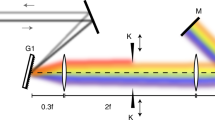
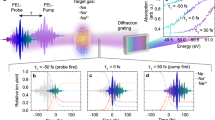
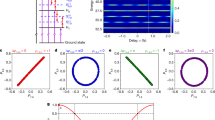
Abstract
Free-electron lasers producing ultrashort pulses with high peak power promise to extend ultrafast non-linear spectroscopic techniques into the extreme-ultraviolet–X-ray regime. Key aspects are the synchronization between pump and probe, and the control of the pulse properties (duration, intensity and coherence). Externally seeded free-electron lasers produce coherent pulses that can be synchronized with femtosecond accuracy. An important goal is to shorten the pulse duration, but the simple approach of shortening the seed is not sufficient because of the finite-gain bandwidth of the conversion process. An alternative is the amplification of a soliton in a multistage, superradiant cascade: here, we demonstrate the generation of few-femtosecond extreme-ultraviolet pulses, whose duration we measure by autocorrelation. We achieve pulses four times shorter, and with a higher peak power, than in the standard high-gain harmonic generation mode and we prove that the pulse duration matches the Fourier transform limit of the spectral intensity distribution.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data are provided with this paper. The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The simulation reported in Fig. 4 was carried out with version 2 and version 4 of the code GENESIS 1.3 available at http://genesis.web.psi.ch and https://github.com/svenreiche/Genesis-1.3-Version4.
References
Schreck, S., Beye, M. & Föhlisch, A. Implications of stimulated resonant X-ray scattering for spectroscopy, imaging, and diffraction in the regime from soft to hard X-rays. J. Mod. Opt. 62, S34–S45 (2015).
Calegari, F. et al. Ultrafast electron dynamics in phenylalanine initiated by attosecond pulses. Science 346, 336–339 (2014).
Berrah, N. A perspective for investigating photo-induced molecular dynamics from within with femtosecond free electron lasers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 19536–19544 (2017).
Rudenko, A. et al. Femtosecond response of polyatomic molecules to ultra-intense hard X-rays. Nature 546, 129–132 (2017).
Bencivenga, F., Capotondi, F., Principi, E., Kiskinova, M. & Masciovecchio, C. Coherent and transient states studied with extreme ultraviolet and X-ray free electron lasers: present and future prospects. Adv. Phys. 63, 327–404 (2015).
Prince, K. C. et al. Coherent control with a short-wavelength free-electron laser. Nat. Photonics 10, 176–179 (2016).
Danailov, M. B. et al. Towards jitter-free pump-probe measurements at seeded free electron laser facilities. Opt. Express 22, 12869–12879 (2014).
Allaria, E. et al. Highly coherent and stable pulses from the FERMI seeded free-electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet. Nat. Photonics 6, 699–704 (2012).
De Ninno, G. et al. Single-shot spectro-temporal characterization of XUV pulses from a seeded free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 6, 8075 (2015).
Gorobtsov, O. Y. et al. Seeded X-ray free-electron laser generating radiation with laser statistical properties. Nat. Commun. 9, 4498 (2018).
Finetti, P. et al. Pulse duration of seeded free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. X 7, 021043 (2017).
Allaria, E. et al. Two-colour pump–probe experiments with a twin-pulse-seed extreme ultraviolet free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 4, 2476 (2013).
McNeil, B. W. J., Thompson, N. R., Dunning, D. J. & Sheehy, B. High harmonic attosecond pulse train amplification in a free electron laser. J. Phys. B 44, 065404 (2011).
Gauthier, D. et al. Chirped pulse amplification in an extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 7, 13688 (2016).
Tanaka, T. & Rebernic Ribič, P. Shortening the pulse duration in seeded free-electron lasers by chirped microbunching. Opt. Express 27, 30875–30892 (2019).
Maroju, P. K. et al. Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser. Nature 578, 386–391 (2020).
Duris, J. et al. Tunable isolated attosecond X-ray pulses with gigawatt peak power from a free-electron laser. Nat. Photonics 14, 30–36 (2020).
Emma, P. et al. Femtosecond and subfemtosecond X-ray pulses from a self-amplified spontaneous-emission based free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 074801 (2004).
Marinelli, A. et al. Optical shaping of X-ray free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 254801 (2016).
Behrens, C. et al. Few-femtosecond time-resolved measurements of X-ray free-electron lasers. Nat. Commun. 5, 3762 (2014).
Ding, Y. et al. Generating femtosecond X-ray pulses using an emittance-spoiling foil in free-electron lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 191104 (2015).
Zholents, A. A. & Penn, G. Obtaining attosecond x-ray pulses using a self-amplified spontaneous emission free electron laser. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 8, 050704 (2005).
Guetg, M. W. et al. Generation of high-power high-intensity short X-ray free-electron-laser pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 014801 (2018).
Ding, Y. et al. Beam shaping to improve the free-electron laser performance at the Linac Coherent Light Source. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 19, 100703 (2016).
Huang, S. et al. Generating single-spike hard X-ray pulses with nonlinear bunch compression in free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 154801 (2017).
Marinelli, A. et al. Experimental demonstration of a single-spike hard-X-ray free-electron laser starting from noise. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 151101 (2017).
Giannessi, L., Musumeci, P. & Spampinati, S. Nonlinear pulse evolution in seeded free-electron laser amplifiers and in free-electron laser cascades. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 043110 (2005).
Bonifacio, R., De Salvo Souza, L., Pierini, P. & Piovella, N. The superradiant regime of a FEL: analytical and numerical results. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 296, 358–367 (1990).
