Abstract
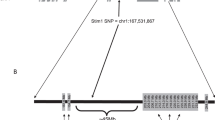
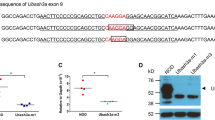
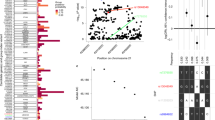
Gold or mercury salts trigger a dramatic IgE response and a CD4 T-cell-dependent nephropathy in Brown-Norway (BN), but not in Lewis (LEW) rats. We previously identified the 1.1-Mb Iresp3 (immunoglobin response QTL3) locus on chromosome 9 that controls these gold salt-triggered immune disorders. In the present work, we investigated the genetic control of HgCl2-induced immunological disorders and assessed the relative contribution of the CD45RChigh and CD45RClow CD4 T-cell subpopulations in this control. By using interval-specific congenic lines, we narrowed down Iresp3 locus to 117-kb and showed that BN rats congenic for the LEW 117-kb were protected from HgCl2-triggered IgE response and nephropathy. This 117-kb interval also controls CD45RC expression by CD4 T cells and the ability of CD45RChigh CD4 T cells to trigger the autoimmune disorders resulting from HgCl2 administration. This 117-kb region contains four genes, including Vav1, a strong candidate gene according to its cellular function and exclusive expression in hematopoietic cells. Thus, this study highlights the role of the CD45RChigh CD4 T-cell subpopulation in the opposite susceptibility of BN and LEW rats to HgCl2-triggered immune disorders and identifies a 117-kb interval on chromosome 9 that has a key role in their functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tubbs RR, Gephardt GN, McMahon JT, Pohl MC, Vidt DG, Barenberg SA et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis associated with industrial mercury exposure. Study of pathogenetic mechanisms. Am J Clin Pathol 1982; 77: 409–413.
Cardenas A, Roels H, Bernard AM, Barbon R, Buchet JP, Lauwerys RR et al. Markers of early renal changes induced by industrial pollutants. I Application to workers exposed to mercury vapour. Br J Ind Med 1993; 50: 17–27.
Moszczynski P, Slowinski S, Rutkowski J, Bem S, Jakus-Stoga D . Lymphocytes, T and NK cells, in men occupationally exposed to mercury vapours. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 1995; 8: 49–56.
Clarkson TW, Magos L, Myers GJ . The toxicology of mercury--current exposures and clinical manifestations. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1731–1737.
Rutowski J, Moszczynski P . Selected markers of subclinical renal damage in men occupationally exposed to mercury vapours. Przeglad Lekarski 2006; 63 (Suppl 7): 65–73.
Gardner RM, Nyland JF, Silva IA, Ventura AM, de Souza JM, Silbergeld EK . Mercury exposure, serum antinuclear/antinucleolar antibodies, and serum cytokine levels in mining populations in Amazonian Brazil: a cross-sectional study. Environ Res 2010; 110: 345–354.
Davis P, Ezeoke A, Munro J, Hobbs JR, Hughes GR . Immunological studies on the mechanism of gold hypersensitivity reactions. Br Med J 1973; 3: 676–678.
Bigazzi PE . Autoimmunity and heavy metals. Lupus 1994; 3: 449–453.
Lazar J, Moreno C, Jacob HJ, Kwitek AE . Impact of genomics on research in the rat. Genome Res 2005; 15: 1717–1728.
Jagodic M, Colacios C, Nohra R, Dejean AS, Beyeen AD, Khademi M et al. A role for VAV1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med 2009; 1: 10ra21.
Fournié GJ, Cautain B, Xystrakis E, Damoiseaux J, Mas M, Lagrange D et al. Cellular and genetic factors involved in the difference between Brown-Norway and Lewis rats to develop respectively type-2 and type-1 immune-mediated diseases. Immunol Rev 2001; 184: 145–160.
Druet E, Sapin C, Gunther E, Feingold N, Druet P . Mercuric chloride-induced anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies in the rat: genetic control. Eur J Immunol 1977; 7: 348–351.
Druet P, Druet E, Potdevin F, Sapin C . Immune type glomerulonephritis induced by HgCl2 in the Brown Norway rat. Annales d'immunologie 1978 129 C; 6: 777–792.
Prouvost-Danon A, Abadie A, Sapin C, Bazin H, Druet P . Induction of IgE synthesis and potentiation of anti-ovalbumin IgE antibody response by HgCl2 in the rat. J Immunol 1981; 126: 699–792.
Sapin C, Hirsch F, Delaporte JP, Bazin H, Druet P . Polyclonal IgE increase after HgCl2 injections in BN and LEW rats: a genetic analysis. Immunogenetics 1984; 20: 227–236.
