Abstract
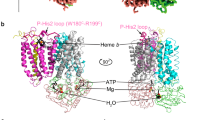
Copper is essential for proper functioning of cytochrome c oxidases, and therefore for cellular respiration in eukaryotes and many bacteria. Here we show that a new periplasmic protein (PCuAC) selectively inserts Cu(I) ions into subunit II of Thermus thermophilus ba3 oxidase to generate a native CuA site. The purported metallochaperone Sco1 is unable to deliver copper ions; instead, it works as a thiol-disulfide reductase to maintain the correct oxidation state of the CuA cysteine ligands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostermeier, C., Iwata, S. & Michel, H. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6, 460–466 (1996).
Maneg, O., Malatesta, F., Ludwig, B. & Drosou, V. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1655, 274–281 (2004).
Carr, H.S. & Winge, D.R. Acc. Chem. Res. 36, 309–316 (2003).
Cobine, P.A., Pierrel, F. & Winge, D.R. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 759–772 (2006).
Banci, L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3994–3999 (2005).
Khalimonchuk, O. & Winge, D.R. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1783, 618–628 (2008).
Banci, L., Bertini, I., Cavallaro, G. & Rosato, A. J. Proteome Res. 6, 1568–1579 (2007).
Horng, Y.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 34113–34122 (2005).
McEwan, A.G. et al. FEBS Lett. 518, 10–16 (2002).
Andruzzi, L., Nakano, M., Nilges, M.J. & Blackburn, N.J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 16548–16558 (2005).
Imriskova-Sosova, I. et al. Biochemistry 44, 16949–16956 (2005).
Banci, L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8595–8600 (2006).
Williams, J.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 15202–15211 (2005).
Balatri, E., Banci, L., Bertini, I., Cantini, F. & Ciofi-Baffoni, S. Structure 11, 1431–1443 (2003).
Ye, Q., Imriskova-Sosova, I., Hill, B.C. & Jia, Z. Biochemistry 44, 2934–2942 (2005).
Abajian, C. & Rosenzweig, A.C. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 11, 459–466 (2006).
Bertini, I. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 11658–11659 (1996).
Arnesano, F., Banci, L., Bertini, I. & Martinelli, M. J. Proteome Res. 4, 63–70 (2005).
Mattatall, N.R., Jazairi, J. & Hill, B.C. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 28802–28809 (2000).
Banci, L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15–20 (2007).
Banci, L. et al. Structure 15, 1132–1140 (2007).
Banci, L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 6803–6808 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Commission (European Network of Research Infrastructures for Providing Access and Technological Advancements in Bio-NMR contract n° 026145, SPINE2-Complexes contract n° LSHG-CT-2006-031220 and Marie Curie host fellowships for early stage research training n° MEST-CT-2004-504391, NMR in Inorganic Structural Biology) and by a grant from Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze. Work in Rosario (Argentina) was supported by the US National Institutes of Health (R01-GM068682), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PME2003-0026 and PICT2002-01-11625) grants to A.J.V. L.A.A. thanks Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científícas y Técnicas for a doctoral fellowship. We thank D. Winge (Departments of Medicine and Biochemistry, University of Utah Health Sciences Center, University of Utah) for kindly providing the expression plasmid for Tt Sco1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.A.A. cloned and expressed Tt Sco1 and Tt CuA proteins and contributed to the NMR structure of Tt Sco1 and NMR titrations; P.G. cloned and expressed PCuAC protein and performed redox experiments; S.W. solved the structures of PCuAC and contributed to the NMR titrations and NMR structure of Tt Sco1; S.C.-B. supervised and coordinated the acquisition of NMR data and structures, and the performance of titration experiments; I.B., L.B., G.A.S. and A.J.V. developed and directed the project and contributed to the writing. All authors were involved in the discussion of the biochemical meaning of the experiments.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Supplementary Tables 1–3, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Data (PDF 1714 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abriata, L., Banci, L., Bertini, I. et al. Mechanism of CuA assembly. Nat Chem Biol 4, 599–601 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.110
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.110