Abstract
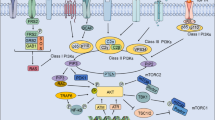
Previously, we reported that Akt inactivation determines the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells to bortezomib. In this study, we report that cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A), a cellular inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), mediates the apoptotic effect of bortezomib in HCC. Silencing PP2A by small interference RNA (siRNA) abolishes bortezomib-induced down-regulation of phospho-Akt and apoptosis. Bortezomib increases PP2A activity in sensitive HCC cells, including Sk-Hep1, Hep3B and Huh-7, but not in resistant PLC5 cells. Bortezomib down-regulates CIP2A in a dose- and time-dependent manner in all sensitive HCC cells, whereas no alterations in CIP2A were found in resistant PLC5 cells. Knockdown of CIP2A by siRNA restored bortezomib’s effects on apoptosis and PP2A activity in PLC5 cells. Moreover, over-expression of CIP2A up-regulated phospho-Akt and protected Sk-Hep1 cells from bortezomib-induced apoptosis. It is significant that, ectopic expression of CIP2A decreased Akt-related PP2A activity, whereas silencing CIP2A increased this activity, indicating that CIP2A negatively regulates Akt-related PP2A activity in HCC cells, furthermore, our in vivo data showed that bortezomib down-regulates CIP2A and up-regulates PP2A activity in Huh-7 tumors, but not in PLC5 tumors. In conclusion, inhibition of CIP2A determines the effects of bortezomib on apoptosis and PP2A-dependent Akt inactivation in HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- PP2A:
-
protein phosphatase 2A
- CIP2A:
-
cancerous inhibitor of PP2A
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- PDK1:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent 1
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- i.p.:
-
intraperitoneal
- s.c.:
-
subcutaneous
References
Bielinski VA, Mumby MC . (2007). Functional analysis of the PP2A subfamily of protein phosphatases in regulating Drosophila S6 kinase. Exp Cell Res 313: 3117–3126.
Chen KF, Yeh PY, Hsu C, Hsu CH, Lu YS, Hsieh HP et al. (2009a). Bortezomib overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in part through the inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem 284: 11121–11133.
Chen KF, Yeh PY, Yeh KH, Lu YS, Huang SY, Cheng AL . (2008). Down-regulation of phospho-Akt is a major molecular determinant of bortezomib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 68: 6698–6707.
Chen KF, Yu HC, Liu TH, Lee SS, Chen PJ, Cheng AL . (2009b). Synergistic interactions between sorafenib and bortezomib in hepatocellular carcinoma involve PP2A-dependent Akt inactivation. J Hepatol 52: 88–95.
Come C, Laine A, Chanrion M, Edgren H, Mattila E, Liu X et al. (2009). CIP2A is associated with human breast cancer aggressivity. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5092–5100.
Davis NB, Taber DA, Ansari RH, Ryan CW, George C, Vokes EE et al. (2004). Phase II trial of PS-341 in patients with renal cell cancer: a University of Chicago phase II consortium study. J Clin Oncol 22: 115–119.
Gao T, Furnari F, Newton AC . (2005). PHLPP: a phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis, and suppresses tumor growth. Mol Cell 18: 13–24.
Janssens V, Goris J . (2001). Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem J 353: 417–439.
Junttila MR, Puustinen P, Niemela M, Ahola R, Arnold H, Bottzauw T et al. (2007). CIP2A inhibits PP2A in human malignancies. Cell 130: 51–62.
Khanna A, Bockelman C, Hemmes A, Junttila MR, Wiksten JP, Lundin M et al. (2009). MYC-dependent regulation and prognostic role of CIP2A in gastric cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101: 793–805.
Li W, Ge Z, Liu C, Liu Z, Bjorkholm M, Jia J et al. (2008). CIP2A is overexpressed in gastric cancer and its depletion leads to impaired clonogenicity, senescence, or differentiation of tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res 14: 3722–3728.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF et al. (2008). Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359: 378–390.
McConkey DJ, Zhu K . (2008). Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor action and resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat 11: 164–179.
Mumby M . (2007). PP2A: unveiling a reluctant tumor suppressor. Cell 130: 21–24.
Neviani P, Santhanam R, Trotta R, Notari M, Blaser BW, Liu S et al. (2005). The tumor suppressor PP2A is functionally inactivated in blast crisis CML through the inhibitory activity of the BCR/ABL-regulated SET protein. Cancer Cell 8: 355–368.
Nikiforov MA, Riblett M, Tang WH, Gratchouck V, Zhuang D, Fernandez Y et al. (2007). Tumor cell-selective regulation of NOXA by c-MYC in response to proteasome inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 19488–19493.
Ocio EM, Mateos MV, Maiso P, Pandiella A, San-Miguel JF . (2008). New drugs in multiple myeloma: mechanisms of action and phase I/II clinical findings. Lancet Oncol 9: 1157–1165.
Orlowski RZ, Baldwin Jr AS . (2002). NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol Med 8: 385–389.
Orlowski RZ, Kuhn DJ . (2008). Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy: lessons from the first decade. Clin Cancer Res 14: 1649–1657.
Richardson P, Wolf J, Jakubowiak A, Zonder J, Lonial S, Irwin DH et al. (2008). Phase I/II Results of a Multicenter Trial of Perifosine (KRX-0401)+Bortezomib in patients with relapsed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who were previously relapsed from or refractory to bortezomib. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 112: 870–87.
Soo Hoo L, Zhang JY, Chan EK . (2002). Cloning and characterization of a novel 90 kDa ′companion′ auto-antigen of p62 overexpressed in cancer. Oncogene 21: 5006–5015.
Verslype C, Van Cutsem E, Dicato M, Arber N, Berlin JD, Cunningham D et al. (2009). The management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Current expert opinion and recommendations derived from the 10th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer, Barcelona, 2008. Ann Oncol 20 (Suppl 7): vii1–vii6.
Voorhees PM, Orlowski RZ . (2006). The proteasome and proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46: 189–213.
Yu C, Friday BB, Lai JP, Yang L, Sarkaria J, Kay NE et al. (2006). Cytotoxic synergy between the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in vitro: induction of apoptosis through Akt and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 2378–2387.
Acknowledgements
Supported by NTUH98P03, NTUH98FTN21 from National Taiwan University Hospital and NSC97-2314-B-002-182, NSC98-2314-B-002-067-MY3, NSC98-3112-B-002-037 from the National Science Council, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KF., Liu, CY., Lin, YC. et al. CIP2A mediates effects of bortezomib on phospho-Akt and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 29, 6257–6266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.357
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.357
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cancer progression by the okadaic acid class of tumor promoters and endogenous protein inhibitors of PP2A, SET and CIP2A
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Targeting protein phosphatases for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases: From signaling to therapy
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Prodigiosin inhibits the proliferation of glioblastoma by regulating the KIAA1524/PP2A signaling pathway
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
CIP2A silencing alleviates doxorubicin resistance in MCF7/ADR cells through activating PP2A and autophagy
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
Effect of miR-375 on non-small cell lung carcinoma invasion, migration, and proliferation through the CIP2A pathway
Oncology and Translational Medicine (2020)