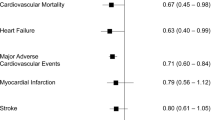
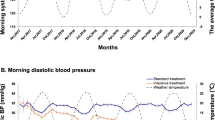
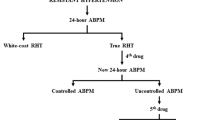
Abstract
Arterial hypertension is particularly prevalent in the elderly and treatment is required according to the literature. Treatment in subjects between 65 and 80 years of age resembles by characteristics and results that obtained in younger population. The treatment of arterial hypertension in the very elderly differs in a relevant percentage of them. It is quite similar in those with a good physical fitness with or without cardiovascular disease. A series of factors as the presence of real sustained hypertension, orthostatic hypotension, frailty and disability, and the boundary of safety recommended by international recent guidelines analysed here are relevant to characterize a clearly elevated risk of complications in the remaining very elderly patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amery A, Birkenhäger W, Brixko P, Bulpitt C, Clement D, Deruyttere M, et al. Mortality and morbidity results from the European Working Party on High Blood Pressure in the Elderly trial. Lancet. 1985;1:1349–54.
Curb JD, Pressel SL, Cutler JA, Savage PJ, Applegate WB, Black H, et al. Effect of diuretic-based antihypertensive treatment on cardiovascular disease risk in older diabetic patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program Cooperative Research Group. JAMA. 1996;276:1886–92.
Dahlöf B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Scherstén B, Ekbom T, Wester PO. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOP-Hypertension). Lancet. 1991;338:1281–5.
Staessen JA, Fagard R, Thijs L, Celis H, Arabidze GG, Birkenhäger WH, et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of placebo and active treatment for older patients with isolated systolic hypertension. The Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Trial Investigators. Lancet. 1997;350:757–64.
Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, Dumitrascu D, et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. N. Engl J Med. 2008;358:1887–98.
Wright JT, Williamson JD, Whelton PK, Snyder JK, Sink KM, Rocco MV, et al. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control. N. Engl J Med. 2015;373:2103–16.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DR Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13–5.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–104.
Fagard RH, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Gasowski J, Bulpitt CJ, Clement D, et al. Response to antihypertensive therapy in older patients with sustained and nonsustained systolic hypertension. Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Trial Investigators. Circulation. 2000;102:1139–44.
Bulpitt CJ, Beckett N, Peters R, Staessen JA. Response to HYVET ambulatory blood pressure substudy. Hypertension. 2013;61:e43.
Bulpitt CJ, Beckett N, Peters R, Staessen JA, Wang JG, Comsa M, et al. Does white coat hypertension require treatment over age 80?: Results of the hypertension in the very elderly trial ambulatory blood pressure side project. Hypertension. 2013;61:89–94.
Kaplan NM. New issues in the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension. Circulation. 2000;102:1079–81.
Ferrucci L, Furberg CD, Penninx BW, DiBari M, Williamson JD, Guralnik JM, et al. Treatment of isolated systolic hypertension is most effective in older patients with high-risk profile. Circulation. 2001;104:1923–6.
Atkins D, Hanusa B, Sefcik T, Kapoor W. Syncope and orthostatic hypotension. Am J Med. 1991;91:179–85.
Walston J, Hadley EC, Ferrucci L, Guralnik JM, Newman AB, Studenski SA, et al. Research agenda for frailty in older adults: toward a better understanding of physiology and etiology: summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:991–1001.
Molander L, Lövheim H, Norman T, Nordström P, Gustafson Y. Lower systolic blood pressure is associated with greater mortality in people aged 85 and older. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:1853–9.
Gijón-Conde T, Graciani A, López-García E, García-Esquinas E, Laclaustra M, Ruilope LM, et al. Frailty, disability, and ambulatory blood pressure in older adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;19:433–8.
Ruilope LM, Ruiz-Hurtado G, Barderas MG, de la Cruz JJ, Lucia A, de la Sierra A, et al. Frequency and Prognosis of Treated Hypertensive Patients According to Prior and New Blood Pressure Goals. Hypertension. 2019;74:130–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruilope, L.M., Ruiz-Hurtado, G. Management of hypertension in the very old: aggressive reduction of blood pressure is harmful in most patients. J Hum Hypertens 34, 557–559 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0346-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0346-0
This article is cited by
-
Primum non nocere
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)