Bonifacio, R., Piovella, N. & McNeil, B. W. J. Superradiant evolution of radiation pulses in a free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. A 44, R3441–R3444 (1991).
Yang, X., Mirian, N. & Giannessi, L. Postsaturation dynamics and superluminal propagation of a superradiant spike in a free-electron laser amplifier. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 010703 (2020).
Watanabe, T. et al. Experimental characterization of superradiance in a single-pass high-gain laser-seeded free-electron laser amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 034802 (2007).
Giannessi, L. et al. High-order-harmonic generation and superradiance in a seeded free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 164801 (2012).
Giannessi, L. et al. Superradiant cascade in a seeded free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 044801 (2013).
Svelto, O. & Hanna, D. C. Principles of Lasers (Springer, 2010).
Allaria, E., Ninno, G. D. & Spezzani, C. Experimental demonstration of frequency pulling in single-pass free-electron lasers. Opt. Express 19, 10619–10624 (2011).
Helml, W. et al. Ultrashort free-electron laser X-ray pulses. Appl. Sci. 7, 915 (2017).
Mitzner, R. et al. Direct autocorrelation of soft-x-ray free-electron-laser pulses by time-resolved two-photon double ionization of He. Phys. Rev. A 80, 025402 (2009).
Svetina, C. et al. The Low Density Matter (LDM) beamline at FERMI: optical layout and first commissioning. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 22, 538–543 (2015).
Zangrando, M. et al. Recent results of PADReS, the Photon Analysis Delivery and REduction System, from the FERMI FEL commissioning and user operations. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 22, 565–570 (2015).
Reiche, S. GENESIS 1.3: a fully 3D time-dependent FEL simulation code. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 429, 243–248 (1999).
Labat, M. et al. Pulse splitting in short wavelength seeded free electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 264801 (2009).
De Ninno, G., Mahieu, B., Allaria, E., Giannessi, L. & Spampinati, S. Chirped seeded free-electron lasers: self-standing light sources for two-color pump-probe experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 064801 (2013).
Mahieu, B. et al. Two-colour generation in a chirped seeded free-electron laser: a close look. Opt. Express 21, 22728–22741 (2013).
Bonifacio, R., Pellegrini, C. & Narducci, L. M. Collective instabilities and high-gain regime in a free electron laser. Opt. Commun. 50, 373–378 (1984).
Allaria, E. et al. Two-stage seeded soft-X-ray free-electron laser. Nat. Photonics 7, 913–918 (2013).
Henke, B. L., Gullikson, E. M. & Davis, J. C. X-ray interactions: photoabsorption, scattering, transmission, and reflection at E = 50–30,000 eV, Z = 1–92. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 54, 181–342 (1993).
Düsterer, S. et al. Development of experimental techniques for the characterization of ultrashort photon pulses of extreme ultraviolet free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 17, 120702 (2014).
Roling, S. & Zacharias, H. in Synchrotron Light Sources and Free-Electron Lasers (eds Jaeschke, E. et al.) 891–925 (Springer, 2014).
Eland, J. H. D. et al. Complete two-electron spectra in double photoionization: the rare gases Ar, Kr, and Xe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 053003 (2003).
Squibb, R. J. et al. Acetylacetone photodynamics at a seeded free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 9, 63 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge S. Reiche for helpful discussions on bandwidth issues in the simulation of a multistage cascade in GENESIS 1.3. We are also grateful to the whole FERMI team for the dedicated work and support during this experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.S.M., S.S. and L.G. conceived the idea of the experiment. C.C. and T.M. conceived the ATI autocorrelation measurement scheme. N.S.M., S.S., E.A., L.B., G.D.N., S.D.M., G.P., P.R., C.S., G.G., M.T., X.Y. and L.G. contributed to the machine operation and tuning for the experiment. S.S., N.S.M. and F.S. simulated the FEL SRC dynamics in the experimental conditions. S.S. and F.S. investigated the energy detuning and the frequency-pulling effect. M.B.D. and A.D. tuned the seed laser for short-pulse operation. N.M., M.M., L.R. and M.Z. designed, aligned and operated the split-and-delay line; O.P., K.C.P., T.M., M.D.F., R.J.S. and C.C. operated the magnetic bottle electron spectrometer, acquired and analysed the cross-correlation data. T.M. and M.D.F. developed the analysis tools used during beam time. N.S.M., C.C., K.C.P. and L.G. wrote the manuscript, which was discussed and agreed by all the coauthors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Photonics thanks Agostino Marinelli and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–4, Discussion and references.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 2
Data file after analysis for Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Data file after analysis for Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Data file after analysis for Fig. 4.
Source Data Fig. 5
Zip file containing 7 + 7 HDF5 datasets of acquisitions of the FEL+linac parameters in SRC and HGHG configurations (Fig. 5a and Fig. 5b). Each file corresponds to a different tuning of the resonance in the final amplifier in the two configurations, SRC (Fig. 5a) and HGHG (Fig. 5b). The spectral raw data, to be averaged to prepare the figures, are in the folder /real time/spectrometer PRESTO/GetSpectrum. Each HDF5 file contains all the linac/undulator/beam data from a machine snapshot taken before the acquisition.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirian, N.S., Di Fraia, M., Spampinati, S. et al. Generation and measurement of intense few-femtosecond superradiant extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses. Nat. Photon. 15, 523–529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00815-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00815-w
This article is cited by
-
Experimental demonstration of attosecond pump–probe spectroscopy with an X-ray free-electron laser
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Full characterization of superradiant pulses generated from a free-electron laser oscillator
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Observation of Rabi dynamics with a short-wavelength free-electron laser
Nature (2022)
-
A step closer to compact X-ray lasers
Nature (2021)