Abstract
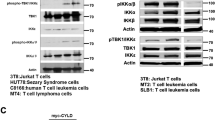
Constitutively active casein kinase 2 (CK2) signaling is a common feature of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). CK2 phosphorylates PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) tumor suppressor, resulting in PTEN stabilization and functional inactivation. Downregulation of PTEN activity has an impact on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling, which is of fundamental importance for T-ALL cell survival. These observations lend compelling weight to the application of CK2 inhibitors in the therapy of T-ALL. Here, we have analyzed the therapeutic potential of CX-4945—a novel, highly specific, orally available, ATP-competitive inhibitor of CK2α. We show that CX-4945 treatment induced apoptosis in T-ALL cell lines and patient T lymphoblasts. CX-4945 downregulated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in leukemic cells. Notably, CX-4945 affected the unfolded protein response (UPR), as demonstrated by a significant decrease in the levels of the main UPR regulator GRP78/BIP, and led to apoptosis via upregulation of the ER stress/UPR cell death mediators IRE1α and CHOP. In vivo administration of CX-4945 to a subcutaneous xenotransplant model of human T-ALL significantly delayed tumor growth. Our findings indicate that modulation of the ER stress/UPR signaling through CK2 inhibition could be exploited for inducing apoptosis in T-ALL cells and that CX-4945 may be an efficient treatment for those T-ALLs displaying upregulation of CK2α/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT . Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2008; 371: 1030–1043.
Van Vlierberghe P, Ferrando A . The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 3398–3406.
Jenkinson S, Koo K, Mansour MR, Goulden N, Vora A, Mitchell C et al. Impact of NOTCH1/FBXW7 mutations on outcome in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients treated on the MRC UKALL 2003 trial. Leukemia 2013; 27: 41–47.
Blackburn JS, Liu S, Raiser DM, Martinez SA, Feng H, Meeker ND et al. Notch signaling expands a pre-malignant pool of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia clones without affecting leukemia-propagating cell frequency. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2069–2078.
Lhermitte L, Ben Abdelali R, Villarese P, Bedjaoui N, Guillemot V, Trinquand A et al. Receptor kinase profiles identify a rationale for multitarget kinase inhibition in immature T-ALL. Leukemia 2013; 27: 305–314.
Cialfi S, Palermo R, Manca S, Checquolo S, Bellavia D, Pelullo M et al. Glucocorticoid sensitivity of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with glucocorticoid receptor-mediated inhibition of Notch1 expression. Leukemia 2013; 27: 485–488.
Malyukova A, Brown S, Papa R, O'Brien R, Giles J, Trahair TN et al. FBXW7 regulates glucocorticoid response in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by targeting the glucocorticoid receptor for degradation. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1053–1062.
Correia NC, Durinck K, Leite AP, Ongenaert M, Rondou P, Speleman F et al. Novel TAL1 targets beyond protein-coding genes: identification of TAL1-regulated microRNAs in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1603–1606.
Lv M, Zhang X, Jia H, Li D, Zhang B, Zhang H et al. An oncogenic role of miR-142-3p in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) by targeting glucocorticoid receptor-alpha and cAMP/PKA pathways. Leukemia 2012; 26: 769–777.
Ross JA, Spadaro M, Rosado DC, Cavallo F, Kirken RA, Pericle F . Inhibition of JAK3 with a novel, selective, and orally active small molecule induces therapeutic response in T-cell malignancies. Leukemia 2013; e-pub ahead of print 23 October 2013; doi:10.1038/leu.2013.309.
Koschmieder S, Burmeister T, Bruggemann M, Berkemeier A, Volpert S, Wieacker P et al. Molecular monitoring in NUP214-ABL-positive T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals clonal diversity and helps to guide targeted therapy. Leukemia 2014; 28: 419–422.
Guo F, Li J, Du W, Zhang S, O'Connor M, Thomas G et al. mTOR regulates DNA damage response through NF-kappaB-mediated FANCD2 pathway in hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2040–2046.
Pinna LA, Allende JE . Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: protein kinase CK2: an ugly duckling in the kinome pond. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 1795–1799.
Duncan JS, Turowec JP, Vilk G, Li SS, Gloor GB, Litchfield DW . Regulation of cell proliferation and survival: convergence of protein kinases and caspases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1804: 505–510.
Ruzzene M, Pinna LA . Addiction to protein kinase CK2: a common denominator of diverse cancer cells? Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1804: 499–504.
Trembley JH, Wang G, Unger G, Slaton J, Ahmed K . Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: CK2: a key player in cancer biology. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 1858–1867.
Piazza F, Manni S, Ruzzene M, Pinna LA, Gurrieri C, Semenzato G . Protein kinase CK2 in hematologic malignancies: reliance on a pivotal cell survival regulator by oncogenic signaling pathways. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1174–1179.
Piazza FA, Ruzzene M, Gurrieri C, Montini B, Bonanni L, Chioetto G et al. Multiple myeloma cell survival relies on high activity of protein kinase CK2. Blood 2006; 108: 1698–1707.
