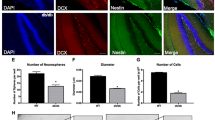
Abstract
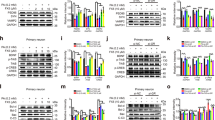
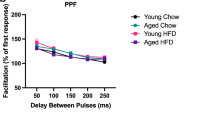
Many organ systems are adversely affected by diabetes, including the brain, which undergoes changes that may increase the risk of cognitive decline. Although diabetes influences the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the role of this neuroendocrine system in diabetes-induced cognitive dysfunction remains unexplored. Here we demonstrate that, in both insulin-deficient rats and insulin-resistant mice, diabetes impairs hippocampus-dependent memory, perforant path synaptic plasticity and adult neurogenesis, and the adrenal steroid corticosterone contributes to these adverse effects. Rats treated with streptozocin have reduced insulin and show hyperglycemia, increased corticosterone, and impairments in hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and learning. Similar deficits are observed in db/db mice, which are characterized by insulin resistance, elevated corticosterone and obesity. Changes in hippocampal plasticity and function in both models are reversed when normal physiological levels of corticosterone are maintained, suggesting that cognitive impairment in diabetes may result from glucocorticoid-mediated deficits in neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven, G.M. The insulin resistance syndrome: definition and dietary approaches to treatment. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 25, 391–406 (2005).
Messier, C. Impact of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes on cognitive aging. Neurobiol. Aging 26 (suppl. 1), S26–S30 (2005).
Greenwood, C.E. & Winocur, G. High-fat diets, insulin resistance and declining cognitive function. Neurobiol. Aging 26 (suppl. 1), 45 (2005).
Desrocher, M. & Rovet, J. Neurocognitive correlates of type 1 diabetes mellitus in childhood. Child Neuropsychol. 10, 36–52 (2004).
Biessels, G.J. et al. Place learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 45, 1259–1266 (1996).
Biessels, G.J. et al. Water maze learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of insulin treatment. Brain Res. 800, 125–135 (1998).
Li, X.L. et al. Impairment of long-term potentiation and spatial memory in leptin receptor–deficient rodents. Neuroscience 113, 607–615 (2002).
Hummel, K.P., Dickie, M.M. & Coleman, D.L. Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science 153, 1127–1128 (1966).
Leuner, B., Gould, E. & Shors, T.J. Is there a link between adult neurogenesis and learning? Hippocampus 16, 216–224 (2006).
Kamal, A., Biessels, G.J., Urban, I.J. & Gispen, W.H. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: impairment of long-term potentiation and facilitation of long-term depression. Neuroscience 90, 737–745 (1999).
Zhang, W.J., Tan, Y.F., Yue, J.T., Vranic, M. & Wojtowicz, J.M. Impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Acta Neurol. Scand., published online 14 September 2007 (doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2007.00928.x).
van Praag, H., Christie, B.R., Sejnowski, T.J. & Gage, F.H. Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13427–13431 (1999).
Fontan-Lozano, A. et al. Caloric restriction increases learning consolidation and facilitates synaptic plasticity through mechanisms dependent on NR2B subunits of the NMDA receptor. J. Neurosci. 27, 10185–10195 (2007).
Lee, J., Duan, W. & Mattson, M.P. Evidence that brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. J. Neurochem. 82, 1367–1375 (2002).
Stranahan, A.M., Khalil, D. & Gould, E. Social isolation delays the positive effects of running on adult neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 526–533 (2006).
Magarinos, A.M. & McEwen, B.S. Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11056–11061 (2000).
Chan, O. et al. Hyperglycemia does not increase basal hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal activity in diabetes but it does impair the HPA response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 289, R235–R246 (2005).
Tokuyama, K. & Himms-Hagen, J. Increased sensitivity of the genetically obese mouse to corticosterone. Am. J. Physiol. 252, 202–208 (1987).
Langley, S.C. & York, D.A. Effects of antiglucocorticoid RU486 on development of obesity in obese fa/fa Zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. 259, 539–544 (1990).
Watts, L.M. et al. Reduction of hepatic and adipose tissue glucocorticoid receptor expression with antisense oligonucleotides improves hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic rodents without causing systemic glucocorticoid antagonism. Diabetes 54, 1846–1853 (2005).
Oei, N.Y., Everaerd, W.T., Elzinga, B.M., van Well, S. & Bermond, B. Psychosocial stress impairs working memory at high loads: an association with cortisol levels and memory retrieval. Stress 9, 133–141 (2006).
MacLullich, A.M. et al. Plasma cortisol levels, brain volumes and cognition in healthy elderly men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 30, 505–515 (2005).
Elgh, E. et al. Cognitive dysfunction, hippocampal atrophy and glucocorticoid feedback in Alzheimer's disease. Biol. Psychiatry 59, 155–161 (2006).
Oitzl, M.S., Fluttert, M., Sutanto, W. & de Kloet, E.R. Continuous blockade of brain glucocorticoid receptors facilitates spatial learning and memory in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3759–3766 (1998).
Wright, R.L., Lightner, E.N., Harman, J.S., Meijer, O.C. & Conrad, C.D. Attenuating corticosterone levels on the day of memory assessment prevents chronic stress–induced impairments in spatial memory. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 595–605 (2006).
