Abstract
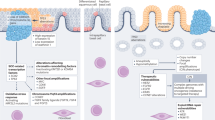
Oesophageal cancer (OC) is an inflammation-associated malignancy linked to gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, obesity and tobacco use. Knowledge of the microenvironment of oesophageal tumours is relevant to our understanding of the development of OC and its biology, and has major implications for understanding the response to standard therapies and immunotherapies, as well as for uncovering novel targets. In this context, we discuss what is known about the TME in OC from tumour initiation to development and progression, and how this is relevant to therapy sensitivity and resistance in the two major types of OC. We provide an immunological characterisation of the OC TME and discuss its prognostic implications with specific comparison with the Immunoscore and immune-hot, -cold, altered-immunosuppressed and -altered-excluded models. Targeted therapeutics for the TME under pre-clinical and clinical investigation in OCs are also summarised. A deeper understanding of the TME will enable the development of combination approaches to concurrently target the tumour cells and TME delivering precision medicine to OC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Then, M., Saleem, S., Gayam, V., Sunkara, T., Culliford, A. & Gaduputi, V. E. O. L. Esophageal cancer: an updated surveillance epidemiology and end results database analysis. World J. Oncol. 11, 55–64 (2020).
Morgan, E., Soerjomataram, I., Gavin, A. T., Rutherford, M. J., Gatenby, P., Bardot, A. et al. International trends in oesophageal cancer survival by histological subtype between 1995 and 2014. Gut 70, 234–232 (2021).
Pennathur, M. K., Jobe, B. A. & Luketich, J. D. A. G. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 381, 400–412 (2013).
Napier, K. J., Scheerer, M. & Misra, S. Esophageal cancer: a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest. Oncol. 6, 112–120 (2014).
Hvid-Jensen, F., Pedersen, L., Drewes, A. M., Sørensen, H. T. & Funch-Jensen, P. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett’s esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 1375–1383 (2011).
Quail, D. F. & Joyce, J. A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 19, 1423–1437 (2013).
Quail, D. F. & Joyce, J. A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 19, 1423–1437 (2013).
Qian, X., Tan, C., Wang, F., Yang, B., Ge, Y., Guan, Z. et al. Esophageal cancer stem cells and implications for future therapeutics. Onco. Targets Ther. 19, 2247–2254 (2016).
Makena, M. R., Ranjan, A., Thirumala, V. & Reddy, A. P. Cancer stem cells: road to therapeutic resistance and strategies to overcome resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol Basis Dis. 4, 1866–165339 (2020).
Lin, E. W., Karakasheva, T. A., Hicks, P. D., Bass, A. J. & Rustgi, A. K. The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. Oncogene 35, 5337–5349 (2016).
Smyth, M. J., Ngiow, S. F., Ribas, A. & Teng, M. W. L. Combination cancer immunotherapies tailored to the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 13, 143–158 (2016).
Hanahan, D., Weinberg, R. A., Adams, J. M., Cory, S., Aguirre-Ghiso, J. A., Ahmed, Z. et al. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011).
Pienta, K. J., Robertson, B. A., Coffey, D. S. & Taichman, R. S. The cancer diaspora: metastasis beyond the seed and soil hypothesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 5849–5855 (2013).
Baba, Y., Nomoto, D., Okadome, K., Ishimoto, T., Iwatsuki, M., Miyamoto, Y. et al. Tumor immune microenvironment and immune checkpoint inhibitors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 111, 3132–3141 (2020).
Lin, E. W., Karakasheva, T. A., Hicks, P. D., Bass, A. J. & Rustgi, A. K. The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. Oncogene 35, 5337–5349 (2016).
Hatogai, K., Kitano, S., Fujii, S., Kojima, T., Daiko, H., Nomura, S. et al. Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of tumor microenvironment immune status in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7, 47252–47264 (2016).
Calibasi Kocal, G., Güven, S., Foygel, K., Goldman, A., Chen, P., Sengupta, S. et al. Dynamic microenvironment induces phenotypic plasticity of esophageal cancer cells under flow. Sci. Rep. 6, 38221 (2016).
Nouraee, N., Khazaei, S., Vasei, M., Razavipour, S. F., Sadeghizadeh, M. & Mowla, S. J. MicroRNAs contribution in tumor microenvironment of esophageal cancer. Cancer Biomarkers 16, 367–376 (2016).