Kim JS, Eom JI, Cheong JW, Choi AJ, Lee JK, Yang WI et al. Protein kinase CK2alpha as an unfavorable prognostic marker and novel therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 1019–1028.
Silva A, Yunes JA, Cardoso BA, Martins LR, Jotta PY, Abecasis M et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3762–3774.
Mishra S, Pertz V, Zhang B, Kaur P, Shimada H, Groffen J et al. Treatment of P190 Bcr/Abl lymphoblastic leukemia cells with inhibitors of the serine/threonine kinase CK2. Leukemia 2007; 21: 178–180.
Prudent R, Moucadel V, Nguyen CH, Barette C, Schmidt F, Florent JC et al. Antitumor activity of pyridocarbazole and benzopyridoindole derivatives that inhibit protein kinase CK2. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 9865–9874.
Siddiqui-Jain A, Drygin D, Streiner N, Chua P, Pierre F, O'Brien SE et al. CX-4945, an orally bioavailable selective inhibitor of protein kinase CK2, inhibits prosurvival and angiogenic signaling and exhibits antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 10288–10298.
Pierre F, Chua PC, O'Brien SE, Siddiqui-Jain A, Bourbon P, Haddach M et al. Discovery and SAR of 5-(3-chlorophenylamino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 2011; 54: 635–654.
Barata JT . The impact of PTEN regulation by CK2 on PI3K-dependent signaling and leukemia cell survival. Adv Enzyme Regul 2011; 51: 37–49.
Kuznetsov JN, Leclerc GJ, Leclerc GM, Barredo JC . AMPK and Akt determine apoptotic cell death following perturbations of one-carbon metabolism by regulating ER stress in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 2011; 10: 437–447.
DeSalvo J, Kuznetsov JN, Du J, Leclerc GM, Leclerc GJ, Lampidis TJ et al. Inhibition of Akt potentiates 2-DG-induced apoptosis via downregulation of UPR in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 10: 969–978.
Wang S, Kaufman RJ . The impact of the unfolded protein response on human disease. J Cell Biol 2012; 197: 857–867.
Luo B, Lee AS . The critical roles of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and unfolded protein response in tumorigenesis and anticancer therapies. Oncogene 2013; 32: 805–818.
Manni S, Brancalion A, Tubi LQ, Colpo A, Pavan L, Cabrelle A et al. Protein kinase CK2 protects multiple myeloma cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis and from the cytotoxic effect of HSP90 inhibition through regulation of the unfolded protein response. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 1888–1900.
Grimaldi C, Chiarini F, Tabellini G, Ricci F, Tazzari PL, Battistelli M et al. AMP-dependent kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: therapeutic implications. Leukemia 2012; 26: 91–100.
Chou TC, Talalay P . Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 1984; 22: 27–55.
Simioni C, Neri LM, Tabellini G, Ricci F, Bressanin D, Chiarini F et al. Cytotoxic activity of the novel Akt inhibitor, MK-2206, in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2336–2342.
Evangelisti C, Ricci F, Tazzari P, Chiarini F, Battistelli M, Falcieri E et al. Preclinical testing of the Akt inhibitor triciribine in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Physiol 2011; 226: 822–831.
Passey S, Pellegrin S, Mellor H . Scanning electron microscopy of cell surface morphology. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 2007; 37: 4.17.1–4.17.13.
Silva A, Laranjeira AB, Martins LR, Cardoso BA, Demengeot J, Yunes JA et al. IL-7 contributes to the progression of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4780–4789.
Georgescu MM, Kirsch KH, Akagi T, Shishido T, Hanafusa H . The tumor-suppressor activity of PTEN is regulated by its carboxyl-terminal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 10182–10187.
Di Maira G, Salvi M, Arrigoni G, Marin O, Sarno S, Brustolon F et al. Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates and upregulates Akt/PKB. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 668–677.
Di Maira G, Brustolon F, Pinna LA, Ruzzene M . Dephosphorylation and inactivation of Akt/PKB is counteracted by protein kinase CK2 in HEK 293T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 3363–3373.
Soga S, Akinaga S, Shiotsu Y . Hsp90 inhibitors as anti-cancer agents, from basic discoveries to clinical development. Curr Pharm Des 2013; 19: 366–376.
Ayala F, Dewar R, Kieran M, Kalluri R . Contribution of bone microenvironment to leukemogenesis and leukemia progression. Leukemia 2009; 23: 2233–2241.
Evangelisti C, Ricci F, Tazzari P, Tabellini G, Battistelli M, Falcieri E et al. Targeted inhibition of mTORC1 and mTORC2 by active-site mTOR inhibitors has cytotoxic effects in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 781–791.
Hosoi T, Korematsu K, Horie N, Suezawa T, Okuma Y, Nomura Y et al. Inhibition of casein kinase 2 modulates XBP1-GRP78 arm of unfolded protein responses in cultured glial cells. PLoS One 2012; 7: e40144 doi:10.1371.
