Abstract
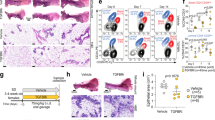
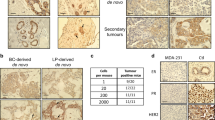
Despite our incomplete understanding of the function of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) in tumorigenesis, IGF-IR targeting agents have entered clinical trials for the treatment of human cancers. Previously, we have shown that downregulation of IGF-IR transgene in mammary tumors in MTB-IGFIR transengic mice results in tumor regression in a majority of the mice and most of these mice do not develop recurrent mammary tumors. In this study, we examined mammary tissue of mice that did not develop recurrent tumors. Areas of tumor regression were visible macroscopically and microscopically these lesions contained cell debris, individual cells, lipofuscin and doxycycline crystals. Three of the 12 mice also presented with considerable lobuloalveolar development. The re-expression of the IGF-IR transgene in mammary tissue with stably regressed tumors resulted in the rapid re-emergence of mammary tumors, some of which seemed to originate from the regressed mammary lesions. Thus, despite stable tumor regression after IGF-IR downregulation, mammary tissue contained preneoplastic lesions and tumors rapidly re-appear upon re-overexpression of IGF-IR transgene. Therefore, IGF-IR-targeting agents may be effective at regressing mammary tumors expressing IGF-IR, but these agents will not completely eradicate all tumor cells or restore the mammary stromal environment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arteaga CL, Kitten LJ, Coronado EB, Jacobs S, Kull Jr FC, Allred DC et al. (1989). Blockade of the type I somatomedin receptor inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic mice. J Clin Invest 84: 1418–1423.
Arteaga CL, Osborne CK . (1989). Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res 49: 6237–6241.
Bahri S, Chen JH, Mehta RS, Carpenter PM, Nie K, Kwon SY et al. (2009). Residual breast cancer diagnosed by MRI in patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with and without bevacizumab. Ann Surg Oncol 16: 1619–1628.
Baserga R, Peruzzi F, Reiss K . (2003). The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int J Cancer 107: 873–877.
Bates P, Fisher R, Ward A, Richardson L, Hill DJ, Graham CF . (1995). Mammary cancer in transgenic mice expressing insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II). Br J Cancer 72: 1189–1193.
Bohula EA, Salisbury AJ, Sohail M, Playford MP, Riedemann J, Southern EM et al. (2003). The efficacy of small interfering RNAs targeted to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is influenced by secondary structure in the IGF1R transcript. J Biol Chem 278: 15991–15997.
Bol DK, Kiguchi K, Gimenez-Conti I, Rupp T, DiGiovanni J . (1997). Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 induces hyperplasia, dermal abnormalities, and spontaneous tumor formation in transgenic mice. Oncogene 14: 1725–1734.
Carboni JM, Lee AV, Hadsell DL, Rowley BR, Lee FY, Bol DK et al. (2005). Tumor development by transgenic expression of a constitutively active insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res 65: 3781–3787.
Chernicky CL, Tan H, Yi L, Loret Jr dM, Ilan J . (2002). Treatment of murine breast cancer cells with antisense RNA to the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor decreases the level of plasminogen activator transcripts, inhibits cell growth in vitro, and reduces tumorigenesis in vivo. Mol Pathol 55: 102–109.
Denys H, Braems G, Lambein K, Pauwels P, Hendrix A, De BA et al. (2009). The extracellular matrix regulates cancer progression and therapy response: implications for prognosis and treatment. Curr Pharm Des 15: 1373–1384.
DiGiovanni J, Kiguchi K, Frijhoff A, Wilker E, Bol DK, Beltran L et al. (2000). Deregulated expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 in prostate epithelium leads to neoplasia in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3455–3460.
Ghajar CM, Bissell MJ . (2008). Extracellular matrix control of mammary gland morphogenesis and tumorigenesis: insights from imaging. Histochem Cell Biol 130: 1105–1118.
Gualberto A, Pollak M . (2009). Emerging role of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in oncology: early clinical trial results and future directions. Oncogene 28: 3009–3021.
