Abstract
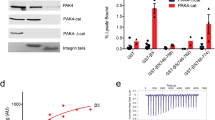
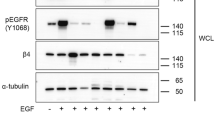
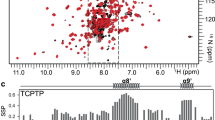
Integrin-mediated cell adhesion regulates a multitude of cellular responses, including proliferation, survival and cross-talk between different cellular signalling pathways1. So far, integrins have been mainly shown to convey permissive signals enabling anchorage-dependent receptor tyrosine kinase signalling2,3,4. Here we show that a collagen-binding integrin α1β1 functions as a negative regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signalling through the activation of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. The cytoplasmic tail of α1 integrin selectively interacts with a ubiquitously expressed protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP (T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase) and activates it after cell adhesion to collagen. The activation results in reduced EGFR phosphorylation after EGF stimulation. Introduction of the α1 cytoplasmic domain peptide into cells induces phosphatase activation and inhibits EGF-induced cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of malignant cells. These data are the first demonstration of the regulation of TCPTP activity in vivo and represent a new molecular paradigm of integrin-mediated negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signalling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hynes, R. O. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110, 673–687 (2002).
Ivaska, J., Bosca, L. & Parker, P. J. PKCε is a permissive link in integrin-dependent IFN-γ signalling that facilitates JAK phosphorylation of STAT1. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 363–369 (2003).
Miyamoto, S., Teramoto, H., Gutkind, J. S. & Yamada, K. M. Integrins can collaborate with growth factors for phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases and MAP kinase activation: roles of integrin aggregation and occupancy of receptors. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1633–1642 (1996).
Moro, L. et al. Integrins induce activation of EGF receptor: role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion-dependent cell survival. EMBO J. 17, 6622–6632 (1998).
Ivaska, J. et al. Integrin α2β1 promotes activation of protein phosphatase 2A and dephosphorylation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3 β. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 1352–1359 (2002).
Howe, A., Aplin, A. E., Alahari, S. K. & Juliano, R. L. Integrin signaling and cell growth control. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10, 220–231 (1998).
Ivaska, J. et al. Integrin α2β1 mediates isoform-specific activation of p38 and upregulation of collagen gene transcription by a mechanism involving the α2 cytoplasmic tail. J. Cell Biol. 147, 401–416 (1999).
Gardner, H., Kreidberg, J., Koteliansky, V. & Jaenisch, R. Deletion of integrin α1 by homologous recombination permits normal murine development but gives rise to a specific deficit in cell adhesion. Dev. Biol. 175, 301–313 (1996).
Mosinger, B., Jr., Tillmann, U., Westphal, H. & Tremblay, M. L. Cloning and characterization of a mouse cDNA encoding a cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 499–503 (1992).
Tiganis, T., Bennett, A. M., Ravichandran, K. S. & Tonks, N. K. Epidermal growth factor receptor and the adaptor protein p52Shc are specific substrates of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 1622–1634 (1998).
Liu, S., Calderwood, D. A. & Ginsberg, M. H. Integrin cytoplasmic domain-binding proteins. J. Cell. Sci. 113, 3563–3571 (2000).
Pankov, R. et al. Specific β1 integrin site selectively regulates Akt/protein kinase B signaling via local activation of protein phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 18671–18681 (2003).
Persson, C. et al. Site-selective regulation of platelet-derived growth factor β receptor tyrosine phosphorylation by T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 2190–2201 (2004).
Galic, S. et al. Regulation of insulin receptor signaling by the protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 2096–2108 (2003).
Simoncic, P. D., Lee-Loy, A., Barber, D. L., Tremblay, M. L. & McGlade, C. J. The T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase is a negative regulator of janus family kinases 1 and 3. Curr. Biol. 12, 446–453 (2002).
Hao, L., Tiganis, T., Tonks, N. K. & Charbonneau, H. The noncatalytic C-terminal segment of the T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase regulates activity via an intramolecular mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29322–29329 (1997).
Alonso, A. et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117, 699–711 (2004).
Tiganis, T., Kemp, B. E. & Tonks, N. K. The protein-tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP regulates epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 27768–27775 (1999).
Pozzi, A., Wary, K. K., Giancotti, F. G. & Gardner, H. A. Integrin α1β1 mediates a unique collagen-dependent proliferation pathway in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 142, 587–594 (1998).
Cool, D. E. et al. Cytokinetic failure and asynchronous nuclear division in BHK cells overexpressing a truncated protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5422–5426 (1992).
Cool, D. E., Tonks, N. K., Charbonneau, H., Fischer, E. H. & Krebs, E. G. Expression of a human T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7280–7284 (1990).
Klingler-Hoffmann, M. et al. The protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP suppresses the tumorigenicity of glioblastoma cells expressing a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 46313–46318 (2001).
Moro, L. et al. Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9405–9414 (2002).
Pan, Y. et al. 5q11, 8p11, and 10q22 are recurrent chromosomal breakpoints in prostate cancer cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 30, 187–195 (2001).
Zienolddiny, S., Ryberg, D., Arab, M. O., Skaug, V. & Haugen, A. Loss of heterozygosity is related to p53 mutations and smoking in lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 84, 226–231 (2001).
Su, A. I. et al. Molecular classification of human carcinomas by use of gene expression signatures. Cancer Res. 61, 7388–7393 (2001).
Flint, A. J., Tiganis, T., Barford, D. & Tonks, N. K. Development of “substrate-trapping” mutants to identify physiological substrates of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci USA 94, 1680–1685 (1997).
Ivaska, J., Whelan, R. D., Watson, R. & Parker, P. J. PKCε controls the traffic of β1 integrins in motile cells. EMBO J. 21, 3608–3619 (2002).
Kim, T. Y. et al. Oncogenic potential of a dominant negative mutant of interferon regulatory factor 3. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 15272–15278 (2003).
Gardner, H., Broberg, A., Pozzi, A., Laato, M. & Heino, J. Absence of integrin α1β1 in the mouse causes loss of feedback regulation of collagen synthesis in normal and wounded dermis. J. Cell Sci. 112, 263–272 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. J. Parker and M. Salmi for valuable comments; T. Tiganis for the TC45 construct; A. Pozzi for the α1 integrin construct; J. Durgan for help with the yeast-two-hybrid assay; C. Nylund for the RT–PCR analysis; S. Käkönen for help with the statistical analysis; J. Heino for the peptides and the α1−/− and α1+/+ fibroblasts; and H. Jalonen, P. Toivonen and A. Raita for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Academy of Finland, the Sigrid Juselius Foundation, Emil Aaltonen Foundation, Finnish Cancer Organisations and Southwestern Finland's Culture Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Fig S1, Fig S2, Fig S3, Fig S4 (PDF 386 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattila, E., Pellinen, T., Nevo, J. et al. Negative regulation of EGFR signalling through integrin-α1β1-mediated activation of protein tyrosine phosphatase TCPTP. Nat Cell Biol 7, 78–85 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1209
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1209
This article is cited by
-
Targeting protein phosphatases in cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune disorders
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2023)
-
The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Identification of X-chromosomal genes that drive sex differences in embryonic stem cells through a hierarchical CRISPR screening approach
Genome Biology (2021)
-
Rapid whole cell imaging reveals a calcium-APPL1-dynein nexus that regulates cohort trafficking of stimulated EGF receptors
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Identification of eQTLs and sQTLs associated with meat quality in beef
BMC Genomics (2020)