Abstract
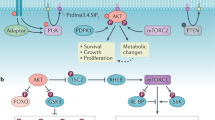
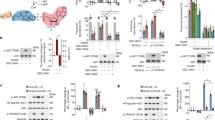
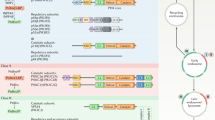
The eight catalytic subunits of the mammalian phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase (PI(3)K) family form the backbone of an evolutionarily conserved signalling pathway; however, the roles of most PI(3)K isoforms in organismal physiology and disease are unknown. To delineate the role of p110α, a ubiquitously expressed PI(3)K involved in tyrosine kinase and Ras signalling, here we generated mice carrying a knockin mutation (D933A) that abrogates p110α kinase activity. Homozygosity for this kinase-dead p110α led to embryonic lethality. Mice heterozygous for this mutation were viable and fertile, but displayed severely blunted signalling via insulin-receptor substrate (IRS) proteins, key mediators of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1 and leptin action. Defective responsiveness to these hormones led to reduced somatic growth, hyperinsulinaemia, glucose intolerance, hyperphagia and increased adiposity in mice heterozygous for the D933A mutation. This signalling function of p110α derives from its highly selective recruitment and activation to IRS signalling complexes compared to p110β, the other broadly expressed PI(3)K isoform, which did not contribute to IRS-associated PI(3)K activity. p110α was the principal IRS-associated PI(3)K in cancer cell lines. These findings demonstrate a critical role for p110α in growth factor and metabolic signalling and also suggest an explanation for selective mutation or overexpression of p110α in a variety of cancers1,2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shayesteh, L. et al. PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nature Genet. 21, 99–102 (1999)
Samuels, Y. et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304, 554 (2004)
Vanhaesebroeck, B., Ali, K., Bilancio, A., Geering, B. & Foukas, L. C. Signalling by PI3K isoforms: Insights from gene-targeted mice. Trends Biochem. Sci. 30, 194–204 (2005)
Bi, L., Okabe, I., Bernard, D. J., Wynshaw-Boris, A. & Nussbaum, R. L. Proliferative defect and embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for a deletion in the p110α subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 10963–10968 (1999)
Bi, L., Okabe, I., Bernard, D. J. & Nussbaum, R. L. Early embryonic lethality in mice deficient in the p110β catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Mamm. Genome 13, 169–172 (2002)
Brachmann, S. M., Ueki, K., Engelman, J. A., Kahn, R. C. & Cantley, L. C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit deletion and regulatory subunit deletion have opposite effects on insulin sensitivity in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 1596–1607 (2005)
Fruman, D. A. et al. Hypoglycemia, liver necrosis and perinatal death in mice lacking all isoforms of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α. Nature Genet. 26, 379–382 (2000)
Dupont, J. & Holzenberger, M. Biology of insulin-like growth factors in development. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 69, 257–271 (2003)
Lawlor, M. A. et al. Essential role of PDK1 in regulating cell size and development in mice. EMBO J. 21, 3728–3738 (2002)
Kozma, S. C. & Thomas, G. Regulation of cell size in growth development and human disease: PI3K, PKB and S6K. Bioessays 24, 65–71 (2002)
Choudhury, A. I. et al. The role of insulin receptor substrate 2 in hypothalamic and β cell function. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 940–950 (2005)
Bouret, S. G., Draper, S. J. & Simerly, R. B. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 304, 108–110 (2004)
White, M. F. Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science 302, 1710–1711 (2003)
Niswender, K. D. et al. Intracellular signalling: Key enzyme in leptin-induced anorexia. Nature 413, 794–795 (2001)
Niswender, K. D. et al. Insulin activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: A key mediator of insulin-induced anorexia. Diabetes 52, 227–231 (2003)
Xu, A. W. et al. PI3K integrates the action of insulin and leptin on hypothalamic neurons. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 951–958 (2005)
Withers, D. J. Insulin receptor substrate proteins and neuroendocrine function. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 29, 525–529 (2001)
Cho, H. et al. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKBβ). Science 292, 1728–1731 (2001)
Wang, Q., Bilan, P. J., Tsakiridis, T., Hinek, A. & Klip, A. Actin filaments participate in the relocalization of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to glucose transporter-containing compartments and in the stimulation of glucose uptake in 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Biochem. J. 331, 917–928 (1998)
Asano, T. et al. p110β is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3–L1 cells and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17671–17676 (2000)
Roche, S., Downward, J., Raynal, P. & Courtneidge, S. A. A function for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase β (p85α-p110β) in fibroblasts during mitogenesis: Requirement for insulin- and lysophosphatidic acid-mediated signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 7119–7129 (1998)
Hooshmand-Rad, R. et al. The PI 3-kinase isoforms p110α and p110β have differential roles in PDGF- and insulin-mediated signaling. J. Cell Sci. 113, 207–214 (2000)
Jackson, S. P. et al. PI 3-kinase p110β: A new target for antithrombotic therapy. Nature Med. 11, 507–514 (2005)
Beeton, C. A., Chance, E. M., Foukas, L. C. & Shepherd, P. R. Comparison of the kinetic properties of the lipid- and protein-kinase activities of the p110α and p110β catalytic subunits of class-Ia phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Biochem. J. 350, 353–359 (2000)
Kurosu, H. et al. Heterodimeric phosphoinositide 3-kinase consisting of p85 and p110β is synergistically activated by the βγ subunits of G proteins and phosphotyrosyl peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24252–24256 (1997)
Kubo, H., Hazeki, K., Takasuga, S. & Hazeki, O. Specific role of p85/p110β in GTP-binding protein-mediated activation of Akt. Biochem. J. 392, 607–614 (2005)
Pollak, M. N., Schernhammer, E. S. & Hankinson, S. E. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 505–518 (2004)
Drees, B. E., Mills, G. B., Rommel, C. & Prestwich, G. D. Therapeutic potential of phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 14, 703–732 (2004)
Amaravadi, R. & Thompson, C. B. The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 2618–2624 (2005)
Klippel, A., Escobedo, J. A., Hirano, M. & Williams, L. T. The interaction of small domains between the subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase determines enzyme activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2675–2685 (1994)
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Camps, T. Ruckle, C. Rommel (Serono Pharmaceutical Research Institute) and PIramed for pharmacological agents; W. Fantl for antibody reagents; and T. Arnett and I. Orriss for providing access and help with the DEXA scanner. Personal support for L.F., M.C. and K.O. was provided in part by a European Union FP5 Programme grant, and for W.P. by a European Union grant. The main grant support for this project was by Diabetes UK and the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (to B.V.) and by the Wellcome Trust and MRC (to D.J.W.), with additional support of the Biotechnology and Biological Science Research Council (to B.V.). The ISCR Gene Targeting Laboratory was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Science Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Notes
This file contains Supplementary Figures and Legends 1–4, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Table 1. These provide a detailed description of the gene targeting strategy, organ and cell size measurements, additional data from glucose and insulin tolerance tests and a list of the organs subjected to histological examination. (PDF 200 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foukas, L., Claret, M., Pearce, W. et al. Critical role for the p110α phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase in growth and metabolic regulation. Nature 441, 366–370 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04694
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04694
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.