Network the cancer genome atlas research. Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma. Nature 541, 169–175 (2017).
Verbeek, R. E., Spittuler, L. F., Peute, A., van Oijen, M. G. H., ten Kate, F. J., Vermeijden, J. R. et al. Familial clustering of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma in a European cohort. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 1656–1663 (2014).
O’Sullivan, J., Lysaght, J., Donohoe, C. L. & Reynolds, J. V. Obesity and gastrointestinal cancer: the interrelationship of adipose and tumour microenvironments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 699–714 (2018).
Picardo, S. L., Maher, S. G., O’Sullivan, J. N. & Reynolds, J. V. Barrett’s to oesophageal cancer sequence: a model of inflammatory-driven upper gastrointestinal cancer. Dig. Surg. 29, 251–260 (2012).
Fitzgerald, R. C., Onwuegbusi, B. A., Bajaj-Elliott, M., Saeed, I. T., Burnham, W. R. & Farthing, M. J. G. Diversity in the oesophageal phenotypic response to gastro-oesophageal reflux: immunological determinants. Gut 50, 451–459 (2002).
Kavanagh, M. E., Conroy, M. J., Clarke, N. E., Gilmartin, N. T., O’Sullivan, K. E., Feighery, R. et al. Impact of the inflammatory microenvironment on T-cell phenotype in the progression from reflux oesophagitis to Barrett oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 370, 117–124 (2016).
Miyashita, T., Tajima, H., Shah, F. A., Oshima, M., Makino, I., Nakagawara, H. et al. Impact of inflammation-metaplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence and inflammatory microenvironment in esophageal carcinogenesis using surgical rat models. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 21, 2012–2019 (2014).
Gao, J., Wu, Y., Su, Z., Amoah Barnie, P., Jiao, Z., Bie, Q. et al. Infiltration of alternatively activated macrophages in cancer tissue is associated with MDSC and Th2 polarization in patients with esophageal cancer. PLoS ONE 9, 104453–104453 (2014).
Song, S., Guha, S., Liu, K., Buttar, N. S. & Bresalier, R. S. COX-2 induction by unconjugated bile acids involves reactive oxygen species-mediated signalling pathways in Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 56, 1512–1521 (2007).
Fischer, K., Hoffmann, P., Voelkl, S., Meidenbauer, N., Ammer, J., Edinger, M. et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells. Blood 109, 3812–3819 (2007).
Lauby-Secretan, C., Loomis, D., Grosse, Y., Bianchini, F. & Straif, K. B. S. Body fatness and cancer—viewpoint of the IARC working group. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 794–798 (2016).
Michelet, X., Dyck, L., Hogan, A., Loftus, R. M., Duquette, D., Wei, K. et al. Metabolic reprogramming of natural killer cells in obesity limits antitumor responses. Nat. Immunol. 19, 1330–1340 (2018).
El-Serag, H. B., Ergun, G. A., Pandolfino, J., Fitzgerald, S., Tran, T. & Kramer, J. R. Obesity increases oesophageal acid exposure. Gut 56, 749–755 (2007).
Reilly, S. M. & Saltiel, A. R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 633–643 (2017).
Andersen, K. E. & Fernandez, M. L. C. J. M. Impact of obesity and metabolic syndrome on immunity. Adv. Nutr. 7, 66–75 (2016).
Duggan, C., Onstad, L., Hardikar, S., Blount, P. L., Reid, B. J. & Vaughan, T. L. Association between markers of obesity and progression from Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 934–943 (2013).
Howard, J. M., Beddy, P., Ennis, D., Keogan, M., Pidgeon, G. P. & Reynolds, J. V. Associations between leptin and adiponectin receptor upregulation, visceral obesity and tumour stage in oesophageal and junctional adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 97, 1020–1027 (2010).
Shurin, R. & Umansky, M. V. The Tumor Immunoenvironment, 94–95 (2013).
Broders-Bondon, F., Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires, T. H., Fernandez-Sanchez, M.-E. & Farge, E. Mechanotransduction in tumor progression: the dark side of the force. J Cell Biol. 217, 1571–1587 (2018).
Martinez, V. G., Park, D. & Acton, S. E. Immunotherapy: breaching the barriers for cancer treatment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 374, 1–7 (2019).
