Abstract
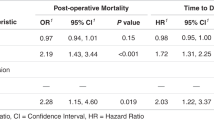
The p53 alteration is the most common alteration found in human cancer. It usually involves missense mutations that stabilize the p53 protein, which in turn accumulates, reaching levels detectable by immunohistochemistry. We1–4 and others5–8 have demonstrated that this overexpression of mutant p53 protein can induce a specific humoral response in cancer patients. This result was assessed by the presence of p53 antibodies in sera of patients with various types of cancers, whereas normal populations do not exhibit such antibodies. In lung cancer, the prevalence of p53 antibodies is high (30%) and is correlated with a very high rate of p53 mutations in this cancer (60–70%)2,8. We show that these antibodies are always present at the time of diagnosis, but never appear during tumour development, an observation strengthened by the fact that these antibodies are mostly IgG, corresponding to a secondary immune response. These results suggest that the humoral response is an early event and that p53 antibodies can be used as a precocious marker of p53 alteration before clinical manifestation of the disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlichtholz, B. et al. The immune response to p53 in breast cancer patients is directed against immunodominant epitopes unrelated to the mutational hot spot. Cancer Res. 52, 6380–6384 (1992).
Schlichtholz, B. et al. Analyses of p53 antibodies in sera of patients with lung carcinoma define immunodominant regions in the p53 protein. Br. J. Cancer 69, 809–816 (1994).
Lubin, R. et al. Analysis of p53 antibodies in patients with various cancers define B-cell epitopes of human p53—distribution on primary structure and exposure on protein surface. Cancer Res. 53, 5872–5876 (1993).
Peyrat, J.P. et al. Prognostic significance of circulating p53 antibodies in patients undergoing surgery for locoregional breast cancer. Lancet 345, 621–622 (1995).
Angelopoulou, K., Diamandis, E.P., Sutherland, D.J.A., Kellen, J.A. & Bunting, P.S. Prevalence of serum antibodies against the p53 tumor suppressor gene protein in various cancers. Int. J. Cancer 58, 480–487 (1994).
Davidoff, A.M., Iglehart, J.D. & Marks, J.R. Immune response to p53 is dependent upon p53/HSP70 complexes in breast cancers. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 3439–3442 (1992).
Crawford, L.V., Pim, D.C. & Bulbrook, R.D. Detection of antibodies against the cellular protein p53 in sera from patients with breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 30, 403–408 (1982).
Winter, S.F. et al. Development of antibodies against p53 in lung cancer patients appears to be dependent on the type of p53 mutation. Cancer Res. 52, 4168–4174 (1992).
Sundaresan, V. et al. p53 and chromosome 3 abnormalities, characteristic of malignant lung tumours, are detectable in preinvasive lesions of the bronchus. Oncogene 7, 1989–1997 (1992).
Bennett, W.P. et al. p53 protein accumulates frequently in early bronchial neoplasia. Cancer Res. 53, 4817–4822 (1993).
Mao, L., Hruban, R.H., Boyle, J.O., Tockman, M. & Sidransky, D. Detection of oncogene mutations in sputum precedes diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancer Res. 54, 1634–1637 (1994).
Idhe, D.C. & Minna, J.D. Non-small cell lung cancer. Part I: Biology, diagnosis and staging. Curr. Probl. Cancer 15, 65–147 (1991).
Tenaud, C. et al. Methods in pathology—p53 immunolabeling in archival paraffin-embedded tissues: Optimal protocol based on microwave heating for eight antibodies on lung carcinomas. Modern Pathol. 7, 853–859 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubin, R., Zalcman, G., Bouchet, L. et al. Serum p53 antibodies as early markers of lung cancer. Nat Med 1, 701–702 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0795-701
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0795-701
This article is cited by
-
An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for p53 antibody based on Zn-MOF/GO nanocomposite and Ag+-DNA amplification
Microchimica Acta (2020)
-
Autoantibodies as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer: A systematic review
Cell Death Discovery (2019)
-
Similarity of autoimmune diseases based on the profile of immune complex antigens
Rheumatology International (2019)
-
NY-ESO-1 autoantibody as a tumor-specific biomarker for esophageal cancer: screening in 1969 patients with various cancers
Journal of Gastroenterology (2016)
-
Prognostic role of serum p53 antibodies in lung cancer
BMC Cancer (2015)