Abstract
Background/Objectives:
The aim of this study is to investigate whether adherence to the Mediterranean diet changed during the period 1991–2006 in an Italian population.
Subjects/Methods:
We derived data from the comparison groups of a network of case–control studies on cancer and acute myocardial infarction conducted in the greater Milan area between 1991 and 2006. Subjects were 3247 adults (1969 women, 1278 men; median age 59 years) admitted to major teaching and general hospitals for a wide spectrum of acute conditions unrelated to long-term modifications of diet. Trained interviewers collected data on selected socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, lifestyle habits and other personal and familial factors. Information on diet was collected through an interviewer-administered, reproducible and validated food-frequency questionnaire. We computed a Mediterranean diet score (MDS) on the basis of nine a priori defined peculiar characteristics of the Mediterranean dietary pattern.
Results:
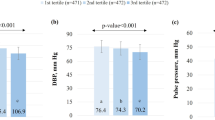
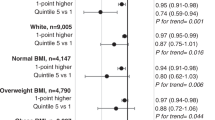
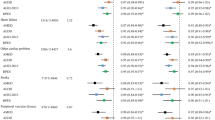
In multiple linear regression models, adjusted for age, education, place of birth and residence, and total energy intake, there was no significant association between the period of interview and MDS in both sexes. Subjects aged 55–64 years, those with high education, and those born in central and southern Italy showed the highest adherence to the Mediterranean diet in both sexes.
Conclusions:
In this population, adherence to the Mediterranean diet showed no significant change over the last 15 years.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti-Fidanza A, Fidanza F, Chiuchiu MP, Verducci G, Fruttini D (1999). Dietary studies on two rural italian population groups of the Seven Countries Study. 3. Trend of food and nutrient intake from 1960 to 1991. Eur J Clin Nutr 53, 854–860.
Bach A, Serra-Majem L, Carrasco JL, Roman B, Ngo J, Bertomeu I et al. (2006). The use of indexes evaluating the adherence to the Mediterranean diet in epidemiological studies: a review. Public Health Nutr 9, 132–146.
Balanza R, Garcia-Lorda P, Perez-Rodrigo C, Aranceta J, Bonet MB, Salas-Salvado J (2007). Trends in food availability determined by the Food and Agriculture Organization′s food balance sheets in Mediterranean Europe in comparison with other European areas. Public Health Nutr 10, 168–176.
Baldini M, Pasqui F, Bordoni A, Maranesi M (2008). Is the Mediterranean lifestyle still a reality? Evaluation of food consumption and energy expenditure in Italian and Spanish university students. Public Health Nutr 12, 148–155.
Belahsen R, Rguibi M (2006). Population health and Mediterranean diet in southern Mediterranean countries. Public Health Nutr 9, 1130–1135.
Bosetti C, Gallus S, Trichopoulou A, Talamini R, Franceschi S, Negri E et al. (2003). Influence of the Mediterranean diet on the risk of cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12, 1091–1094.
da Silva R, Bach-Faig A, Raido Quintana B, Buckland G, Vaz de Almeida MD, Serra-Majem L (2009). Worldwide variation of adherence to the Mediterranean diet, in 1961–1965 and 2000–2003. Public Health Nutr 12, 1676–1684.
Darmon N, Drewnowski A (2008). Does social class predict diet quality? Am J Clin Nutr 87, 1107–1117.
Decarli A, Franceschi S, Ferraroni M, Gnagnarella P, Parpinel MT, La Vecchia C et al. (1996). Validation of a food-frequency questionnaire to assess dietary intakes in cancer studies in Italy. Results for specific nutrients. Ann Epidemiol 6, 110–118.
Dernini S (2006). Towards the advancement of the Mediterranean food cultures. Public Health Nutr 9, 103–104.
Edefonti V, Randi G, La Vecchia C, Ferraroni M, Decarli A (2009). Dietary patterns and breast cancer: a review with focus on methodological issues. Nutr Rev 67, 297–314.
Ferro-Luzzi A, Branca F (1995). Mediterranean diet, Italian-style: prototype of a healthy diet. Am J Clin Nutr 61, 1338S–1345S.
Franceschi S, Negri E, Salvini S, Decarli A, Ferraroni M, Filiberti R et al. (1993). Reproducibility of an Italian food frequency questionnaire for cancer studies: results for specific food items. Eur J Cancer 29A, 2298–2305.
Galeone C, Pelucchi C, Levi F, Negri E, Franceschi S, Talamini R et al. (2006). Onion and garlic use and human cancer. Am J Clin Nutr 84, 1027–1032.