Pelletier L, Hirsch F, Rossert J, Druet E, Druet P . Experimental mercury-induced glomerulonephritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol 1987; 9: 359–369.
Pelletier L, Pasquier R, Guettier C, Vial MC, Mandet C, Nochy D et al. HgC12 induces T and B cells to proliferate and differentiate in BN rats. Clin Exper Immunol 1988; 71: 336–342.
Pusey CD, Bowman C, Morgan A, Weetman AP, Hartley B, Lockwood CM . Kinetics and pathogenicity of autoantibodies induced by mercuric chloride in the brown Norway rat. Clin Exper Immunol 1990; 81: 76–82.
Pelletier L, Pasquier R, Rossert J, Vial MC, Mandet C, Druet P . Autoreactive T cells in mercury-induced autoimmunity. Ability to induce the autoimmune disease. J Immunol 1988; 140: 750–754.
Goldman M, Druet P, Gleichmann E . TH2 cells in systemic autoimmunity: insights from allogeneic diseases and chemically-induced autoimmunity. Immunol Today 1991; 12: 223–227.
Prigent P, Saoudi A, Pannetier C, Graber P, Bonnefoy JY, Druet P et al. Mercuric chloride, a chemical responsible for T helper cell (Th)2-mediated autoimmunity in brown Norway rats, directly triggers T cells to produce interleukin-4. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 1484–1489.
Gillespie KM, Qasim FJ, Tibbatts LM, Thiru S, Oliveira DB, Mathieson PW . Interleukin-4 gene expression in mercury-induced autoimmunity. Scand J Immunol 1995; 41: 268–272.
Gillespie KM, Saoudi A, Kuhn J, Whittle CJ, Druet P, Bellon B et al. Th1/Th2 cytokine gene expression after mercuric chloride in susceptible and resistant rat strains. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 2388–2392.
de Vries JE, Gauchat JF, Aversa GG, Punnonen J, Gascan H, Yssel H . Regulation of IgE synthesis by cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol 1991; 3: 851–858.
Tournade H, Guery JC, Pasquier R, Nochy D, Hinglais N, Guilbert B et al. Experimental gold-induced autoimmunity. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation: official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association—European Renal Association 1991; 6: 621–630.
Savignac M, Badou A, Delmas C, Subra JF, De Cramer S, Paulet P et al. Gold is a T cell polyclonal activator in BN and LEW rats but favors IL-4 expression only in autoimmune prone BN rats. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 2266–2276.
Mas M, Subra JF, Lagrange D, Pilipenko-Appolinaire S, Kermarrec N, Gauguier D et al. Rat chromosome 9 bears a major susceptibility locus for IgE response. Eur J Immunol 2000; 30: 1698–1705.
Mas M, Cavailles P, Colacios C, Subra JF, Lagrange D, Calise M et al. Studies of congenic lines in the Brown Norway rat model of Th2-mediated immunopathological disorders show that the aurothiopropanol sulfonate-induced immunological disorder (Aiid3) locus on chromosome 9 plays a major role compared to Aiid2 on chromosome 10. J Immunol 2004; 172: 6354–6361.
Subra JF, Cautain B, Xystrakis E, Mas M, Lagrange D, van der Heijden H et al. The balance between CD45RChigh and CD45RClow CD4 T cells in rats is intrinsic to bone marrow-derived cells and is genetically controlled. J Immunol 2001; 166: 2944–2952.
Xystrakis E, Bernard I, Dejean AS, Alsaati T, Druet P, Saoudi A . Alloreactive CD4 T lymphocytes responsible for acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease are contained within the CD45RChigh but not the CD45RClow subset. Eur J Immunol 2004; 34: 408–417.
Furuya T, Salstrom JL, McCall-Vining S, Cannon GW, Joe B, Remmers EF et al. Genetic dissection of a rat model for rheumatoid arthritis: significant gender influences on autosomal modifier loci. Hum Mol Genet 2000; 9: 2241–2250.
Griffiths MM, Wang J, Joe B, Dracheva S, Kawahito Y, Shepard JS et al. Identification of four new quantitative trait loci regulating arthritis severity and one new quantitative trait locus regulating autoantibody production in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 1278–1289.
Dahlman I, Jacobsson L, Glaser A, Lorentzen JC, Andersson M, Luthman H et al. Genome-wide linkage analysis of chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat identifies a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 9. J Immunol 1999; 162: 2581–2588.
Colacios C, Casemayou A, Dejean AS, Gaits-Iacovoni F, Pedros C, Bernard I et al. The p.Arg63Trp polymorphism controls Vav1 functions and Foxp3 regulatory T cell development. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 2183–2191.
Kemeny DM, Noble A, Holmes BJ, Diaz-Sanchez D . Immune regulation: a new role for the CD8+ T cell. Immunol Today 1994; 15: 107–110.
