Abstract
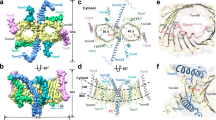
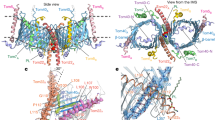
A majority of the proteins targeted to the mitochondria are transported through the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex. Tom70 is a major surface receptor for mitochondrial protein precursors in the TOM complex. To investigate how Tom70 receives the mitochondrial protein precursors, we have determined the crystal structure of yeast Tom70p to 3.0 Å. Tom70p forms a homodimer in the crystal. Each subunit consists primarily of tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motifs, which are organized into a right-handed superhelix. The TPR motifs in the N-terminal domain of Tom70p form a peptide-binding groove for the C-terminal EEVD motif of Hsp70, whereas the C-terminal domain of Tom70p contains a large pocket that may be the binding site for mitochondrial precursors. The crystal structure of Tom70p provides insights into the mechanisms of precursor transport across the mitochondrion's outer membrane.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Sickmann, A. et al. The proteome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13207–13212 (2003).
Gray, M.W., Burger, G. & Lang, B.F. Mitochondrial evolution. Science 283, 1476–1481 (1999).
Neupert, W. Protein import into mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 863–917 (1997).
Neupert, W. & Brunner, M. The protein import motor of mitochondria. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 555–565 (2002).
Pfanner, N. Protein sorting: recognizing mitochondrial presequences. Curr. Biol. 10, R412–R415 (2000).
Abe, Y. et al. Structural basis of presequence recognition by the mitochondrial protein import receptor Tom20. Cell 100, 551–560 (2000).
Rehling, P. et al. Protein insertion into the mitochondrial inner membrane by a twin-pore translocase. Science 299, 1747–1751 (2003).
Koehler, C.M. New developments in mitochondrial assembly. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 309–335 (2004).
Sollner, T., Pfaller, R., Griffiths, G., Pfanner, N. & Neupert, W. A mitochondrial import receptor for the ADP/ATP carrier. Cell 62, 107–115 (1990).
Sollner, T., Griffiths, G., Pfaller, R., Pfanner, N. & Neupert, W. MOM19, an import receptor for mitochondrial precursor proteins. Cell 59, 1061–1070 (1989).
Brix, J., Dietmeier, K. & Pfanner, N. Differential recognition of preproteins by the purified cytosolic domains of the mitochondrial import receptors Tom20, Tom22, and Tom70. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 20730–20735 (1997).
Pfanner, N. & Geissler, A. Versatility of the mitochondrial protein import machinery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 339–349 (2001).
Young, J.C., Hoogenraad, N.J. & Hartl, F.U. Molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Hsp70 deliver preproteins to the mitochondrial import receptor Tom70. Cell 112, 41–50 (2003).
Claros, M.G. et al. Limitations to in vivo import of hydrophobic proteins into yeast mitochondria. The case of a cytoplasmically synthesized apocytochrome b. Eur. J. Biochem. 228, 762–771 (1995).
Beddoe, T. & Lithgow, T. Delivery of nascent polypeptides to the mitochondrial surface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1592, 35–39 (2002).
Wiedemann, N., Pfanner, N. & Ryan, M.T. The three modules of ADP/ATP carrier cooperate in receptor recruitment and translocation into mitochondria. EMBO J. 20, 951–960 (2001).
Brix, J. et al. The mitochondrial import receptor Tom70: identification of a 25 kDa core domain with a specific binding site for preproteins. J. Mol. Biol. 303, 479–488 (2000).
Jinek, M. et al. The superhelical TPR-repeat domain of O-linked GlcNAc transferase exhibits structural similarities to importin alpha. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 1001–1007 (2004).
Demand, J., Luders, J. & Hohfeld, J. The carboxy-terminal domain of Hsc70 provides binding sites for a distinct set of chaperone cofactors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 2023–2028 (1998).
Ballinger, C.A. et al. Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 4535–4545 (1999).
Connell, P. et al. The co-chaperone CHIP regulates protein triage decisions mediated by heat-shock proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 93–96 (2001).
Scheufler, C. et al. Structure of TPR domain-peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine. Cell 101, 199–210 (2000).
Brix, J., Rudiger, S., Bukau, B., Schneider-Mergener, J. & Pfanner, N. Distribution of binding sequences for the mitochondrial import receptors Tom20, Tom22, and Tom70 in a presequence-carrying preprotein and a non-cleavable preprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16522–16530 (1999).
Wu, Y., McCombs, D., Nagy, L., DeLucas, L. & Sha, B.D. Preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of yeast mitochondria translocon member Tom70p. Acta Crystallogr. F 62, 265–267 (2006).
Terwilliger, T.C. & Berendzen, J. Automated MAD and MIR structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 55, 849–861 (1999).
Terwilliger, T.C. Maximum-likelihood density modification. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 56, 965–972 (2000).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Wang, J.W., Chen, J.R., Gu, Y.X., Zheng, C.D. & Fan, H.F. Direct-method SAD phasing with partial-structure iteration: towards automation. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 1991–1996 (2004).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54, 905–921 (1998).
Lovell, S.C. et al. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi,psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins 50, 437–450 (2003).
Carson, M. Ribbons 2.0. Ribbon models for macromolecules. J. Mol. Graph. 5, 103–106 (1987).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the staff scientists at APS beamline SER-CAT for their help in data collection. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (R01 DK56203 and R01 GM65959) and the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.W. contributed to cloning, protein expression and purification, crystallization and structure determination. B.D.S. contributed to data collection and structure determination.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Electron density map for Tom70p from SAD phasing (PDF 300 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Sha, B. Crystal structure of yeast mitochondrial outer membrane translocon member Tom70p. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 589–593 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1106
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1106
This article is cited by
-
Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions
Nature Communications (2021)
-
The selectivity filter of the mitochondrial protein import machinery
BMC Biology (2020)
-
Hsp70 at the membrane: driving protein translocation
BMC Biology (2018)
-
Singlet oxygen triplet energy transfer-based imaging technology for mapping protein–protein proximity in intact cells
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Visualizing active membrane protein complexes by electron cryotomography
Nature Communications (2014)