Garcia-Closas R, Berenguer A, Gonzalez CA (2006). Changes in food supply in Mediterranean countries from 1961 to 2001. Public Health Nutr 9, 53–60.
Hirvonen T, Mannisto S, Roos E, Pietinen P (1997). Increasing prevalence of underreporting does not necessarily distort dietary surveys. Eur J Clin Nutr 51, 297–301.
Keys A (1980). Coronary heart disease, serum cholesterol, and the diet. Acta Med Scand 207, 153–160.
La Vecchia C, Bosetti C (2006). Diet and cancer risk in Mediterranean countries: open issues. Public Health Nutr 9, 1077–1082.
Panagiotakos D, Kalogeropoulos N, Pitsavos C, Roussinou G, Palliou K, Chrysohoou C et al. (2009). Validation of the MedDietScore via the determination of plasma fatty acids. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60 (Suppl 5), 168–180.
Pelucchi C, Bosetti C, Rossi M, Negri E, La Vecchia C (2009). Selected aspects of Mediterranean diet and cancer risk. Nutr Cancer 61, 756–766.
Serra-Majem L, Bach A, Roman B (2006). Recognition of the Mediterranean diet: going a step further. Public Health Nutr 9, 101–102.
Sofi F, Cesari F, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Casini A (2008). Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: meta-analysis. BMJ 337, a1344.
Sofi F, Vecchio S, Giuliani G, Martinelli F, Marcucci R, Gori AM et al. (2005). Dietary habits, lifestyle and cardiovascular risk factors in a clinically healthy Italian population: the ‘Florence’ diet is not Mediterranean. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 584–591.
Tavani A, Spertini L, Bosetti C, Parpinel M, Gnagnarella P, Bravi F et al. (2006). Intake of specific flavonoids and risk of acute myocardial infarction in Italy. Public Health Nutr 9, 369–374.
Tessier S, Gerber M (2005). Factors determining the nutrition transition in two Mediterranean islands: Sardinia and Malta. Public Health Nutr 8, 1286–1292.
Trichopoulou A, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D (2005). Mediterranean diet and survival among patients with coronary heart disease in Greece. Arch Intern Med 165, 929–935.
Trichopoulou A, Costacou T, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D (2003). Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N Engl J Med 348, 2599–2608.
Trichopoulou A, Kouris-Blazos A, Wahlqvist ML, Gnardellis C, Lagiou P, Polychronopoulos E et al. (1995). Diet and overall survival in elderly people. BMJ 311, 1457–1460.
Trichopoulou A, Lagiou P, Kuper H, Trichopoulos D (2000). Cancer and Mediterranean dietary traditions. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9, 869–873.
Tur JA, Romaguera D, Pons A (2004a). Adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern among the population of the Balearic Islands. Br J Nutr 92, 341–346.
Tur JA, Romaguera D, Pons A (2004b). Food consumption patterns in a mediterranean region: does the mediterranean diet still exist? Ann Nutr Metab 48, 193–201.
Valdes J, Grau M, Subirana I, Marrugat J, Covas MI, Schroder H (2009). Secular trends in energy intake and diet quality in a Mediterranean population. Ann Nutr Metab 54, 177–183.
WCRF/AICR (2007). Dietary patterns. In: Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective. World Cancer Research Fund International: Washington, DC, pp 190–196.
WHO (2008). World Health Statistics 2008. Mortality and Burden of Disease. World Health Organization: Geneva, p 36–55.
Willett W, Stampfer MJ (1986). Total energy intake: implications for epidemiologic analyses. Am J Epidemiol 124, 17–27.
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted with contributions from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) and the Italian League Against Cancer. We thank Ms I Garimoldi for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelucchi, C., Galeone, C., Negri, E. et al. Trends in adherence to the Mediterranean diet in an Italian population between 1991 and 2006. Eur J Clin Nutr 64, 1052–1056 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.158
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.158
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Trends in the adherence to the Mediterranean diet in Israeli adolescents: results from two national health and nutrition surveys, 2003 and 2016
European Journal of Nutrition (2021)
-
High adherence to Mediterranean diet, but not individual foods or nutrients, is associated with lower likelihood of being obese in a Mediterranean cohort
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2018)
-
Comparison of Health and Risk Factors of Older, Working-age Australians, Italians and Italian-born Migrants to Australia, with Data from an Italian (PASSI), and an Australian (SAMSS) Risk Factor Surveillance System
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health (2018)
-
Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effect on Insulin Resistance
American Journal of Gastroenterology (2017)
-
Obesity and urolithiasis: evidence of regional influences
Urolithiasis (2017)