication in Intensive Care Unit and Emergency Room (SPICE) study, comprising the SPICE-ER and SPICE-ICU cohort. The main study of the SPICE-ER cohort externally validated the accuracy of the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score for predicting mortality in patients suspected of having an infection in the emergency department. The JAAM SPICE-ER study used samples from 35 emergency departments in tertiary hospitals. The patient recruitment and data collection were conducted from December 2017 to February 2018 and the included patients were followed up to their discharge of the hospital. The JAAM SPICE-ER was registered in the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trial Registry (UMIN-CTR ID: UMIN000027258).
This study was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the JAAM and the Ethics Committee of each hospital waiving written informed consent (JAAM, 2016-01; Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, head institute of the SPICE group, 016-0385).
Participants
The JAAM SPICE-ER study enrolled patients >16 years old who (1) were suspected of having an infection by the emergency physicians and (2) had received any kind of antibiotics, had their body fluid cultured, or had imagining done for the detection of infection sites during their stay in the emergency department. Patients were excluded if they were transferred to another hospital without first being hospitalized at the participating hospital.
Variables, definition, and outcome measures
In addition to the baseline characteristics of the patients, the clinical frailty index14, Charlson comorbidity index15, lactate levels, and parameters for calculating SIRS criteria and qSOFA score were obtained. The SIRS criteria were defined according to the original consensus study (Sepsis-1)2 and the qSOFA score was based on the Sepsis-3 definition1. SIRS criteria >2 and qSOFA score >2 met the definition of SIRS and qSOFA, respectively. The suspected infection sites were classified into 12 regions, including the respiratory tract, urinary tract, abdomen, central nervous system, skin and soft tissue, bone and joint, wounds, intravascular catheter, endocardium, any kind of implant aside from an intravascular catheter, others, and unknown origin. The ultimately confirmed sites of infection after hospitalization were classified into the same categories and final diagnosis of infection or non-infection was also determined after admission to the hospital. The primary outcome of this study was an ultimate diagnosis of infection after admission.
Statistical analyses
The statistical parameters required for the original study sample size estimation were not available from previous studies, therefore, the original study employed an adaptive sample size estimation design.
Numeric variables are expressed as the median with the 25th–75th interquartile range and nominal variables are shown as the number (percentage). The chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test for nominal variables was used when required. The ROC curve was constructed, and the AUC was used to assess the predictive ability of an ultimate infection diagnosis. Missing values were used without manipulation. Differences with a two-tailed p value of <0.05 were considered statistically significant. The IBM SPSS 25.0 for MAC OSX software program (IBM Japan, Tokyo, Japan) was used for the statistical analyses and calculations.
Results
Demographics and characteristics of the patients
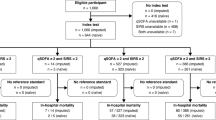
The flow diagram showing the study population as well as inclusions and exclusions is presented in Fig. 1. Of the 1,060 registered patients, a total of 1,045 patients were ultimately analyzed. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the patients who met the SIRS criteria or qSOFA definition. As shown in Fig. 2, there were huge overlaps between the two groups.
Distribution of the patients with suspected infection who presented to the emergency department. SIRS refers to patients who met >2 SIRS criteria, and qSOFA refers to patients with qSOFA score >2. (A), patients met both the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score; (B), patients met only the SIRS criteria; (C), patients met only the qSOFA score; (D), patients met neither the SIRS criteria nor qSOFA score. The SIRS patients included almost all (91.6%) qSOFA patients. qSOFA, quick sequential organ failure assessment; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Distribution of the patients diagnosed by the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score
Figure 2 shows the incidence of SIRS criteria- and qSOFA-based diagnosis, indicating the overlap between SIRS patients and qSOFA patients. Almost all patients (80.3%, 839/1045) met the SIRS criteria, while 395 (37.8%) patients met the qSOFA definition. The SIRS patients included 91.6% (362/395) of the patients who met the qSOFA definition. One hundred and seventy-three patients met neither the SIRS criteria nor the qSOFA definition.