Gordon-Alonso, M., Hirsch, T., Wildmann, C. & van der Bruggen, P. Galectin-3 captures interferon-gamma in the tumor matrix reducing chemokine gradient production and T-cell tumor infiltration. Nat. Commun. 8, 793 (2017).
Davern, M. & Lysaght, J. Cooperation between chemotherapy and immunotherapy in gastroesophageal cancers. Cancer Lett. 495, 89–99 (2020).
Dhupar, R., Van Der Kraak, L., Pennathur, A., Schuchert, M. J., Nason, K. S., Luketich, J. D. et al. Targeting immune checkpoints in esophageal cancer: a high mutational load tumor. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 103, 1340–1349 (2017).
Turley, S. J., Cremasco, V. & Astarita, J. L. Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 15, 669–682 (2015).
Feig, C., Jones, J. O., Kraman, M., Wells, R. J. B., Deonarine, A., Chan, D. S. et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 20212–20217 (2013).
Wang, J., Zhang, G., Wang, J., Wang, L., Huang, X. & Cheng, Y. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in esophageal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 14, 30 (2016).
Sun, X., Cheng, G., Hao, M., Zheng, J., Zhou, X., Zhang, J. et al. CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 709–722 (2010).
Underwood, T. J., Hayden, A. L., Derouet, M., Garcia, E., Noble, F., White, M. J. et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts predict poor outcome and promote periostin-dependent invasion in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 235, 466–477 (2015).
Koide, A., Sato, T., Sugiyama, A. & Miyagawa, S. N. N. Significance of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 expression and macrophage infiltration in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 99, 1667–1674 (2004).
Hao N.-B., Lü M.-H., Fan Y.-H., Cao Y.-L., Zhang Z.-R. & Yang S.-M. Macrophages in tumor microenvironments and the progression of tumors. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 948098 (2012).
Chen, M.-F., Kuan, F.-C., Yen, T.-C., Lu, M.-S., Lin, P.-Y., Chung, Y.-H. et al. IL-6-stimulated CD11b+ CD14+ HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells, are associated with progression and poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncotarget. 5, 8716–8728 (2014).
Li, H., Han, Y., Guo, Q., Zhang, M. & Cao, X. Cancer-expanded myeloid-derived suppressor cells induce anergy of NK cells through membrane-bound TGF-beta 1. J. Immunol. 182, 240–249 (2009).
Waldron, T. J., Quatromoni, J. G., Karakasheva, T. A., Singhal, S. & Rustgi, A. K. Myeloid derived suppressor cells: targets for therapy. Oncoimmunology. 2, 24117 (2013).
Hashemi Goradel, N., Najafi, M., Salehi, E., Farhood, B. & Mortezaee, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: a review. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 5683–5699 (2019).
Sharma, S., Stolina, M., Yang, S.-C., Baratelli, F., Lin, J. F., Atianzar, K. et al. Tumor cyclooxygenase 2-dependent suppression of dendritic cell function. Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 961–968 (2003).
Morris, C. D., Armstrong, G. R., Bigley, G., Green, H. & Attwood, S. E. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in the Barrett’s metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96, 990–996 (2001).
Zhi, H., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Zhou, C., Ding, F., Luo, A. et al. Significance of COX-2 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 27, 1214–1221 (2006).
Jablonska-Trypuc, M. & Rosochacki, S. A. M. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 31, 177–183 (2016).
Fong, S. F., Dietzsch, E., Fong, K. S., Hollosi, P., Asuncion, L., He, Q. et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 expression is increased in colon and esophageal tumors and associated with less differentiated colon tumors. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 46, 644–655 (2007).
Gu, Z. D., Li, J. Y., Li, M., Gu, J., Shi, X. T., Ke, Y. et al. Matrix metalloproteinases expression correlates with survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 100, 1835–1843 (2005).
Singer, K., Cheng, W.-C., Kreutz, M., Ho, P.-C. & Siska, P. J. Immunometabolism in cancer at a glance. Dis Model Mech. 11, dmm034272 (2018).
Krock, B. L., Skuli, N. & Simon, M. C. Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: good and evil. Genes Cancer. 2, 1117–1133 (2011).
Albini, A., Bruno, A., Noonan, D. M. & Mortara, L. Contribution to tumor angiogenesis from innate immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: Implications for Immunotherapy. Front. Imunnol. 9, 527 (2018).
