Abstract
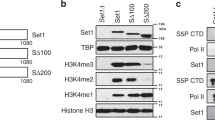
Mono-ubiquitylation of histone H2B correlates with transcriptional activation and is required for di- and trimethylation at Lys 4 on the histone H3 tail (H3K4) by the SET1/COMPASS methyltransferase complex through a poorly characterized trans-tail pathway1,2. Here we show that mono-ubiquitylation of histone H2B promotes ubiquitylation at Lys 68 and Lys 69 of Swd2, the essential component of SET1/COMPASS in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We found that Rad6/Bre1 ubiquitylation enzymes responsible for H2B ubiquitylation also participate directly in Swd2 modification. Preventing Swd2 or H2B ubiquitylation did not affect Set1 stability, interaction of Swd2 with Set1 or the ability of Swd2 to interact with chromatin. However, we found that mutation of Lys 68 and Lys 69 of Swd2 markedly reduced trimethylation, and to a lesser extent dimethylation, of H3K4 at the 5′-end of transcribing genes without affecting monomethylation. This effect results from the ability of Swd2 ubiquitylation to control recruitment of Spp1, a COMPASS subunit necessary for trimethylation. Our results further indicate that Swd2 is a major H3-binding component of COMPASS. Swd2 thus represents a key factor that mediates crosstalk between H2B ubiquitylation and H3K4 trimethylation on chromatin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger, S. L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447, 407–412 (2007).
Li, B., Carey, M., & Workman, J. L. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell 128, 707–719 (2007).
Dover, J. et al. Methylation of histone H3 by COMPASS requires ubiquitination of histone H2B by Rad6. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28368–28371 (2002).
Sun, Z. W. & Allis, C. D. Ubiquitination of histone H2B regulates H3 methylation and gene silencing in yeast. Nature 418, 104–108 (2002).
Dehe, P. M. et al. Histone H3 lysine 4 mono-methylation does not require ubiquitination of histone H2B. J. Mol. Biol. 353, 477–484 (2005).
Shahbazian, M. D., Zhang, K., & Grunstein, M. Histone H2B ubiquitylation controls processive methylation but not monomethylation by Dot1 and Set1. Mol. Cell 19, 271–277 (2005).
Ezhkova, E. & Tansey, W. P. Proteasomal ATPases link ubiquitylation of histone H2B to methylation of histone H3. Mol. Cell 13, 435–442 (2004).
Laribee, R. N. et al. CCR4/NOT complex associates with the proteasome and regulates histone methylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 5836–5841 (2007).
Mulder, K. W., Brenkman, A. B., Inagaki, A., van den Broek, N. J., & Marc Timmers, H. T. Regulation of histone H3K4 tri-methylation and PAF complex recruitment by the Ccr4-Not complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 2428–2439 (2007).
Ng, H. H., Robert, F., Young, R. A., & Struhl, K. Targeted recruitment of Set1 histone methylase by elongating Pol II provides a localized mark and memory of recent transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell 11, 709–719 (2003).
Krogan, N. J. et al. The Paf1 complex is required for histone H3 methylation by COMPASS and Dot1p: linking transcriptional elongation to histone methylation. Mol. Cell 11, 721–729 (2003).
Dehe, P. M. & Geli, V. The multiple faces of Set1. Biochem. Cell Biol. 84, 536–548 (2006).
Cheng, H., He, X., & Moore, C. The essential WD repeat protein Swd2 has dual functions in RNA polymerase II transcription termination and lysine 4 methylation of histone H3. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 2932–2943 (2004).
Dichtl, B., Aasland, R., & Keller, W. Functions for S. cerevisiae Swd2p in 3′ end formation of specific mRNAs and snoRNAs and global histone 3 lysine 4 methylation. RNA 10, 965–977 (2004).
Lee, J. S. et al. Histone crosstalk between H2B monoubiquitination and H3 methylation mediated by COMPASS. Cell 131, 1084–1096 (2007).
Nedea, E. et al. The Glc7 phosphatase subunit of the cleavage and polyadenylation factor is essential for transcription termination on snoRNA genes. Mol. Cell 29, 577–587 (2008).
