Abstract
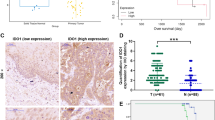
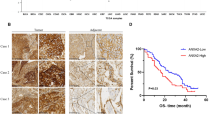
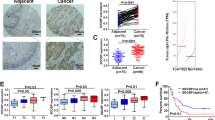
Many reports have described DGKα as an oncogene, hence, we investigated its function and the underlying mechanisms in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression. This study demonstrated that DGKα was upregulated by inflammatory stimulants and formed feedforward loop with Akt/NF-κB signaling in ESCC cells. Mechanistically, DGKα-activated Akt/NF-κB signaling via stimulating PA production to reduce cAMP level and PTEN activity, and specifically, independently of its kinase function, through direct interaction with the FERM domain of FAK to relieve the auto-inhibitory effect of FERM domain on FAK. Overexpression of DGKα promoted cancer malignant progression both in vitro and in vivo, whereas depletion of DGKα suppressed these effects. Importantly, DGKα expression was tightly correlated with the malignancy of various inflammation-related squamous carcinomas and the oncogenic Akt/NF-κB activity. Therefore, DGKα is critically involved in inflammation-mediated ESCC progression, supporting DGKα as a potential target for ESCC therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luzzato L, Pandolfi PP. Causality and chance in the development of cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:84–88.
Chechlinska M, Kowalewska M, Nowak R. Systemic inflammation as a confounding factor in cancer biomarker discovery and validation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:2–3.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin C, Flavell RA. Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:759–71.
Wang F, Arun P, Friedman J, Chen Z, Van Waes C. Current and potential inflammation targeted therapies in head and neck cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:389–95.
Li Y, Li J, Luo M, Zhou C, Shi X, Yang W, et al. Novel noncoding RNA NMR promotes tumor progression via NSUN2 and BPTF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2018;430:57–66.
Song L, Gong H, Lin C, Wang C, Liu L, Wu J, et al. Flotillin-1 promotes tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor signaling and activation of NF-κB in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:995–1005. e1012
Merida I, Avila-Flores A, Merino E. Diacylglycerol kinases: at the hub of cell signalling. Biochem J. 2008;409:1–18.
Martinez K, Shyamasundar S, Kennedy A, Chuang CC, Marsh A, Kincaid J, et al. Diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor R59022 attenuates conjugated linoleic acid-mediated inflammation in human adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:662–70.
Okada M, Hozumi Y, Iwazaki K, Misaki K, Yanagida M, Araki Y, et al. DGKζ is involved in LPS-activated phagocytosis through IQGAP1/Rac1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420:479–84.
Takeishi K, Taketomi A, Shirabe K, Toshima T, Motomura T, Ikegai T, et al. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activation of Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. J Hepatol. 2012;57:77–83.
Torres-Ayuso P, Daza-Martin M, Martin-Perez J, Avila-Flores A, Merida I. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha promotes 3D cancer cell growth and limits drug sensitivity through functional interaction with Src. Oncotarget. 2014;5:9710–26.
Dominguez CL, Floyd DH, Xiao A, Mullins GR, Kefas BA, Xin W, et al. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha is a critical signaling node and novel therapeutic target in glioblastoma and other cancers. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:782–97.
Dan HC, Cooper MJ, Cogswell PC, Duncan JA, Ting JP, Baldwin AS. Akt-dependent regulation of NF-κB is controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1490–1500.
Wu DW, Lee MC, Hsu NY, Wu TC, Wu JY, Wang YC, et al. FHIT loss confers cisplatin resistance in lung cancer via the AKT/NF-κB/Slug-mediated PUMA reduction. Oncogene . 2015;34:3882–3.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:489–501.
Chen J, Lan T, Zhang W, Dong L, Kang N, Zhang S, et al. Platelet-activating factor receptor-mediated PI3K/AKT activation contributes to the malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2015;34:5114–27.
Castellano E, Sheridan C, Thin MZ, Nye E, Spencer-Dene B, Diefenbacher ME, et al. Requirement for interaction of PI3-kinasep110α with RAS in lung tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:617–30.
Hu P, Margolis B, Skolnik EY, Lammers R, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:981–90.
Hellyer NJ, Cheng K, Koland JG. ErbB3 (HER3) interaction with the p85 regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1998;333:757–63.