Lin, Q. & Yun, Z. Impact of the hypoxic tumor microenvironment on the regulation of cancer stem cell characteristics. Cancer Biol. Ther. 9, 949–956 (2010).
Ippolito, L., Morandi, A., Giannoni, E. & Chiarugi, P. Lactate: a metabolic driver in the tumour landscape. Trends Biochem. Sci. 44, 153–166 (2019).
Damgaci, S., Ibrahim-Hashim, A., Enriquez-Navas, P. M., Pilon-Thomas, S., Guvenis, A. & Gillies, R. J. Hypoxia and acidosis: immune suppressors and therapeutic targets. Immunology 154, 354–362 (2018).
Jain, R. K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307, 58–62 (2005).
Tang, N. N., Zhu, H., Zhang, H. J., Zhang, W. F., Jin, H. L., Wang, L. et al. HIF-1α induces VE-cadherin expression and modulates vasculogenic mimicry in esophageal carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol 20, 17894–17904 (2014).
Gebauer, F., Krämer, M., Bruns, C., Schlößer, H. A., Thelen, M., Lohneis, P. et al. Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG3) mRNA and protein expression on tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 146, 2319–2327 (2020).
Wang, W., Chen, D., Zhao, Y., Zhao, T., Wen, J., Mao, Y. et al. Characterization of LAG-3, CTLA-4, and CD8+ TIL density and their joint influence on the prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 7, 776 (2019).
Zhao, Y., Chen, D., Wang, W., Zhao, T., Wen, J., Zhang, F. et al. Significance of TIM-3 expression in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 109, 1551–1557 (2020).
Ohigashi, Y., Sho, M., Yamada, Y., Tsurui, Y., Hamada, K., Ikeda, N. et al. Clinical Significance of Programmed Death-1 Ligand-1 and Programmed Death-1 Ligand-2 Expression in Human Esophageal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 2947–2953 (2005).
Chen, H., Lu, M., Xu, B., Wang, Q., Jiang, J. & Wu, C. L. D. B7-H1 expression associates with tumor invasion and predicts patient’s survival in human esophageal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 7, 6015–6023 (2014).
Derks, S., Nason, K. S., Liao, X., Stachler, M. D., Liu, K. X., Liu, J. B. et al. Epithelial PD-L2 expression marks barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. Immunol Res. 3, 1123–1129 (2015).
Loke, J. P. P. A. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially regulated by Th1 and Th2 cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5336–5341 (2003).
MacCarty. Principles of prognosis in cancer. JAMA. 96, 30–33 (1931).
Galon, J., Costes, A., Sanchez-Cabo, F., Kirilovsky, A., Mlecnik, B., Lagorce-Pagès, C. et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 313, 1960–1964 (2006).
Angell, H. K., Bruni, D., Barrett, J. C., Herbst, R. & Galon, J. The immunoscore: colon cancer and beyond. Clin. Cancer Res. 26, 332–339 (2020).
Pagès, F., Mlecnik, B., Marliot, F., Bindea, G., Ou, F.-S., Bifulco, C. et al. International validation of the consensus Immunoscore for the classification of colon cancer: a prognostic and accuracy study. Lancet 391, 2128–2139 (2018).
Stein, A. V., Dislich, B., Blank, A., Guldener, L., Kröll, D., Seiler, C. A. et al. High intratumoural but not peritumoural inflammatory host response is associated with better prognosis in primary resected oesophageal adenocarcinomas. Pathology 49, 30–37 (2017).
Noble, F., Mellows, T., McCormick Matthews, L. H., Bateman, A. C., Harris, S., Underwood, T. J. et al. Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with improved survival in patients with oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 65, 651–662 (2016).
Matthews, L. M., Noble, F., Tod, J., Jaynes, E., Harris, S., Primrose, J. N. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of immunohistochemical prognostic biomarkers in resected oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 113, 107–118 (2015).
Humphries, M. P., Craig, S. G., Kacprzyk, R., Fisher, N. C., Bingham, V., McQuaid, S. et al. The adaptive immune and immune checkpoint landscape of neoadjuvant treated esophageal adenocarcinoma using digital pathology quantitation. BMC Cancer 20, 500 (2020).
Yoshioka, T., Miyamoto, M., Cho, Y., Ishikawa, K., Tsuchikawa, T., Kadoya, M. et al. Infiltrating regulatory T cell numbers is not a factor to predict patient’s survival in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 98, 1258–1263 (2008).
