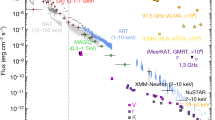
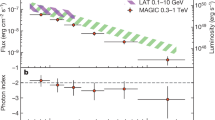
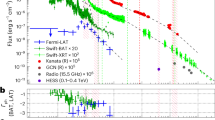
Abstract
THE distribution of more than 150 γ-ray bursts detected by the BATSE experiment is isotropic on the sky but radially non-uniform1,2. This raises the possibility that bursts are cosmological (at z≲l) and therefore very energetic events, releasing ∼1050 erg sr−1 on a timescale of seconds. The coalescence of two neutron stars3–7 or the accretion-induced collapse of a white dwarf8 can release up to 1053 erg in the form of neutrino-antineutrino pairs, so that the conversion of <1% into γ-rays by annihilation9 could generate γ-ray bursts, but in all such models an optically thick wind tends to form10,11, preventing the γ-rays from escaping and converting their energy into kinetic energy of the ejected material. We present here a possible solution to this difficulty. When a stellar-mass neutron star is disrupted by a black hole, it forms a thick disk which emits νν̄ pairs. These neutrinos expel a wind from the disk, but angular momentum conservation means that a clear funnel forms along the rotation axis. Neutrino annihilation within the matter-free funnel can then create γ-rays which escape to the distant observer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fishman, G. J. et al. Second Gamma Ray Observatory Science Workshop (Annapolis, Maryland, 1991).
Meegan, C. A. et al. IAU Circ. No. 5358 (1991).
Paczyński, B. Astrophys. J. 308, L43–L46 (1986).
Eichler, D., Livio, M., Piran, T. & Schramm, D. N. Nature 340, 126–128 (1989).
Shemi, A. & Piran, T. Astrophys. J. 365, L55–L58 (1990).
Paczyński, B. in Proc. Huntsville GRO Mtg (eds Paciesas, W. S. & Fishman, G. J.) (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1992).
Piran, T., Narayan, R. & Shemi, A. in Proc. Huntsville GRO Mtg (Paciesas, W. S. & Fishman, G. J.) (in the press).
Ramaty, R. & Dar, A. in Proc. COSPAR Mtg (in the press).
Goodman, J., Dar, A. & Nussimov, S. Astrophys. J. 314, L7–L10 (1987).
Paczyński, B. Astrophys. J. 363, 218–226 (1990).
Woosley, S. E. & Baron, E. Astrophys. J. (in the press).
Goodman, J. Astrophys. J. 308, L47–L50 (1986).
Duncan, R. C., Shapiro, S. L. & Wasserman, I. Astrophys. J 309, 141–160 (1986).
Lattimer, J. M. & Schramm D. N. Astrophys. J. 192, L145–L147 (1974).
Clark, J. P. A. & Eardley, D. M. Astrophys. J. 215, 311–322 (1977).
Mészáros, P. & Rees, M. J. Astrophys. J. 397, 570–575 (1992).
Flammang, R. A. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 199, 833–867 (1982).
Higdon, J. C. & Lingenfelter, R. E. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 28, 401–436 (1990).
Schaefer, B. E. et al. Astrophys. J. 393, L51–L54 (1992).
Narayan, R., Paczyński, B. & Piran, T. Astrophys. J. 395, L83–L86 (1992).
Narayan, R., Piran, T. & Shemi, A. Astrophys. J. 379, L17–L20 (1991).
Mao, S. & Paczyński, B. Astrophys. J. 388, L45–L48 (1992).
Mészáros, P. & Rees, M. J. Astrophys. J. 397, 570; Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 257, 29p; 258, 41p (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochkovitch, R., Hernanz, M., Isern, J. et al. Gamma-ray bursts as collimated jets from neutron star/black hole mergers. Nature 361, 236–238 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361236a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361236a0
This article is cited by
-
Coalescence of black hole–neutron star binaries
Living Reviews in Relativity (2021)
-
Neutron star mergers and how to study them
Living Reviews in Relativity (2020)
-
The Theory of Gamma-Ray Bursts
Space Science Reviews (2017)
-
Possible Outflow Formation in the Central Engine of GRBs
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2011)
-
An origin in the local Universe for some short γ-ray bursts
Nature (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.