Alfarez, D.N., Joels, M. & Krugers, H.J. Chronic unpredictable stress impairs long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal CA1 area and dentate gyrus in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 1928–1934 (2003).
Kerr, D.S., Campbell, L.W., Hao, S.Y. & Landfield, P.W. Corticosteroid modulation of hippocampal potentials: increased effect with aging. Science 245, 1505–1509 (1989).
Korz, V. & Frey, J.U. Stress-related modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats: Involvement of adrenal steroid receptors. J. Neurosci. 23, 7281–7287 (2003).
Pavlides, C., Watanabe, Y. & McEwen, B.S. Effects of glucocorticoids on hippocampal long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 3, 183–192 (1993).
Gould, E., Cameron, H.A., Daniels, D.C., Woolley, C.S. & McEwen, B.S. Adrenal hormones suppress cell division in the adult rat dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 12, 3642–3650 (1992).
Montaron, M.F. et al. Lifelong corticosterone level determines age-related decline in neurogenesis and memory. Neurobiol. Aging 27, 645–654 (2006).
Tanapat, P., Hastings, N.B., Rydel, T.A., Galea, L.A. & Gould, E. Exposure to fox odor inhibits cell proliferation in the hippocampus of adult rats via an adrenal hormone-dependent mechanism. J. Comp. Neurol. 437, 496–504 (2001).
Karten, Y.J., Jones, M.A., Jeurling, S.I. & Cameron, H.A. GABAergic signaling in young granule cells in the adult rat and mouse dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 16, 312–320 (2006).
Ge, S. et al. GABA regulates synaptic integration of newly generated neurons in the adult brain. Nature 439, 589–593 (2006).
Saxe, M.D. et al. Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17501–17506 (2006).
Snyder, J.S., Kee, N. & Wojtowicz, J.M. Effects of adult neurogenesis on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 2423–2431 (2001).
Moosavi, M., Naghdi, N., Maghsoudi, N. & Zahedi Asl, S. Insulin protects against stress-induced impairments in water maze performance. Behav. Brain Res. 176, 230–236 (2007).
Revest, J.M. et al. The MAPK pathway and Egr-1 mediate stress-related behavioral effects of glucocorticoids. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 664–672 (2005).
Piroli, G.G. et al. Corticosterone impairs insulin-stimulated translocation of GLUT4 in the rat hippocampus. Neuroendocrinology 85, 71–80 (2007).
Sapolsky, R.M. Glucocorticoid toxicity in the hippocampus: reversal by supplementation with brain fuels. J. Neurosci. 6, 2240–2244 (1986).
McNay, E.C., Fries, T.M. & Gold, P.E. Decreases in rat extracellular hippocampal glucose concentration associated with cognitive demand during a spatial task. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2881–2885 (2000).
Reagan, L.P. et al. Localization and regulation of GLUTx1 glucose transporter in the hippocampus of streptozotocin diabetic rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 2820–2825 (2001).
Shors, T.J., Townsend, D.A., Zhao, M., Kozorovitskiy, Y. & Gould, E. Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus 12, 578–584 (2002).
Kee, N., Teixeira, C.M., Wang, A.H. & Frankland, P.W. Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 355–362 (2007).
Bruel-Jungerman, E., Laroche, S. & Rampon, C. New neurons in the dentate gyrus are involved in the expression of enhanced long-term memory following environmental enrichment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 513–521 (2005).
Sandeep, T.C. et al. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibition improves cognitive function in healthy elderly men and type 2 diabetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 6734–6739 (2004).
Cameron, H.A. & McKay, R.D. Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 435, 406–417 (2001).
Kozorovitskiy, Y. et al. Experience induces structural and biochemical changes in the adult primate brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 17478–17482 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by US National Institutes of Health National Research Service Award Predoctoral fellowship F31AG024690-03 to A.M.S. through Princeton University, and by the Intramural Research Program of the US National Institute on Aging. We thank D.L. Longo for suggestions and T. Lamb, O. Carlson, J.S. Villareal and R. Telljohann for technical assistance. We are also grateful to E. Gould and H. van Praag for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.M.S., M.P.M. and J.M.E. contributed to the conceptual design and development of the experiments. A.M.S., K.L., T.V.A. and R.G.C. performed surgeries, ran experiments and contributed data. All authors assisted with writing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods (PDF 430 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stranahan, A., Arumugam, T., Cutler, R. et al. Diabetes impairs hippocampal function through glucocorticoid-mediated effects on new and mature neurons. Nat Neurosci 11, 309–317 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2055
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2055
This article is cited by
-
Assessing the mechanisms of brain plasticity by transcranial magnetic stimulation
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Memory deficits in a juvenile rat model of type 1 diabetes are due to excess 11β-HSD1 activity, which is upregulated by high glucose concentrations rather than insulin deficiency
Diabetologia (2023)
-
Palmitoylated prolactin-releasing peptide treatment had neuroprotective but not anti-obesity effect in fa/fa rats with leptin signaling disturbances
Nutrition & Diabetes (2022)
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to the decline in doublecortin expression in the immature neurons of mice with long-term obesity
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Diabetic patients treated with metformin during early stages of Alzheimer’s disease show a better integral performance: data from ADNI study
GeroScience (2022)