Schumacher, K., Haensch, W., Röefzaad, C. & Schlag, P. M. Prognostic significance of activated CD8(+) T cell infiltrations within esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 61, 3932–3936 (2001).
Shang, B., Liu, Y., Jiang, S. & Liu, Y. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5, 15179 (2015).
Dunne, M. R., Michielsen, A. J., O’Sullivan, K. E., Cathcart, M. C., Feighery, R., Doyle, B. et al. HLA-DR expression in tumor epithelium is an independent prognostic indicator in esophageal adenocarcinoma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 66, 841–850 (2017).
Altomonte, M., Fonsatti, E., Visintin, A. & Maio, M. Targeted therapy of solid malignancies via HLA class II antigens: a new biotherapeutic approach? Oncogene. 22, 6564–6569 (2003).
Dunne, M. R., Phelan, J. J., Michielsen, A. J., Maguire, A. A., Dunne, C., Martin, P. et al. Characterising the prognostic potential of HLA-DR during colorectal cancer development. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 69, 1577–1588 (2020).
Vonderheide, R. H. The immune revolution: a case for priming, not checkpoint. Cancer Cell 33, 563–569 (2018).
Yagi, T., Baba, Y., Okadome, K., Kiyozumi, Y., Hiyoshi, Y., Ishimoto, T. et al. Tumour-associated macrophages are associated with poor prognosis and programmed death ligand 1 expression in oesophageal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 111, 38–49 (2019).
Shigeoka, M., Urakawa, N., Nakamura, T., Nishio, M., Watajima, T., Kuroda, D. et al. Tumor associated macrophage expressing CD204 is associated with tumor aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104, 1112–1119 (2013).
Chen, M. F., Chen, P. T., Lu, M. S., Lin, P. Y., Chen, W. C. & Lee, K. D. IL-6 expression predicts treatment response and outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Mol. Cancer 12, 26 (2013).
Chai, D., Bao, Z., Hu, J., Ma, L., Feng, Z. & Tao, Y. Vasculogenic mimicry and aberrant expression of HIF-lα/E-cad are associated with worse prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Medical Sci. 33, 385–391 (2013).
Hu, Z., Yang, Y., Zhao, Y. & Huang, Y. The prognostic value of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in patients with esophageal cancer: evidence from a meta-analysis. Onco. Targets Ther. 10, 2893–2901 (2017).
Camus, M., Tosolini, M., Mlecnik, B., Pages, F., Kirilovsky, A., Berger, A. et al. Coordination of intratumoral immune reaction and human colorectal cancer recurrence. Cancer Res. 69, 2685–2693 (2009).
Derks, S., de Klerk, L. K., Xu, X., Fleitas, T., Liu, K. X., Liu, Y. et al. Characterizing diversity in the tumor-immune microenvironment of distinct subclasses of gastroesophageal adenocarcinomas. Ann Oncol. 31, 1011–1020 (2020).
Chen, M., Cai, E., Huang, J., Yu, P. & Li, K. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 21, 1126–1134 (2012).
Clarke, J. M. & Hurwitz, H. I. Understanding and targeting resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. J. Gastrointest Oncol. 4, 253–263 (2013).
Qian, C.-N., Tan, M.-H., Yang, J.-P. & Cao, Y. Revisiting tumor angiogenesis: vessel co-option, vessel remodeling, and cancer cell-derived vasculature formation. Chin J Cancer 35, 10 (2016).
Kim, R., Emi, M., Tanabe, K. & Arihiro, K. Tumor-driven evolution of immunosuppressive networks during malignant progression. Cancer Res. 66, 5527–5536 (2006).
Lapeyre-Prost, A., Terme, M., Pernot, S., Pointet, A.-L., Voron, T., Tartour, E. et al. Chapter seven—immunomodulatory activity of VEGF in cancer. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 330, 295–342 (2017).
Lloyd, B. W. S. C. Current strategies in chemoradiation for esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest. Oncol. 5, 156–165 (2014).
Donlon, N. E., Elliott, J. A., Donohoe, C. L., Murphy, C. F., Nugent, T., Moran, B. et al. Adverse biology in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction impacts survival and response to neoadjuvant therapy independent of anatomic subtype. Ann. Surg. 272, 814–819 (2020).