Castedo M, Pelletier L, Rossert J, Pasquier R, Villarroya H, Druet P . Mercury-induced autoreactive anti-class II T cell line protects from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by the bias of CD8+ antiergotypic cells in Lewis rats. J Exp Med 1993; 177: 881–889.
Field AC, Caccavelli L, Bloch MF, Bellon B . Regulatory CD8+ T cells control neonatal tolerance to a Th2-mediated autoimmunity. J Immunol 2003; 170: 2508–2515.
Bowman C, Mason DW, Pusey CD, Lockwood CM . Autoregulation of autoantibody synthesis in mercuric chloride nephritis in the Brown Norway rat. I. A role for T suppressor cells. Eur J Immunol 1984; 14: 464–470.
Mathieson PW, Stapleton KJ, Oliveira DB, Lockwood CM . Immunoregulation of mercuric chloride-induced autoimmunity in Brown Norway rats: a role for CD8+ T cells revealed by in vivo depletion studies. Eur J Immunol 1991; 21: 2105–2109.
Roos A, Schilder-Tol EJ, Weening JJ, Aten J . Strong expression of CD134 (OX40), a member of the TNF receptor family, in a T helper 2-type cytokine environment. J Leukoc Biol 1998; 64: 503–510.
Mirtcheva J, Pfeiffer C, De Bruijn JA, Jacquesmart F, Gleichmann E . Immunological alterations inducible by mercury compounds. III. H-2A acts as an immune response and H-2E as an immune ‘suppression’ locus for HgCl2-induced antinucleolar autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol 1989; 19: 2257–2261.
Aten J, Veninga A, De Heer E, Rozing J, Nieuwenhuis P, Hoedemaeker PJ et al. Susceptibility to the induction of either autoimmunity or immunosuppression by mercuric chloride is related to the major histocompatibility complex class II haplotype. Eur J Immunol 1991; 21: 611–616.
Hultman P, Turley SJ, Enestrom S, Lindh U, Pollard KM . Murine genotype influences the specificity, magnitude and persistence of murine mercury-induced autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 1996; 9: 139–149.
Kermarrec N, Dubay C, De Gouyon B, Blanpied C, Gauguier D, Gillespie K et al. Serum IgE concentration and other immune manifestations of treatment with gold salts are linked to the MHC and IL4 regions in the rat. Genomics 1996; 31: 111–114.
Abedi-Valugerdi M, Moller G . Contribution of H-2 and non-H-2 genes in the control of mercury-induced autoimmunity. Int Immunol 2000; 12: 1425–1430.
Kono DH, Park MS, Szydlik A, Haraldsson KM, Kuan JD, Pearson DL et al. Resistance to xenobiotic-induced autoimmunity maps to chromosome 1. J Immunol 2001; 167: 2396–2403.
Spickett GP, Brandon MR, Mason DW, Williams AF, Woollett GR . MRC OX-22, a monoclonal antibody that labels a new subset of T lymphocytes and reacts with the high molecular weight form of the leukocyte-common antigen. J Exp Med 1983; 158: 795–810.
Powrie F, Mason D . OX-22high CD4+ T cells induce wasting disease with multiple organ pathology: prevention by the OX-22low subset. J Exp Med 1990; 172: 1701–1708.
Fowell D, Mason D . Evidence that the T cell repertoire of normal rats contains cells with the potential to cause diabetes. Characterization of the CD4+ T cell subset that inhibits this autoimmune potential. J Exp Med 1993; 177: 627–636.
Powrie F, Correa-Oliveira R, Mauze S, Coffman RL . Regulatory interactions between CD45RBhigh and CD45RBlow CD4+ T cells are important for the balance between protective and pathogenic cell-mediated immunity. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 589–600.
Mason D, Powrie F . Control of immune pathology by regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Immunol 1998; 10: 649–655.
Mathieson PW, Thiru S, Oliveira DB . Regulatory role of OX22high T cells in mercury-induced autoimmunity in the brown Norway rat. J Exp Med 1993; 177: 1309–1316.
Grunig G, Corry DB, Leach MW, Seymour BW, Kurup VP, Rennick DM . Interleukin-10 is a natural suppressor of cytokine production and inflammation in a murine model of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 1089–1099.
Cohn L, Homer RJ, Niu N, Bottomly K . T helper 1 cells and interferon gamma regulate allergic airway inflammation and mucus production. J Exp Med 1999; 190: 1309–1318.
Powrie F, Mason D . The MRC OX-22- CD4+ T cells that help B cells in secondary immune responses derive from naive precursors with the MRC OX-22+ CD4+ phenotype. J Exp Med 1989; 169: 653–662.