Hadsell DL, Murphy KL, Bonnette SG, Reece N, Laucirica R, Rosen JM . (2000). Cooperative interaction between mutant p53 and des(1-3)IGF-I accelerates mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 19: 889–898.
Jain M, Arvanitis C, Chu K, Dewey W, Leonhardt E, Trinh M et al. (2002). Sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype by brief inactivation of MYC. Science 297: 102–104.
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Gunther EJ, Chodosh LA, Petrik JJ, Khokha R et al. (2007). Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene 26: 1636–1644.
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Wood GA, Petrik JJ, Moorehead RA . (2009). Reversibility and recurrence of IGF-IR-induced mammary tumors. Oncogene 28: 2152–2162.
Kaplan-Lefko PJ, Sutherland BW, Evangelou AI, Hadsell DL, Barrios RJ, Foster BA et al. (2008). Enforced epithelial expression of IGF-1 causes hyperplastic prostate growth while negative selection is requisite for spontaneous metastogenesis. Oncogene 27: 2868–2876.
LeRoith D, Roberts Jr CT . (2003). The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett 195: 127–137.
Linnerth NM, Siwicky MD, Campbell CI, Watson KL, Petrik JJ, Whitsett JA et al. (2009). Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor induces pulmonary tumorigenesis. Neoplasia 11: 672–682.
Lu Y, Zi X, Zhao Y, Mascarenhas D, Pollak M . (2001). Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). J Natl Cancer Inst 93: 1852–1857.
Miranda MB, Duan R, Thomas SM, Grandis JR, Redner RL, Jones JE et al. (2008). Gefitinib potentiates myeloid cell differentiation by ATRA. Leukemia 22: 1624–1627.
Moorehead RA, Sanchez OH, Baldwin RM, Khokha R . (2003). Transgenic overexpression of IGF-II induces spontaneous lung tumors: a model for human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 22: 853–857.
Morris GJ, Robinson PA, Lo S, Samuel TA, Sheikh AA, Jordan III WE et al. (2010). Residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Semin Oncol 37: 1–10.
Nahta R, Esteva FJ . (2006). Herceptin: mechanisms of action and resistance. Cancer Lett 232: 123–138.
Nahta R, Yuan LX, Zhang B, Kobayashi R, Esteva FJ . (2005). Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 11118–11128.
Peintinger F, Kuerer HM, McGuire SE, Bassett R, Pusztai L, Symmans WF . (2008). Residual specimen cellularity after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Br J Surg 95: 433–437.
Pravtcheva DD, Wise TL . (1998). Metastasizing mammary carcinomas in H19 enhancers-Igf2 transgenic mice. J Exp Zool 281: 43–57.
Pure E . (2009). The road to integrative cancer therapies: emergence of a tumor-associated fibroblast protease as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13: 967–973.
Sachdev D, Yee D . (2001). The IGF system and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 8: 197–209.
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A et al. (2001). Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344: 783–792.
Surmacz E . (2000). Function of the IGF-I receptor in breast cancer. J Mam Gland Biol Neoplasia 5: 95–105.
Surmacz E . (2003). Growth factor receptors as therapeutic targets: strategies to inhibit the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Oncogene 22: 6589–6597.
Wilker E, Lu J, Rho O, Carbajal S, Beltran L, DiGiovanni J . (2005). Role of PI3K/Akt signaling in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) skin tumor promotion. Mol Carcinog 44: 137–145.
Wise TL, Pravtcheva DD . (2006). Delayed onset of Igf2-induced mammary tumors in Igf2r transgenic mice. Cancer Res 66: 1327–1336.
Zhang D, LaFortune TA, Krishnamurthy S, Esteva FJ, Cristofanilli M, Liu P et al. (2009). Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor reverses mesenchymal to epithelial phenotype and inhibits metastasis in inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15: 6639–6648.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Cancer Research Society grant and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research grant to RAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, R., Petrik, J. & Moorehead, R. Preneoplastic changes persist after IGF-IR downregulation and tumor regression. Oncogene 29, 4779–4786 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.231
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.231