Jiang X, Kanda T, Tanaka T, Wu S, Nakamoto S, Imazeki F et al. Lipopolysaccharide blocks induction of unfolded protein response in human hepatoma cell lines. Immunol Lett 2013; 152: 8–15.
Leclerc GM, Leclerc GJ, Kuznetsov JN, DeSalvo J, Barredo JC . Metformin induces apoptosis through AMPK-dependent inhibition of UPR signaling in ALL lymphoblasts. PLoS One 2013; 8: e74420 doi:10.1371.
Walter P, Ron D . The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011; 334: 1081–1086.
Matsuo J, Tsukumo Y, Saito S, Tsukahara S, Sakurai J, Sato S et al. Hyperactivation of 4E-binding protein 1 as a mediator of biguanide-induced cytotoxicity during glucose deprivation. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 1082–1091.
Healy SJ, Gorman AM, Mousavi-Shafaei P, Gupta S, Samali A . Targeting the endoplasmic reticulum-stress response as an anticancer strategy. Eur J Pharmacol 2009; 625: 234–246.
Borgo C, Cesaro L, Salizzato V, Ruzzene M, Massimino ML, Pinna LA et al. Aberrant signalling by protein kinase CK2 in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia cells: Biochemical evidence and therapeutic perspectives. Mol Oncol 2013; 7: 1103–1115.
Prins RC, Burke RT, Tyner JW, Druker BJ, Loriaux MM, Spurgeon SE . CX-4945 a selective inhibitor of casein kinase-2 (CK2), exhibits anti-tumor activity in hematologic malignancies including enhanced activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia when combined with fludarabine and inhibitors of the B-cell receptor pathway. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2094–2096.
Martins LR, Lucio P, Melao A, Antunes I, Cardoso BA, Stansfield R et al. Activity of the clinical-stage CK2-specific inhibitor CX-4945 against chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2014; 28: 179–182.
Perea SE, Baladron I, Garcia Y, Perera Y, Lopez A, Soriano JL et al. CIGB-300, a synthetic peptide-based drug that targets the CK2 phosphoaceptor domain. Translational and clinical research. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 356: 45–50.
Shepherd C, Banerjee L, Cheung CW, Mansour MR, Jenkinson S, Gale RE et al. PI3K/mTOR inhibition upregulates NOTCH-MYC signalling leading to an impaired cytotoxic response. Leukemia 2013; 27: 650–660.
Hales EC, Orr SM, Larson Gedman A, Taub JW, Matherly LH . Notch1 receptor regulates AKT protein activation loop (Thr308) dephosphorylation through modulation of the PP2A phosphatase in phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-null T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 22836–22848.
O'Neill AK, Niederst MJ, Newton AC . Suppression of survival signalling pathways by the phosphatase PHLPP. FEBS J 2013; 280: 572–583.
St-Denis NA, Litchfield DW . Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: From birth to death: the role of protein kinase CK2 in the regulation of cell proliferation and survival. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 1817–1829.
Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, Soto N, Wei S, Jung SY et al. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell 2006; 127: 125–137.
Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hall MN . Bidirectional crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mTOR signaling. Trends Cell Biol 2012; 22: 274–282.
Schneider CC, Ampofo E, Montenarh M . CK2 regulates ATF4 and CHOP transcription within the cellular stress response signalling pathway. Cell Signal 2012; 24: 1797–1802.
Davenport EL, Moore HE, Dunlop AS, Sharp SY, Workman P, Morgan GJ et al. Heat shock protein inhibition is associated with activation of the unfolded protein response pathway in myeloma plasma cells. Blood 2007; 110: 2641–2649.
Acknowledgements
We thank Cylene Pharmaceuticals for generously providing CX-4945 for our in vivo studies. This work was supported by a grant from MIUR FIRB 2010 (RBAP10447J_003) to AMM and by grants PTDC/SAU-OBD/104816/2008 and PTDC/SAU-ONC/113202/2009 from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, to JTB. LRM and IA received FCT-SFRH PhD and Post-Doc fellowships, respectively. FL was supported by Special Project AIRC 5x1000 n. 9962 and Progetto di rilevante Interesse Nazionale, PRIN 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buontempo, F., Orsini, E., Martins, L. et al. Cytotoxic activity of the casein kinase 2 inhibitor CX-4945 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: targeting the unfolded protein response signaling. Leukemia 28, 543–553 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.349
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.349
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The chromosome 21 kinase DYRK1A: emerging roles in cancer biology and potential as a therapeutic target
Oncogene (2022)
-
Protein kinase CK2: a potential therapeutic target for diverse human diseases
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Influence of Casein kinase II inhibitor CX-4945 on BCL6-mediated apoptotic signaling in B-ALL in vitro and in vivo
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Notch3 contributes to T-cell leukemia growth via regulation of the unfolded protein response
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
Therapeutic targeting of CK2 in acute and chronic leukemias
Leukemia (2018)