Abstract
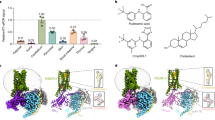
Prostanoids are a series of bioactive lipid metabolites that function in an autacoid manner via activation of cognate G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Here, we report the crystal structure of human prostaglandin (PG) E receptor subtype EP3 bound to endogenous ligand PGE2 at 2.90 Å resolution. The structure reveals important insights into the activation mechanism of prostanoid receptors and provides a molecular basis for the binding modes of endogenous ligands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The atomic coordinates and structure factor files have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession codes 6AK3.
References
Woodward, D. F., Jones, R. L. & Narumiya, S. Pharmacol. Rev. 63, 471–538 (2011).
Toyoda, Y. et al. Nat. Chem. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0131-3 (2018).
Ballesteros, J. A. & Weinstein, H. in Methods in Neurosciences. Vol. 25, (ed. Sealfon, S.) 366–428 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1995).
Jin, J., Mao, G. F. & Ashby, B. Br. J. Pharmacol. 121, 317–323 (1997).
Zhang, H. et al. Nature 544, 327–332 (2017).
Kedzie, K. M., Donello, J. E., Krauss, H. A., Regan, J. W. & Gil, D. W. Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 584–590 (1998).
Neuschäfer-Rube, F., Engemaier, E., Koch, S., Böer, U. & Püschel, G. P. Biochem. J. 371, 443–449 (2003).
Stitham, J., Stojanovic, A., Merenick, B. L., O’Hara, K. A. & Hwa, J. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 4250–4257 (2003).
Funk, C. D., Furci, L., Moran, N. & Fitzgerald, G. A. Mol. Pharmacol. 44, 934–939 (1993).
Scheerer, P. et al. Nature 455, 497–502 (2008).
Koehl, A. et al. Nature 558, 547–552 (2018).
Draper-Joyce, C. J. et al. Nature 558, 559–563 (2018).
García-Nafría, J., Nehmé, R., Edwards, P. C. & Tate, C. G. Nature 558, 620–623 (2018).
Katritch, V. et al. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 39, 233–244 (2014).
Hanson, M. A. et al. Science 335, 851–855 (2012).
Chrencik, J. E. et al. Cell 161, 1633–1643 (2015).
Hua, T. et al. Cell 167, 750–762.e14 (2016).
Hua, T. et al. Nature 547, 468–471 (2017).
Choe, H. W. et al. Nature 471, 651–655 (2011).
Shiroishi, M. et al. Microb. Cell. Fact. 11, 78 (2012).
Hattori, M., Hibbs, R. E. & Gouaux, E. Structure 20, 1293–1299 (2012).
Chu, R. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 323, 253–262 (2002).
Caffrey, M. & Cherezov, V. Nat. Protoc. 4, 706–731 (2009).
Ueno, G. et al. AIP Conf. Proc. 1741, 050021 (2016).
Hirata, K., Foadi, J., Evans, G., Hasegawa, K. & Zeldin, O. B. in Advanced Methods in Structural Biology. (eds. Senda, T. & Maenaka, K.) 241–273 (Springer Protocol Handbooks, 2016).
Yamashita, K., Hirata, K. & Yamamoto, M. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 74, 441–449 (2018).
Kabsch, W. Acta Crystallogr, D. Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 125–132 (2010).
Foadi, J. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 69, 1617–1632 (2013).
McCoy, A. J. et al. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 486–501 (2010).
Murshudov, G. N. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 355–367 (2011).
Adams, P. D. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 (2010).
Inoue, A. et al. Nat. Methods 9, 1021–1029 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by AMED under grant Numbers JP18gm0910007 (CREST; T.K.) and JP18am0101079 (S.I.), JP18am0101070 (M.Y.) (Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery and Life Science Research; Basis for Supporting Innovative Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (BINDS)) and JSPS KAKENHI grant Number 15J00102 (K.M.). The authors acknowledge support from the Toray Science Foundation (T.K.), Takeda Science Foundation (R.S. and T.K.), Naito Foundation (T.K.), and Koyanagi Foundation (T.K.). The synchrotron radiation experiments were performed at BL32XU of SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal No. 2017A2524, 2017B2524, and BINDS0483). We thank the staff members of BL32XU for help with X-ray data collection. DNA sequencing analysis was performed at the Medical Research Support Center, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University. We are grateful to A. Inoue for providing instruction on the TGFα shedding assay, M. Shiroishi for providing instruction on FSEC-TS, D. Im and T. Shimamura (Kyoto University) for providing the plasmid encoding mbIIG2, S. Horita for support for structure refinement, and H. Tsujimoto and M. Sasanuma for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.M. initiated the project; optimized the construct; developed the purification procedure; purified the EP3 protein for crystallization; performed crystallization trials, ligand-binding assay, and TGFα shedding assay; and wrote the manuscript. Y.H. helped with construct optimization. R.S. collected X-ray diffraction data and solved the structure. K.Y. and K.H. helped with data collection. M.Y. oversaw data collection. S.N. helped with interpretation and edited the manuscript. S.I. helped with structure analysis and interpretation and edited the manuscript. T.K. supervised the research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–15, Supplementary Tables 1–2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morimoto, K., Suno, R., Hotta, Y. et al. Crystal structure of the endogenous agonist-bound prostanoid receptor EP3. Nat Chem Biol 15, 8–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0171-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0171-8
This article is cited by
-
Docking for EP4R antagonists active against inflammatory pain
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Structures of human prostaglandin F2α receptor reveal the mechanism of ligand and G protein selectivity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Functional screening and rational design of compounds targeting GPR132 to treat diabetes
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Cryo-EM structure of the human MT1–Gi signaling complex
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2021)