Gabitass, R. F., Annels, N. E., Stocken, D. D., Pandha, H. A. & Middleton, G. W. Elevated myeloid-derived suppressor cells in pancreatic, esophageal and gastric cancer are an independent prognostic factor and are associated with significant elevation of the Th2 cytokine interleukin-13. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 60, 1419–1430 (2011).
Akutsu, Y., Hanari, N., Yusup, G., Komatsu-Akimoto, A., Ikeda, N., Mori, M. et al. COX2 expression predicts resistance to chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 18, 2946–2951 (2011).
Vacchelli, E., Semeraro, M., Enot, D. P., Chaba, K., Colame, V. P., Dartigues, P. et al. Negative prognostic impact of regulatory T cell infiltration in surgically resected esophageal cancer post-radiochemotherapy. Oncotarget 6, 20840–20850 (2015).
Gray, L. H., Conger, A., Ebert, M., Hornsey, S. & Scott, O. C. A. The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 26, 638–648 (1953).
Tao, R., Ager, B., Lloyd, S., Torgeson, A., Denney, M., Gaffney, D. et al. Hypoxia imaging in upper gastrointestinal tumors and application to radiation therapy. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 9, 1044–1053 (2018).
Melsens, E., De Vlieghere, E., Descamps, B., Vanhove, C., Kersemans, K., De Vos, F. et al. Hypoxia imaging with 18F-FAZA PET/CT predicts radiotherapy response in esophageal adenocarcinoma xenografts. Radiat Oncol. 13, 39 (2018).
Peerlings, J., Van De Voorde, L., Mitea, C., Larue, Ruben, Yaromina, A., Sandeleanu, S. et al. Hypoxia response-associated molecular markers in esophageal cancer: A systematic review. Methods 130, 51–62 (2017).
National cancer institute. Trastuzumab—National Cancer Institute, https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/trastuzumab (2016).
Fuchs, C. S., Doi, T., Jang, R. W.-J., Muro, K., Satoh, T., Machado, M. et al. KEYNOTE-059 cohort 1: Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab (pembro) monotherapy in patients with previously treated advanced gastric cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 4003 (2017).
Bersanelli, M. Tumour mutational burden as a driver for treatment choice in resistant tumours (and beyond). Lancet Oncol. 21, 1255–1257 (2020).
Bang, Y. J., Van Cutsem, E., Feyereislova, A., Chung, H. C., Shen, L., Sawaki, A. et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376, 687–697 (2010).
National cancer institute. FDA Approval for Ramucirumab—National Cancer Institute, https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/fda-ramucirumab (2015).
Van Cutsem, E., Bang, Y.-J., Feng-yi, F., Xu, J. M., Lee, K.-W., Jiao, S.-C. et al. HER2 screening data from ToGA: targeting HER2 in gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Gastric Cancer 18, 476–484 (2015).
Wilke, H., Muro, K., Van Cutsem, E., Oh, S. C., Bodoky, G., Shimada, Y. et al. Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15, 1224–1235 (2014).
Kato, K., Cho, B. C., Takahashi, M., Okada, M., Lin, C. Y., Chin, K. et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20, 1506–1517 (2019).
Kato, K., Cho, B. C., Takahashi, M., Okada, M., Lin, C.-Y., Chin, K. et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20, 1506–1517 (2019).
Alexandrov, L. B., Nik-Zainal, S., Wedge, D. C., Aparicio, S. A., Behjati, S., Biankin, A. V. et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 500, 415–421 (2013).
Samstein, R. M., Lee, C. H., Shoushtari, A. N., Hellmann, M. D., Shen, R., Janjigian, Y. Y. et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat Genet. 51, 202–206 (2019).
Zeng, D., Li, M., Zhou, R., Zhang, J., Sun, H., Shi, M. et al. Tumor microenvironment characterization in gastric cancer identifies prognostic and immunotherapeutically relevant gene signatures. Cancer Immunol. Res. 7, 737–750 (2019).
Forde, P. M., Chaft, J. E., Smith, K. N., Anagnostou, V., Cottrell, T. R., Hellmann, M. D. et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 1976–1986 (2018).
Tauriello, D. V. F., Palomo-Ponce, S., Stork, D., Berenguer-Llergo, A., Badia-Ramentol, J., Iglesias, M. et al. TGFβ drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis. Nature 554, 538–543 (2018).
