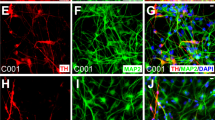
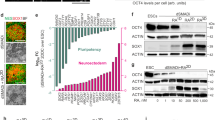
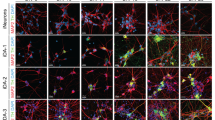
Abstract
Cell-replacement therapy using human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) holds great promise in treating Parkinson's disease. We have recently reported a highly efficient method to generate functional dopaminergic (DA) neurons from hESCs. Our method includes a unique step, the formation of spherical neural masses (SNMs), and offers the highest yield of DA neurons ever achieved so far. In this report, we describe our method step by step, covering not only how to differentiate hESCs into DA neurons at a high yield, but also how to amplify, freeze and thaw the SNMs, which are the key structures that make our protocol unique and advantageous. Although the whole process of generation of DA neurons from hESCs takes about 2 months, only 14 d are needed to derive DA neurons from the SNMs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Youdim, M.B. & Riederer, P. Understanding Parkinson's disease. Sci. Am. 276, 52–59 (1997).
Olanow, C.W. & Obeso, J.A. Levodopa motor complications in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 47, 167–178 (2000).
Brederlau, A. et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cells to a rat model of Parkinson's disease: effect of in vitro differentiation on graft survival and teratoma formation. Stem Cells 24, 1433–1440 (2006).
Yang, D., Zhang, Z.J., Oldenburg, M., Ayala, M. & Zhang, S.C. Human embryonic stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons reverse functional deficit in parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells 26, 55–63 (2008).
Park, C.H. et al. In vitro and in vivo analyses of human embryonic stem cell-derived dopamine neurons. J. Neurochem. 92, 1265–1276 (2005).
Perrier, A.L. et al. Derivation of midbrain dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12543–12548 (2004).
Ueno, M. et al. Neural conversion of ES cells by an inductive activity on human amniotic membrane matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 9554–9559 (2006).
Sonntag, K.C. et al. Enhanced yield of neuroepithelial precursors and midbrain-like dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells using the bone morphogenic protein antagonist noggin. Stem Cells 25, 411–418 (2007).
Roy, N.S. et al. Functional engraft of human ES cell-derived dopaminergic neurons enriched by coculture with telomerase-immortalized midbrain astrocytes. Nat. Med. 12, 1259–1268 (2006).
Cho, M.S. et al. Highly efficient and large-scale generation of functional dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3392–3397 (2008).
Kim, D.W. et al. Stromal cell-derived inducing activity, Nurr1, and signaling molecules synergistically induce dopaminergic neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 24, 557–567 (2006).
Cho, Y.H. et al. Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells efficiently induce behavioral recovery in a Parkinsonian rat model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 341, 6–12 (2006).
Kim, D.S., Kim, J.Y., Kang, M., Cho, M.S. & Kim, D.W. Derivation of functional dopamine neurons from embryonic stem cells. Cell Transplant. 16, 117–123 (2007).
Reynolds, B.A. & Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 255, 1707–1710 (1992).
Oh, S.K. et al. Derivation and characterization of new human embryonic stem cell lines, SNUhES1, SNUhES2 and SNUhES3. Stem Cells 23, 211–219 (2005).
Oh, S.K. et al. Methods for expansion of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 23, 605–609 (2005).
Kang, S.M. et al. Efficient induction of oligodendrocytes from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 25, 419–424 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants (codes: SC3150, SC5170 and SC1110) from the Stem Cell Research Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, MS., Hwang, DY. & Kim, DW. Efficient derivation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells on a large scale. Nat Protoc 3, 1888–1894 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.188
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.188
This article is cited by
-
The role of Smo-Shh/Gli signaling activation in the prevention of neurological and ageing disorders
Biogerontology (2023)
-
Genome-wide screening for deubiquitinase subfamily identifies ubiquitin-specific protease 49 as a novel regulator of odontogenesis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Downregulated miR-18b-5p triggers apoptosis by inhibition of calcium signaling and neuronal cell differentiation in transgenic SOD1 (G93A) mice and SOD1 (G17S and G86S) ALS patients
Translational Neurodegeneration (2020)
-
iPS Cell Cultures from a Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker Patient with the Y218N PRNP Mutation Recapitulate tau Pathology
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Effects of short-term exposure to sevoflurane on the survival, proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of neural precursor cells derived from human embryonic stem cells
Journal of Anesthesia (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.