Zhou H, Liu W, Su Y, Wei Z, Liu J, Kolluri SK, et al. NSAID sulindac and its analog bind RXRα and inhibit RXRα-dependent AKT signaling. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:560–73.
Balkwill F. TNF-α in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastas-Rev. 2006;25:409–16.
Voronov E, Shouval DS, Krelin Y, Cagnano E, Benharroch D, Iwakura Y, et al. IL-1 is required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2645–50.
Chen MF, Lu MS, Chen PT, Chen WC, Lin PY, Lee KD. Role of interleukin 1 beta in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med. 2012;90:89–100.
Guo W, Wang N, Li Y, Zhang JH. Polymorphisms in tumor necrosis factor genes and susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma in a population of high incidence region of North China. Chin Med J. 2005;118:1870–8.
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD. Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:56–68.
Xia H, Nho RS, Kahm J, Kleidon J, Henke CA. Focal adhesion kinase is upstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt in regulating fibroblast survival in response to contraction of type I collagen matrices via a beta 1 integrin viability signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33024–34.
Poullet P, Gautreau A, Kadare G, Girault JA, Louvard D, Arpin M. Ezrin interacts with focal adhesion kinase and induces its activation independently of cell-matrix adhesion. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:37686–91.
Streblow DN, Vomaske J, Smith P, Melnychuk R, Hall L, Pancheva D, et al. Human cytomegalovirus chemokine receptor US28-induced smooth muscle cell migration is mediated by focal adhesion kinase and Src. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:50456–65.
Rainero E, Caswell PT, Muller PA, Grindlay J, McCaffrey MW, Zhang Q, et al. Diacylglycerol kinase α controls RCP-dependent integrin trafficking to promote invasive migration. J Cell Biol. 2012;196:277–95.
Nemoz G, Sette C, Conti M. Selective activation of rolipram-sensitive, cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase isoforms by phosphatidic acid. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;51:242–9.
Sugimoto N, Miwa S, Ohno-Shosaku T, Tsuchiya H, Hitomi Y, Nakamura H, et al. Activation of tumor suppressor protein PTEN and induction of apoptosis are involved in cAMP-mediated inhibition of cell number in B92 glial cells. Neurosci Lett. 2011;497:55–59.
Lin C, Song L, Gong H, Liu A, Lin X, Wu J, et al. Nkx2-8 downregulation promotes angiogenesis and activates NF-κB in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3638–48.
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, IIic D, Klingbeil CK, Schaefer E, Damsky CH, et al. FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:249–56.
van Blitterswijk WJ, Houssa B. Properties and functions of diacylglycerol kinases. Cell Signal. 2000;12:595–605.
Lou L, Urbani J, Ribeiro-Neto F, Altschuler DL. cAMP inhibition of Akt is mediated by activated and phosphorylated Rap1b. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32799–806.
Andl CD, Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Oyama K, Harada H, Chruma K, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1824–30.
Zhang B, Sun N, Mu X, Zhi L, Zhai L, Jiang Y, et al. G protein alpha S subunit promotes cell proliferation of renal cell carcinoma with involvement of protein kinase A signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36:237–42.
Guo ST, Chi MN, Yang RH, Guo XY, Zan LK, Wang CY, et al. INPP4B is an oncogenic regulator in human colon cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35:3049–61.
Chen J, Lan T, Zhang W, Dong L, Kang N, Zhang S, et al. Feed-forward reciprocal activation of PAFR and Stat3 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small celll lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4198–210.
Ito T, Shimada Y, Kan T, David S, Cheng Y, Mori Y, et al. Pituitary tumor-transforming 1 increases cell motility and promotes lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3214–24.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National 973 Program (2015CB553904) and National Natural Fund of China (81830086, 81490753, 81502110, and 81772504). Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals’s Youth Program, code: QML20171105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zhang, W., Wang, Y. et al. The diacylglycerol kinase α (DGKα)/Akt/NF-κB feedforward loop promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression via FAK-dependent and FAK-independent manner. Oncogene 38, 2533–2550 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0604-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0604-6
This article is cited by
-
AKT2S128/CCTαS315/319/323-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) mediate focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitors resistance via secreting phosphatidylcholines (PCs)
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2024)
-
ESCCAL-1 promotes cell-cycle progression by interacting with and stabilizing galectin-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
npj Precision Oncology (2022)
-
Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-derived CCL22 induces FAK addiction in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2022)
-
The diversity and breadth of cancer cell fatty acid metabolism
Cancer & Metabolism (2021)