Prediction of a final diagnosis of infection
Table 2 shows significant differences in the percentage of final diagnosis of infection among 4 groups (p = 0.04). The patients who simultaneously met both the SIRS criteria and qSOFA definition showed a higher prevalence of an ultimate diagnosis of infection (95.6%) than the other groups and the highest mortality rate (20.4%). The SIRS patients had a higher percentage of an ultimate diagnosis of infection than the non-SIRS patients irrespective meeting the qSOFA definition (785/839, 93.6% vs. 180/206, 87.4%, p = 0.005). Both SIRS (p < 0.001) and qSOFA (p = 0.015) showed stepwise increases in the rates of infection in parallel with the increases in the number of criteria and scores, respectively. Of note however, the rates of non-infectious patients among non-SIRS patients (12.6%) tended to higher than among non-qSOFA patients (9.4%). The results are shown in Fig. 3.
Bar graphs showing the prevalence of an ultimate infection after admission. Both SIRS (p < 0.001) and qSOFA (p = 0.015) showed stepwise increases in the rates of infection in parallel with the increases in the number of criteria and scores, respectively. Rates of patients without infection among non-SIRS patients (12.6%) tended to higher than among non-qSOFA patients (9.4%). SIRS (−), non-SIRS patients who did not meet SIRS criteria >2; qSOFA (−), non-qSOFA patients who did not meet qSOFA >2. qSOFA, quick sequential organ failure assessment; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Figure 4A shows that the AUC of the SIRS criteria was significant for predicting an ultimate infection diagnosis (AUC, 0.647; standard error [SE], 0.03, p < 0.001), with a sensitivity of 81.3% and specificity of 32.5%. The AUC of the qSOFA score for predicting an established infection diagnosis was 0.582 (SE 0.03) (p = 0.015), which was narrower than that of SIRS criteria. In patients with suspected of having an infection who both met SIRS criteria and fit the qSOFA definition simultaneously, the SIRS criteria were significantly more accurate for predicting an ultimate infection diagnosis than the qSOFA score (AUC, 0.675; SE, 0.06, p = 0.018). The AUC of qSOFA non-significantly predicted an ultimate infection diagnosis (AUC, 0.619; SE0.06, p = 0.107) (Fig. 4B).
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses for predicting an ultimately established diagnosis of infection in patients with suspected infection at the presentation to the emergency department. (A), All patients presented to the emergency department; (B), Patients who met both the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score. Numbers indicate the AUC (SE), p-value. AUC, area under the ROC curve; qSOFA, quick sequential organ failure assessment; SE, standard error; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Discussion
Brief summary
According to the present study, the SIRS patients included almost all qSOFA patients, and the SIRS patients showed a higher percentage of an ultimately established diagnosis of infection than the non-SIRS patients irrespective of the qSOFA score. The SIRS criteria, especially in patients who met both the SIRS criteria and the qSOFA score, showed a significant AUC for predicting an ultimate infection diagnosis after admission to the hospital.
A systematic review and meta-analysis including a large patient population showed that the qSOFA score had greater ability than the SIRS criteria for predicting sepsis mortality and secondary outcomes such as organ dysfunction, ICU admission, ventilatory support, a prolonged ICU stay, and the 30-day outcome11. However, information regarding an established diagnosis of infection, sepsis, and septic shock was lacking in that meta-analysis. The main reason for replacing the sepsis definition in 1992 (Sepsis-1)2 with Sepsis-33 was that SIRS criteria were extremely sensitive, leading to the misdiagnosis of non-infectious insults such as trauma, burns, pancreatitis, and ischemia-reperfusion events, as true infection16. However, in contrast to those previous findings, the present study showed a good predictive ability of the SIRS criteria for an ultimate diagnosis of infection.
In the current study, the AUC of the qSOFA score for predicting real infection was narrower than that of the SIRS criteria in patients with suspected infection. In addition, a non-significant AUC of the qSOFA score for predicting established infection was observed in patients who met both the SIRS criteria and qSOFA definitions. Not all patients with infection progress to sepsis. However, a systematic review and meta-analysis concluded that the SIRS criteria were significantly more accurate than the qSOFA score for diagnosing sepsis according to Sepsis-312. The results of present study and this meta-analysis are inevitable as the qSOFA score has been established and validated as a prognostic tool for hospital death in the patients with suspected infection17, while the SIRS criteria are used as a screening tool for severe sepsis which is defined as systemic inflammation with organ dysfunction according to Sepsis-12.