Bell EB, Sparshott SM, Bunce C . CD4+ T-cell memory, CD45R subsets and the persistence of antigen--a unifying concept. Immunol Today 1998; 19: 60–64.
Bell EB, Hayes S, McDonagh M, Bunce C, Yang C, Sparshott SM . Both CD45R(low) and CD45R(high) ‘revertant’ CD4 memory T cells provide help for memory B cells. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 1685–1695.
Seddon B, Mason D . Regulatory T cells in the control of autoimmunity: the essential role of transforming growth factor beta and interleukin 4 in the prevention of autoimmune thyroiditis in rats by peripheral CD4(+)CD45RC- cells and CD4(+)CD8(-) thymocytes. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 279–288.
Rickert RC . Regulation of B lymphocyte activation by complement C3 and the B cell coreceptor complex. Curr Opin Immunol 2005; 17: 237–243.
Pekkarinen PT, Vaali K, Junnikkala S, Rossi LH, Tuovinen H, Meri S et al. A functional complement system is required for normal T helper cell differentiation. Immunobiology 2011; 216: 737–743.
Sohn JH, Bora PS, Suk HJ, Molina H, Kaplan HJ, Bora NS . Tolerance is dependent on complement C3 fragment iC3b binding to antigen-presenting cells. Nat Med 2003; 9: 206–212.
La Flamme AC, MacDonald AS, Huxtable CR, Carroll M, Pearce EJ . Lack of C3 affects Th2 response development and the sequelae of chemotherapy in schistosomiasis. J Immunol 2003; 170: 470–476.
Drouin SM, Corry DB, Kildsgaard J, Wetsel RA . Cutting edge: the absence of C3 demonstrates a role for complement in Th2 effector functions in a murine model of pulmonary allergy. J Immunol 2001; 167: 4141–4145.
Capron M, Bascou C, Vial MC, Grossetete J, Hinglais N, Girard JF et al. Effects of decomplementation on mercuric chloride-induced glomerulonephritis in Brown-Norway rats. Clin Exp Immunol 1982; 49: 611–617.
Cauvi DM, Toomey CB, Pollard KM . Depletion of complement does not impact initiation of xenobiotic-induced autoimmune disease. Immunology 2012; 135: 333–343.
Tybulewicz VL, Ardouin L, Prisco A, Reynolds LF . Vav1: a key signal transducer downstream of the TCR. Immunol Rev 2003; 192: 42–52.
Katzav S . Vav1: an oncogene that regulates specific transcriptional activation of T cells. Blood 2004; 103: 2443–2451.
Wakeland E, Morel L, Achey K, Yui M, Longmate J . Speed congenics: a classic technique in the fast lane (relatively speaking). Immunol Today 1997; 18: 472–477.
Tacke M, Hanke G, Hanke T, Hunig T . CD28-mediated induction of proliferation in resting T cells in vitro and in vivo without engagement of the T cell receptor: evidence for functionally distinct forms of CD28. Eur J Immunol 1997; 27: 239–247.
Cautain B, Damoiseaux J, Bernard I, Xystrakis E, Fournie E, van Breda Vriesman P et al. The CD8 T cell compartment plays a dominant role in the deficiency of Brown-Norway rats to mount a proper type 1 immune response. J Immunol 2002; 168: 162–170.
Druet E, Praddaude F, Druet P, Dietrich G . Non-immunoglobulin serum proteins prevent the binding of IgG from normal rats and from rats with Th2-mediated autoimmune glomerulonephritis to various autoantigens including glomerular antigens. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 183–192.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Daniel Dunia, Anne S Dejean and Philippe Druet for their critical comments on the manuscript. We would also like to thank Fatima L’Faqihi, Valérie Duplan-Eche and Delphine Lestrade from the flow-cytometry core facility (CPTP), the animal house staff members and the histopathology core facility for their technical assistance (UMS 06). This work was supported by INSERM, the Arthritis Fondation Courtin, Association Française contre les Myopathies, Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-08-GENO-041-01), Association de Recherche sur la Sclérose En Plaques, Région Midi-Pyrénées and Fight-MG (FP7-Health-2009-242210). CP is supported by grants from Ministère de l'Education Nationale, de la Recherche et de la Technologie and from Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale. AS is supported by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique GJF, IB and DL by INSERM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author contributions
CP, OP, CC, AS and GJF conceived and designed the experiments. CP, OP, CC, AC, IB, VG, DL, BM and OA performed the experiments. CP OP, CC, IB and OA analyzed the data. CP, OP, CC, GJF and AS wrote the paper. GJF and AS supervised overall project.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedros, C., Papapietro, O., Colacios, C. et al. Genetic control of HgCl2-induced IgE and autoimmunity by a 117-kb interval on rat chromosome 9 through CD4 CD45RChigh T cells. Genes Immun 14, 258–267 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.21
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.21