Woo, J., Cohen, S. A. & Grim, J. E. Targeted therapy in gastroesophageal cancers: past, present and future. Gastroenterol. Rep. 3, 316–329 (2015).
Derks, S., Liao, X., Chiaravalli, A. M., Xu, X., Camargo, M. C., Solcia, E. et al. Abundant PD-L1 expression in Epstein-Barr Virus-infected gastric cancers. Oncotarget 7, 32925–32932 (2016).
Kim, S. T., Cristescu, R., Bass, A. J., Kim, K.-M., Odegaard, J. I., Kim, K. et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat Med. 24, 1449–1458 (2018).
Thorsson, V., Gibbs, D. L., Brown, S. D., Wolf, D., Bortone, D. S., Ou Yang, T.-H. et al. The immune landscape of cancer. Immunity 48, 812–830 (2018).
Frankell, A. M., Jammula, S., Li, X., Contino, G., Killcoyne, S., Abbas, S. et al. The landscape of selection in 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas defines genomic biomarkers for the clinic. Nat. Genet. 51, 506–516 (2019).
Adler, F. R. & Gordon, D. M. Cancer ecology and evolution: positive interactions and system vulnerability. Curr Opin. Syst. Biol. 17, 1–7 (2019).
Hellmann, M. D., Friedman, C. F. & Wolchok, J. D. Chapter six—combinatorial cancer immunotherapies. Adv. Immunol. 130, 251–277 (2016).
Kershaw, M. H., Devaud, C., John, L. B., Westwood, J. A. & Darcy, P. K. Enhancing immunotherapy using chemotherapy and radiation to modify the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2, 25962 (2013).
Christensen, S., Van der Roest, B., Besselink, N., Janssen, R., Boymans, S., Martens, J. W. M. et al. 5-Fluorouracil treatment induces characteristic T>G mutations in human cancer. Nat. Commun. 10, 4571 (2019).
Galon, J. & Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 18, 197–218 (2019).
Nagarsheth, N., Wicha, M. S. & Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 559–572 (2017).
van der Woude, L. L., Gorris, M. A. J., Halilovic, A., Figdor, C. G. & de Vries, I. J. M. Migrating into the tumor: a roadmap for T cells. Trends in Cancer 3, 797–808 (2017).
Galon, J. & Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 18, 197–218 (2019).
Gockel, I., Schimanski, C.C., Heinrich, C., Wehler, T., Frerichs, C., Drescher, D. et al. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in esophageal squamous cell and adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 6, 290 (2006).
Lu, C. L., Guo, J., Gu, J., Ge, D., Hou, Y. Y., Lin, Z. W. et al. CXCR4 heterogeneous expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer and stronger metastatic potential with CXCR4-positive cancer cells. Dis. Esophagus 27, 294–302 (2013).
HHuang, E. H., Singh, B., Cristofanilli, M., Gelovani, J., Wei, C., Vincent, L. et al. A CXCR4 antagonist CTCE-9908 inhibits primary tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. J. Surg. Res. 155, 231–236 (2009).
Wong, P., Korz, W. & Chinni, S. R. D. K. Targeting CXCR4 with CTCE-9908 inhibits prostate tumor metastasis. BMC Urol. 14, 12 (2014).
Karakasheva, T. A., Waldron, T. J., Eruslanov, E., Kim, S.-B., Lee, J.-S, O'Brien, S. et al. CD38-Expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote tumor growth in a murine model of esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 75, 4074–4085 (2015).
Lokhorst, H. M., Plesner, T., Laubach, J. P., Nahi, H., Gimsing, P., Hansson, M. et al. Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 1207–1219 (2015).
Joller, E., Lozano, E., Burkett, P. R., Patel, B., Xiao, S., Zhu, C. et al. Treg cells expressing the coinhibitory molecule TIGIT selectively inhibit proinflammatory Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Immunity 40, 569–581 (2014).
Tian, L., Goldstein, A., Wang, H., Lo, H. C., Kim, I. S., Welte, T. et al. Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming. Nature 544, 250–254 (2017).
Zhu, H., Yang, X., Ding, Y., Liu, J., Lu, J., Zhan, L. et al. Recombinant human endostatin enhances the radioresponse in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by normalizing tumor vasculature and reducing hypoxia. Sci. Rep. 5, 14503 (2015).
