Abstract
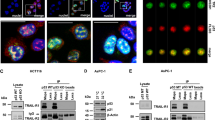
The nonreceptor, protein-tyrosine kinase Syk is a suppressor of breast cancer progression whose expression is inversely correlated with the invasive behavior of cancer cells. In contrast, Syk has a positive function in murine mammary tumor virus-mediated tumorigenesis. A yeast two-hybrid screen using a library from human mammary gland identified tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor-interacting protein (TRIP) as an Syk-binding partner. This interaction is mediated by the C-terminal region of TRIP and is enhanced by the treatment of cells with TNF and the tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk. Syk and TRIP have opposing functions in TNF-signaling pathways. Syk enhances the activation of nuclear factor-κB by TNF and this is antagonized by TRIP. The overexpression of TRIP sensitizes cells to TNF-induced apoptosis, an effect that can be reversed by the coexpression of Syk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besse A, Campos AD, Webster WK, Darnay BG . (2007). TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) is a RING-dependent ubiquitin ligase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359: 660–664.
Coopman PJ, Do MT, Barth M, Bowden ET, Hayes AJ, Basyuk E et al. (2000). The Syk tyrosine kinase suppresses malignant growth of human breast cancer cells. Nature 406: 742–747.
Eliopoulos AG, Das S, Tsichlis PN . (2006). The tyrosine kinase Syk regulates TPL2 activation signals. J Biol Chem 281: 1371–1380.
Katz E, Lareef MH, Rassa JC, Grande SM, King LB, Russo J et al. (2005). MMTV Env encodes an ITAM responsible for transformation of mammary epithelial cells in three-dimensional culture. J Exp Med 201: 431–439.
Keshvara LM, Isaacson CC, Yankee TM, Sarac R, Harrison ML, Geahlen RL . (1998). Syk- and Lyn-dependent phosphorylation of Syk on multiple tyrosines following B cell activation includes a site that negatively regulates signaling. J Immunol 161: 5276–5283.
Kurosaki T . (2000). Functional dissection of BCR signaling pathways. Curr Opin Immunol 12: 276–281.
Latour S, Veillette A . (2001). Proximal protein tyrosine kinases in immunoreceptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol 13: 299–306.
Lee SY, Lee SY, Choi Y . (1997). TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP): a novel component of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)- and CD30-TRAF signaling complexes that inhibits TRAF2-mediated NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med 185: 1275–1285.
Lu J, Lin W-H, Chen S-Y, Longnecker R, Tsai S-C, Chen C-L et al. (2006). Syk tyrosine kinase mediates Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A-induced cell migration in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 281: 8806–8814.
Ma H, Yankee TM, Hu J, Asai DJ, Harrison ML, Geahlen RL . (2001). Visualization of Syk-antigen receptor interactions using green fluorescent protein: differential roles for Syk and Lyn in the regulation of receptor capping and internalization. J Immunol 166: 1507–1516.
Moon KD, Post CB, Durden DL, Zhou Q, De P, Harrison ML et al. (2004). Molecular basis for a direct interaction between the Syk protein-tyrosine kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 280: 1543–1551.
Moroni M, Soldatenkov V, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Stoica G, Gehan E et al. (2004). Progressive loss of Syk and abnormal proliferation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 64: 7346–7354.
Peters JD, Furlong MT, Asai DJ, Harrison ML, Geahlen RL . (1996). Syk, activated by cross-linking the B-cell antigen receptor, localizes to the cytosol where it interacts with and phosphorylates alpha-tubulin on tyrosine. J Biol Chem 271: 4755–4762.
Regamey A, Hohl D, Liu JW, Roger T, Kogerman P, Toftgard R et al. (2003). The tumor suppressor CYLD interacts with TRIP and regulates negatively nuclear factor kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 198: 1959–1964.
Salomoni P, Khelifi AF . (2006). Daxx: death or survival protein? Trends Cell Biol 16: 97–104.
Takada Y, Aggarwal BB . (2004). TNF activates Syk protein tyrosine kinase leading to TNF-induced MAPK activation, NF-kappaB activation, and apoptosis. J Immunol 173: 1066–1077.
Toyama T, Iwase H, Yamashita H, Hara Y, Omoto Y, Sugiura H et al. (2003). Reduced expression of the Syk gene is correlated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 189: 97–102.
Ulanova M, Puttagunta L, Marcet-Palacios M, Duszyk M, Steinhoff U, Duta F et al. (2005). Syk tyrosine kinase participates in beta1-integrin signaling and inflammatory responses in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L497–L507.
Wang L, Devarajan E, He J, Reddy SP, Dai JL . (2005). Transcription repressor activity of spleen tyrosine kinase mediates breast tumor suppression. Cancer Res 65: 10289–10297.
Wilson J, Balkwill F . (2002). The role of cytokines in the epithelial cancer microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol 12: 113–120.
Zhou F, Hu J, Ma H, Harrison ML, Geahlen RL . (2006). Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of the Syk protein-tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 26: 3478–3491.
Zyss D, Montcourrier P, Vidal B, Anguille C, Mérezègue F, Sahuquet A et al. (2005). The Syk tyrosine kinase localizes to the centrosomes and negatively affects mitotic progression. Cancer Res 65: 10872–10880.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by United States Public Health Services grant CA115465 awarded by the National Cancer Institute and US Army Breast Cancer Research Program award DAMD17-02-1-0554.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Geahlen, R. The protein-tyrosine kinase Syk interacts with TRAF-interacting protein TRIP in breast epithelial cells. Oncogene 28, 1348–1356 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.493
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.493
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TRAIP modulates the IGFBP3/AKT pathway to enhance the invasion and proliferation of osteosarcoma by promoting KANK1 degradation
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
TRAIP is involved in chromosome alignment and SAC regulation in mouse oocyte meiosis
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
TRAIP regulates replication fork recovery and progression via PCNA
Cell Discovery (2016)
-
NOPO modulates Egr-induced JNK-independent cell death in Drosophila
Cell Research (2012)
-
The TRAF-Interacting Protein (TRIP) Is a Regulator of Keratinocyte Proliferation
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2011)