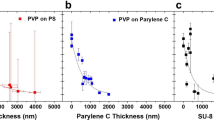
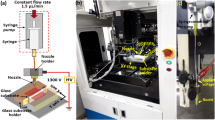
Abstract
The manufacture of high-performance electronic devices with micrometre or even submicrometre dimensions by solution processing and direct printing, requires the ability to control accurately the flow and spread of functional liquid inks on surfaces. This can be achieved with the help of surface-energy patterns causing inks to be repelled and dewetted from pre-defined regions of the substrate. To exploit this principle for the fabrication of submicrometre device structures, a detailed understanding of the factors causing ink droplets to dewet on patterned surfaces is required. Here, we use hydrophobic surface-energy barriers of different geometries to study the influence of solution viscosity, ink volume, and contact angle on the process of dewetting of inkjet-printed droplets of a water-based conducting polymer. We demonstrate polymer field-effect transistor devices with channel length of 500 nm fabricated by surface-energy-assisted inkjet printing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garnier, F., Hajlaoui, R., Yassar, A. & Srivastava, P. All-polymer field-effect transistor realized by printing techniques. Science 265, 1684–1686 (1994).
Bao, Z., Feng, Y., Dodabalapur, A., Raju, V.R. & Lovinger, A.J. High-performance plastic transistors fabricated by printing techniques. Chem. Mater. 9, 1299–1301 (1997).
Paul, K.E., Wong, W.S., Ready, S.E. & Street, R.A. Additive jet printing of polymer thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2070–2072 (2003).
Sirringhaus, H. et al. High-resolution inkjet printing of all-polymer transistor circuits. Science 290, 2123–2126 (2000).
Kagan, R., Breen, T.L. & Kosbar, L.L. Patterning organic–inorganic thin-film transistors using microcontact printed templates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3536–3538 (2001).
Chabinyc, M.L., Wong, W.S., Salleo, A., Paul, K.E. & Street, R.A. Organic polymeric thin-film transistors fabricated by selective dewetting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4260–4262 (2002).
Gau, H., Herminghaus, S., Lenz, P. & Lipowsky, R. Liquid morphologies on structured surfaces: from microchannels to microchips. Science 283, 46–49 (1999).
Lenz, P. & Lipowsky, R. Morphological transitions of wetting layers on structured surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1920–1923 (1998).
Brinkmann, M. & Lipowsky, R. Wetting morphologies on substrates with striped surface domains. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 4296–4306 (2002).
Kargupta, K. & Sharma, A. Morphological self-organization by dewetting in thin films on chemically patterned substrates. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 3042–3051 (2002).
Rascon, C. & Parry, A.O. Surface phase diagrams for wetting on heterogenous substrates. J. Chem. Phys. 115, 5258–5271 (2001).
Darhuber, A.A., Troian, S.M., Miller, S.M. & Wagner, S. Morphology of liquid microstructures on chemically patterned surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 7768–7775 (2000).
Bauer, C. & Dirtrich, S. Phase diagram for morphological transitions of wetting films on chemically structured substrates. Phys. Rev. E. 61, 1664–1669 (2000).
Schneemilch, M., Quirke, N. & Henderson, J.R. Wetting of nanopatterned surfaces: the striped surface. J. Chem. Phys. 118, 816–829 (2003).
Maboudian, R., Robert, A.W. & Carraro, C. Self-assembled monolayers as anti-stiction coatings for MEMS: characteristics and recent developments. Sens. Actuat. 82, 219–223 (2000).
Srinivasan, U., Houston, M.R., Howe, R.T. & Maboudian, R. Alkyltrichlorosilane-based self-assembled monolayer films for stiction reduction in silicon micromachines. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 7, 252–260 (1998).
Bong, H.K. et al. A new organic modifier for anti-stiction. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 10, 33–40 (2001).
Salleo, A., Chabinyc, M.L., Yang, M.S. & Street, R.A. Polymer thin-film transistors with chemically modified dielectric interfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4383–4385 (2002).
Sirringhaus, H. et al. Mobility enhancement in conjugated polymer field-effect transistors through chain alignment in a liquid-crystalline phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 406–408 (2000).
Grell, M., Bradley, D.D.C., Ungar, G., Hill, J. & Whitehead, K.S. Interplay of physical structure and photophysics for a liquid crystalline polyfluorene. Macromolecules 32, 5810–5817 (1999).
Sirringhaus, H. et al. Two-dimensional charge transport in self-organized, high-mobility conjugated polymers. Nature 401, 685–688 (1999).
Collet, J. & Vuillaume, D. Nano-field effect transistor with an organic self-assembled monolayer as gate insulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2681–2683 (1998).
Collet, J., Tharaud, O., Chapoton, A. & Vuillaume, D. Low-voltage, 30 nm channel length, organic transistors with a self-assembled monolayer as gate insulating films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1941–1943 (2000).
Austin, M.D. & Chou, S.Y. Fabrication of 70 nm channel length polymer organic thin-film transistors using nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4431–4433 (2002).
Zaumseil, J. et al. Nanoscale organic transistors that use source/drain electrodes supported by high resolution rubber stamps. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 793–795 (2003).
Stutzmann, N., Friend, R.H. & Sirringhaus, H. Self-aligned, vertical-channel, polymer field-effect transistors. Science 299, 1881–1884 (2003).
Gelinck, G.H., Geuns, T.C.T. & de Leeuw, D.M. High-performance all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1487–1489 (2000).
Halik, M. et al. Fully patterned all-organic thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 289–291 (2002).
Touwslager, F.J., Willard, N.P. & de Leeuw, D.M. I-Line lithography of poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) electrodes and application in all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4556–4558 (2002).
Blanchet, G.B., Loo, Y.L., Rogers, J.A., Gao, F. & Fincher, C.R. Large area, high resolution, dry printing of conducting polymers for organic electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 463–465 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Dow Chemical Company for supply of semiconducting polymers, and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zheng, Z., Li, H. et al. Dewetting of conducting polymer inkjet droplets on patterned surfaces. Nature Mater 3, 171–176 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1073
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1073
This article is cited by
-
Laser printed microelectronics
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Self-assembly of highly ordered micro- and nanoparticle deposits
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Influence of Fundamental Parameters on the Intrinsic Voltage Gain of Organic Thin Film Transistors
Electronic Materials Letters (2021)
-
Quantifying defects in thin films using machine vision
npj Computational Materials (2020)
-
Control and Patterning of Various Hydrophobic Surfaces: In-situ Modification Realized by Flexible Atmospheric Plasma Stamp Technique
Journal of Bionic Engineering (2020)