Lv, J., Li, T., Deng, X., Li, F., Song, Y., Li, C. et al. Randomized phase II study of recombinant human endostatin combined with definitive chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 4035 (2015).
O’Sullivan, K. E., Michielsen, A. J., O’Regan, E., Cathcart, M. C., Moore, G., Breen, E. et al. pSTAT3 Levels have divergent expression patterns and associations with survival in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1720 (2018).
Zhang, S., Zhang, X.-Q., Ding, X.-W., Yang, R.-K., Huang, S.-L., Kastelein, F. et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors use is associated with reduced risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: a meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 110, 2378–2388 (2014).
Li, G., Yang, T. & Yan, J. Cyclooxygenase-2 increased the angiogenic and metastatic potential of tumor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299, 886–890 (2002).
Bardou, A. N., Ghosn, J., Hudson, M. & Rahme, E. M. B. Effect of chronic intake of NSAIDs and cyclooxygenase 2-selective inhibitors on esophageal cancer incidence. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 880–887 (2004).
O’Sullivan, J., Lysaght, J., Donohoe, C. L. & Reynolds, J. V. Obesity and gastrointestinal cancer: the interrelationship of adipose and tumour microenvironments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 699–714 (2018).
Vijayaraghavan, S., Moulder, S., Keyomarsi, K. & Layman, R. M. Inhibiting CDK in cancer therapy: current evidence and future directions. Target Oncol. 13, 21–38 (2018).
Chen, L. & Pan, J. Dual cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition by PD-0332991 induces apoptosis and senescence in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 174, 2427–2443 (2017).
Galon, J., Angell, H. K., Bedognetti, D. & Marincola, F. M. The continuum of cancer immunosurveillance: prognostic, predictive, and mechanistic signatures. Immunity 39, 11–26 (2013).
Mongan, A. M., Lynam-Lennon, N., Doyle, S. L., Casey, R., Carr, E., Cannon, A. et al. Visceral adipose tissue modulates radiosensitivity in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 16, 519–528 (2019).
Maley, C. C., Aktipis, A., Graham, T. A., Sottoriva, A., Boddy, A. M., Janiszewska, M. et al. Classifying the evolutionary and ecological features of neoplasms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 605–619 (2017).
Gatenbee, C. D., Minor, E. S., Slebos, R. J. C., Chung, C. H. & Anderson, A. R. A. Histoecology: applying ecological principles and approaches to describe and predict tumor ecosystem dynamics across space and time. Cancer Control. 27, 1073274820946804–1073274820946804 (2020).
Korolev, K. S., Xavier, J. B. & Gore, J. Turning ecology and evolution against cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 371–380 (2014).
Peters, M. K., Classen, A., Müller, J. & Steffan-Dewenter, I. Increasing the phylogenetic coverage for understanding broad-scale diversity gradients. Oecologia 192, 629–639 (2020).
Zheng, Y., Li, Y., Lian, J., Yang, H., Li, F., Zhao, S. et al. TNF-α-induced Tim-3 expression marks the dysfunction of infiltrating natural killer cells in human esophageal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 17, 165 (2019).
Kavanagh, M. E., Conroy, M. J., Clarke, N. E., Gilmartin, N. T., Feighery, R., MacCarthy, F. et al. Altered T cell migratory capacity in the progression from Barrett oesophagus to oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Microenviron. 12, 57–66 (2019).
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.V.R. proposed the review topic and coordinated the review. M.D., N.E.D. and M.R.D. contributed equally to manuscript preparation and all researched and wrote sections of the review. R.P., C.H. and R.K. researched literature and contributed to writing of manuscript. M.D., N.E.D. and R.P. constructed the tables. C.H. designed figures for the manuscript. All authors provided feedback on the entire review and approved submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Funding information
No funding.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davern, M., Donlon, N.E., Power, R. et al. The tumour immune microenvironment in oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer 125, 479–494 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01331-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01331-y
This article is cited by
-
Visceral adipose tissue secretome from early and late-stage oesophageal cancer patients differentially affects effector and regulatory T cells
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Nutrient deprivation and hypoxia alter T cell immune checkpoint expression: potential impact for immunotherapy
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
PD-1 blockade enhances chemotherapy toxicity in oesophageal adenocarcinoma
Scientific Reports (2022)