Abstract
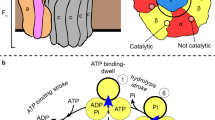
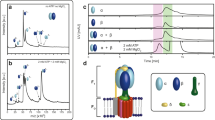
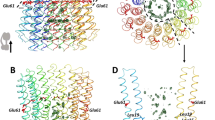
THE enzyme ATP synthase, or F-ATPase, is present in the membranes of bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria. Its structure is bipartite, with a proton-conducting, integral membrane portion, F0, and a peripheral portion, F1. Solubilized F1 is composed of five different subunits, (αβ)3γδη, and is active as an ATPase1,2. The function of F-ATPase is to couple proton translocation through F0 with ATP synthesis in F1 (ref. 3). Several lines of evidence support the spontaneous formation of ATP on F1 (refs 4,5) and its endergonic release6 at cooperative and rotating (or at least alternating) sites7. The release of ATP at the expense of protonmotive force might involve mechanical energy transduction from F0 into F1 by rotation of the smaller subunits (mainly γ) within (αβ)3, the catalytic hexagon of F1 as suggested by electron microscopy8, by X-ray crystal structure analysis9 and by the use of cleavable crosslinkers10. Here we record an intersubunit rotation in real time in the functional enzyme by applying polarized absorption relaxation after photobleaching to immobilized F1 with eosin-labelled γ. We observe the rotation of γ relative to immobilized (αβ)3 in a timespan of 100 ms, compatible with the rate of ATP hydrolysis by immobilized F1. Its angular range, which is of at least 200 degrees, favours a triple-site mechanism of catalysis7,11, with γ acting as a crankshaft in (αβ)3. The rotation of γ is blocked when ATP is substituted with its non-hydrolysable analogue AMP-PNP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Senior, A. E. A. Rev. Biophys. biophys. Chem. 19, 7–41 (1990).
Walker, J. E. The Biochemist 16, 31–351 (1994).
Mitchell, P. Nature 191, 144–148 (1961).
Boyer, P. D., Cross, R. L. & Momsen, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2837–2839 (1973).
Grubmeyer, C., Cross, R. L. & Penefsky, H. S. J. biol. Chem. 25, 12092–120100 (1982).
Penefsky, H. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1589–1593 (1985).
Boyer, P. D. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1140, 215–250 (1993).
Gogol, E. P., Johnston, E., Aggeler, R. & Capaldi, R. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 9585–9589 (1990).
Abrahams, J. P., Leslie, A. G. W., Lutter, R. & Walker, J. E. Nature 370, 621–628 (1994).
Duncan, T. M., Bulygin, V. V., Zhou, Y., Hutcheon, M. L. & Cross, R. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 10964–10968 (1995).
Weber, J. Wilke-Mounts, S. & Senior, A. E. J. biol. Chem. 269, 20462–20467 (1994).
Junge, W. Schaffernicht, H. & Nelson, N. Biochim. biophys. Acta 462, 73–85 (1977).
Perrin, F. Le Journal de Physique et le Radium 7, 1–11 (1936).
Jablonski, A. Z. Physik 96, 236–246 (1935).
Wahl, P. Chem. Phys. 7, 210–219 (1975).
Moroney, J. V., Fullmer, C. S. & McCarty, R. E. J. biol. Chem. 259, 7281–7285 (1984).
Miki, J., Maeda, M., Mukohata, Y. & Futai, M. FEBS Lett. 232, 221–226 (1988).
Wagner, R. & Junge, W. Biochemistry 21, 1890–1899 (1982).
Engelbrecht, S., Schürmantn, K. & Junge, W. Eur. J. Biochem. 179, 117–122 (1989).
Engelbrecht, S., Lill, H. & Junge, W. Eur. J. Biochem. 160, 635–643 (1986).
LeBel, D., Poirier, G. G. & Beaudoin, A. R. Analyt. Biochem. 85, 86–89 (1978).
Parker, C. A. & Hatchard, C. G. Trans. Faraday Soc. 57, 1894–1909 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbert, D., Engelbrecht, S. & Junge, W. Intersubunit rotation in active F-ATPase. Nature 381, 623–625 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/381623a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/381623a0
This article is cited by
-
Remembering James Barber (1940–2020)
Photosynthesis Research (2022)
-
Oscillating Electric Field Measures the Rotation Rate in a Native Rotary Enzyme
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
A reciprocating motion-driven rotation mechanism for the ATP synthase
Science China Life Sciences (2016)
-
Biased Brownian stepping rotation of FoF1-ATP synthase driven by proton motive force
Nature Communications (2013)
-
The nonlinear chemo-mechanic coupled dynamics of the F 1 -ATPase molecular motor
Journal of Biological Physics (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.