Despite the above issues, the international consensus of Sepsis-3 used the qSOFA score as a screening tool for diagnosing sepsis, namely dysregulated host responses to infection associated with organ dysfunction (SOFA > 2)1. In the first large validation study of Sepsis-3 in patients suspected of having infection who presented to the emergency department, the patients without infection were excluded from the validation, and the conclusion was that the qSOFA score had a greater prognostic accuracy for hospital mortality than the SIRS criteria18. There may be some inconsistencies between the original paper and the validation study1,18. It is a time to become aware that the primary outcome of the study attempting to compare the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score is not the prediction of hospital mortality but the prediction of infection that progresses to sepsis or prediction of sepsis itself.
Among patients with suspected infection, a significant portion (91.6%) of those who met the qSOFA definition were included in those who met the SIRS criteria. These results were consistent with those obtained by Henning et al.13, who showed that the SIRS patients include almost all qSOFA patients among the infectious patients. The present and previous findings suggest that the SIRS criteria can replace the qSOFA score as a screening tool for sepsis in patients with suspected infection1. Alternatively, the combined application of those two tests for patients with suspected infection may improve the accuracy of both as screening and prognostic tools.
On comparing the SIRS criteria, qSOFA score, and the National Early Warning score (NEWS), the qSOFA score had the lowest sensitivity and was recognized as a poor tool for use in emergency department sepsis screening19. That study further showed that the NEWS was more accurate for detecting sepsis than the SIRS criteria (AUC of NEWS vs. SIRS criteria: 0.91 vs. 0.88) and recommended the NEWS as a screening tool for sepsis in the emergency department. However, screening of sepsis should be performed based on the pathophysiology of sepsis rather than using the simple warning score like the NEWS. Namely, SIRS, defined as systemic inflammatory responses to the infection would be good screening tool for sepsis, because the SIRS criteria are based on the sepsis pathophysiology as described in Sepsis-12.
Limitations
The strength of this study was our use of prospective data collected by the emergency physicians immediately after presentation to the emergency department. However, several limitations associated with the present study also warrant mention. The retrospective nature of the analyses may have limited the robustness of the study. The sample size was determined for the validation of hospital mortality predicted by the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score in the original study. Diagnostic data on non-infectious insults were lacking. The present study was a single national study conducted in a developed country in an emergency department setting, which may limit the generalizability of the obtained results. However, we believe that our study highlighted important discussion points for the future studies, supporting the further comparison of the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score.
Conclusions
In the emergency department patients with suspected infection, the SIRS patients included almost all qSOFA patients and were associated with higher incidence of an ultimate infection diagnosis than non-SIRS patients irrespective of the qSOFA diagnosis. The SIRS criteria were significantly more accurate in predicting an established infection, especially in those who met both the SIRS criteria and the qSOFA definition. These results may suggest that the qSOFA score can be replaced with the SIRS criteria as a screening tool of infection likely to progress to sepsis. Alternatively, the combined application of both the SIRS criteria and qSOFA score in patients with suspected of having infection may improve the screening and prognostic accuracy of these factors for predicting infection and/or sepsis and a poor outcome.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the JAAM and the Ethics Committee of each hospital waiving written informed consent (JAAM, 2016-01; Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, head institute of the SPICE group, 016-0385).
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Singer, M. et al. The third internal consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315, 801–810 (2016).
Members of the American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: Definition for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 20, 864–874 (1992).
Levy, M. M. et al. For the International Sepsis Definition Conference. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 31, 1250–1256 (2003).
Franchini, S., Scarallo, L., Carlucci, M., Cabrini, L. & Tresoldi, M. SIRS or qSOFA? Is that the question? Clinical and methodological observations from meta-analysis and critical review on the prognostication of patients with suspected sepsis outside the ICU. Intern Emerg Med. 14, 593–602 (2019).
Jiang, J., Yang, J., Jin, Y., Cao, J. & Lu, Y. Role of qSOFA in predicting mortality of pneumonia. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 97(40), e12634 (2018).