Gwizdek, C. et al. The mRNA nuclear export factor Hpr1 is regulated by Rsp5-mediated ubiquitylation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 13401–13405 (2005).
Pickart, C. M. & Eddins, M. J. Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1695, 55–72 (2004).
Wood, A. et al. Bre1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase required for recruitment and substrate selection of Rad6 at a promoter. Mol. Cell 11, 267–274 (2003).
Hwang, W. W. et al. A conserved RING finger protein required for histone H2B monoubiquitination and cell size control. Mol. Cell 11, 261–266 (2003).
Robzyk, K., Recht, J., & Osley, M. A. Rad6-dependent ubiquitination of histone H2B in yeast. Science 287, 501–504 (2000).
Alber, F. et al. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature 450, 683–694 (2007).
Dehe, P. M. et al. Protein interactions within the Set1 complex and their roles in the regulation of histone 3 lysine 4 methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 35404–35412 (2006).
Morillon, A., Karabetsou, N., Nair, A., & Mellor, J. Dynamic lysine methylation on histone H3 defines the regulatory phase of gene transcription. Mol. Cell 18, 723–734 (2005).
Shi, X. et al. Proteome-wide analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identifies several PHD fingers as novel direct and selective binding modules of histone H3 methylated at either lysine 4 or lysine 36. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 2450–2455 (2007).
Couture, J. F., Collazo, E., & Trievel, R. C. Molecular recognition of histone H3 by the WD40 protein WDR5. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 698–703 (2006).
Ruthenburg, A. J. et al. Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 704–712 (2006).
Han, Z. et al. Structural basis for the specific recognition of methylated histone H3 lysine 4 by the WD-40 protein WDR5. Mol. Cell 22, 137–144 (2006).
Schuetz, A. et al. Structural basis for molecular recognition and presentation of histone H3 by WDR5. EMBO J. 25, 4245–4252 (2006).
Wysocka, J. et al. WDR5 associates with histone H3 methylated at K4 and is essential for H3 K4 methylation and vertebrate development. Cell 121, 859–872 (2005).
Cohen, M., Stutz, F., Belgareh, N., Haguenauer-Tsapis, R., & Dargemont, C. Ubp3 requires a cofactor, Bre5, to specifically de-ubiquitinate the COPII protein, Sec23. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 661–667 (2003).
Gwizdek, C. et al. Ubiquitin-associated domain of Mex67 synchronizes recruitment of the mRNA export machinery with transcription. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 16376–16381 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank P. Nagy for antibodies, G. Divita for help with molecular modelling and V. Oreal for reagents. We are most grateful to S. Dokudovskaya and A. Morillon for very helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. This study was funded by grants from the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (grant BLAN06-1_134099 to CD) and the Ligue contre le Cancer (C.D. and V.G. laboratories are 'Equipes labellisées'). A.V.P. and M.H. are supported by the Ministère de l'Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche and the Association de Recherche contre le Cancer respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.G., V.G. and C.D. designed the experiments; A.V.P., A. M., M.H. and C.G. performed the experiments; A.V.P., A.M., M.H., C.G., V.G.and C.D. analysed the data; V.G. and C.D. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 826 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitaliano-Prunier, A., Menant, A., Hobeika, M. et al. Ubiquitylation of the COMPASS component Swd2 links H2B ubiquitylation to H3K4 trimethylation. Nat Cell Biol 10, 1365–1371 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1796
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1796
This article is cited by
-
The dynamics and functional mechanisms of H2B mono-ubiquitination
Crop Health (2024)
-
Diverse and dynamic forms of gene regulation by the S. cerevisiae histone methyltransferase Set1
Current Genetics (2023)
-
Trans-tail regulation-mediated suppression of cryptic transcription
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
The Set1 N-terminal domain and Swd2 interact with RNA polymerase II CTD to recruit COMPASS
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Normal transcription of cellulolytic enzyme genes relies on the balance between the methylation of H3K36 and H3K4 in Penicillium oxalicum
Biotechnology for Biofuels (2019)