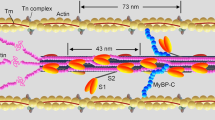
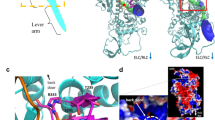
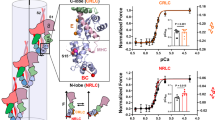
Abstract
MUSCLE contraction is driven by a cyclical interaction between the globular head domain of myosin and the actin filaments1-6. We used quick stretches of 5 nm per half sarcomere to synchronize the movements of myosin heads in active single muscle fibres5,7,8. The intensity of the 14.5 nm X-ray reflection decreased during the stretch, showing that the instantaneous elasticity of muscle1,5 involves distortion of myosin heads. Head movement continued at about 1,500s-1 after the stretch, accompanied by partial force recovery. This indicates a reversal of the force-generating 'working stroke' in the myosin heads5,8,9 that is smaller and faster than assumed previously5,10,11. By 50 ms after the stretch, myosin heads have regained both their original conformation and the ability to execute a normal working stroke. This 'repriming' process is slower than that following shortening12 but much faster than the ATP turnover rate per myosin head.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huxley, A. F. Prog. Biophys. biophys. Chem. 7, 255–318 (1957).
Reedy, M. K., Holmes, K. C. & Tregear, R. T. Nature 207, 1276–1280 (1965).
Lymn, R. W. & Taylor, E. W. Biochemistry 10, 4617–4624 (1971).
Huxley, H. E. Science 164, 1356–1366 (1969).
Huxley, A. F. & Simmons, R. M. Nature 233, 533–538 (1971).
Rayment, I. et al. Science 261, 58–65 (1993).
Huxley, H. E. et al. J. molec. Biol. 169, 469–506 (1983).
Irving, M., Lombardi, V., Piazzesi, G. & Ferenczi, M. A. Nature 357, 156–158 (1992).
Ford, L. E., Huxley, A. F. & Simmons, R. M. J. Physiol., Lond. 269, 441–515 (1977).
Eisenberg, E. & Hill, T. L. Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 33, 55–82 (1978).
Lombardi, V. & Piazzesi, G. J. Physiol., Lond. 431, 141–171 (1990).
Lombardi, V., Piazzesi, G. & Linari, M. Nature 355, 638–641 (1992).
Huxley, H. E., Faruqi, A. R., Kress, M., Bordas, J. & Koch, M. H. J. J. molec biol. 159, 637–684 (1982).
Piazzesi, G. et al. Biophys J. 68, 92–98s (1995).
Piazzesi, G., Francini, F., Linari, M. & Lombardi, V. J. Physiol., Lond. 445, 659–711 (1992).
Kushmerick, M. J. & Davies, R. E. Proc. R. Soc. B174, 315–353 (1969).
Curtin, N. A. & Davies, R. E. J. Mechanochem. Cell Motil. 3, 147–154 (1975).
Cecchi, G., Colomo, F. & Lombardi, V. Boll. Soc. ital. Biol. sper. 52, 733–736 (1976).
Huxley, A. F. & Lombardi, V. J. Physiol., Lond. 305, 15–16P (1981).
Huxley, A. F., Lombardi, V. & Peachey, L. D. J. Physiol. Lond. 317, 12–13P (1981).
Towns-Andrews, E. et al. Rev. scient. Instrum. 60, 2346–2349 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lombard, V., Piazzesi, G., Ferenczi, M. et al. Elastic distortion of myosin heads and repriming of the working stroke in muscle. Nature 374, 553–555 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/374553a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/374553a0
This article is cited by
-
Calcium-dependent titin–thin filament interactions in muscle: observations and theory
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2020)
-
Monitoring the myosin crossbridge cycle in contracting muscle: steps towards ‘Muscle—the Movie’
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2019)
-
Strain in shock-loaded skeletal muscle and the time scale of muscular wobbling mass dynamics
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Temperature effect on the chemomechanical regulation of substeps within the power stroke of a single Myosin II
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
A new mechanokinetic model for muscle contraction, where force and movement are triggered by phosphate release
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.