Jiang, J., Yang, J., Mei, J., Jin, Y. & Lu, Y. Head-to-head comparison of qSOFA and SIRS criteria in predicting the mortality of infected patients in the emergency department: a meta-analysis. Scand J Trauma, Resuscitation and Emerg Med. 26, 56 (2018).
Song, J. U., Sin, C. K., Park, H. K., Shim, S. R. & Lee, J. Performance of the quick sequential (sepsis-related) organ failure assessment as a prognostic tool in infected patients outside the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 22, 28 (2018).
Fernando, S. M. et al. Prognostic accuracy of the quick sequential organ failure assessment for mortality in patients with suspected infection. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 168, 266–275 (2018).
Maitra, S., Som, A. & Bhattacharjee, S. Accuracy of quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) score and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with suspected infection: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin Microbiol Infect. 24, 1123–1129 (2018).
Liu, Y. C. et al. Quick sequential organ failure assessment as a prognostic factor for infected patients outside the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern Emerg Med. 14, 603–615 (2019).
Herwanto, V. et al. Accuracy of quick sequential organ failure assessment score to predict sepsis mortality in 121 studies including 1,716,017 individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Explorations. 1, e0043 (2019).
Serafim, R., Gomes, J. A., Salluh, J. & Póvoa, P. A comparison of the quick SOFA and systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria for the diagnosis of sepsis and prediction mortality. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 153, 646–655 (2018).
Henning, D. J. et al. An emergency department validation of the SEP-3 sepsis and septic shock definitions and comparison with 1992 consensus definitions. Ann Emerg Med. 70, 544–552 (2017).
Rockwood, K. et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ. 173, 489–495 (2005).
Charlson, M. E., Pompei, P., Ales, K. L. & MacKenzie, C. R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 40, 373–383 (1987).
Vincent, J. L., Opal, S. M., Marshall, J. C. & Tracy, K. J. Sepsis definition: time for change. Lancet. 381(9868), 774–775 (2013).
Seymour, C. W. et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315, 762–774 (2016).
Freund, Y. et al. for the French Society of Emergency Medicine Collaborators Group. Prognostic accuracy of Sepsis-3 criteria for in-hospital mortality among patients with suspected infection presenting to the emergency department. JAMA. 373, 301–308 (2017).
Usman, O. A., Usman, A. A. & Ward, M. A. Comparison of SIRS, qSOFA and NEWS for the early identification of sepsis in the emergency department. Am J Emerg Med. 37, 1490–1497 (2019).
Acknowledgements
The JAAM SPICE Study Group thanks Shuta Fukuda for his special assistance in completing the study. This work was supported by the J.A.A.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
S.G. analyzed the data, interpreted the results, drafted the figures and tables and wrote the manuscript. Concept and design: A.S., S.G., T.A., S.K., T.M., Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors, Drafting of the manuscript: A.S., S.G., Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: S.G., A.S., S.K., T.M., S.F., A.H., Y.S., S.S., T.H., Y.O., K.O., J.S., K.T., K.Y., Administrative, technical, or material support: A.S., Supervision: A.S. All authors read and approved final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Gando S reported receiving personal fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma America Inc. and Asahi Kasei Pharma Japan Inc. Shiraishi A reported receiving personal fees from CSL Behring. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gando, S., Shiraishi, A., Abe, T. et al. The SIRS criteria have better performance for predicting infection than qSOFA scores in the emergency department. Sci Rep 10, 8095 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64314-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64314-8
This article is cited by
-
Serial measurements of SIRS and SEP scores to identify unique phenotypes of sepsis
Internal and Emergency Medicine (2024)
-
Performance of qSOFA, SIRS, and the qSOFA + SIRS combinations for predicting 30-day adverse outcomes in patients with suspected infection
Medizinische Klinik - Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin (2022)
-
Comparison of QSOFA and sirs scores for the prediction of adverse outcomes of secondary peritonitis among patients admitted on the adult surgical ward in a tertiary teaching hospital in Uganda: a prospective cohort study
BMC Emergency Medicine (2021)
-
Comparison of qSOFA score, SOFA score, and SIRS criteria for the prediction of infection and mortality among surgical intermediate and intensive care patients
World Journal of Emergency Surgery (2020)
-
The sensitivity of qSOFA calculated at triage and during emergency department treatment to rapidly identify sepsis patients
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.