Abstract
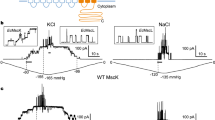
MECHANOSENSITIVE channels have been found in more than 30 cell types, including bacterial1,2, yeast3, plant4 and animal cells5–9. Whether tension is transferred to the channel through the lipid bilayer and/or underlying cytoskeleton is not clear. Using the patch-clamp method10, we found that amphipathic compounds, which are molecules having hydrophobic and hydrophilic character with positive, negative or no net electric charge at pH7, could slowly activate the mechanosensitive channels of giant Escherichia coli spheroplasts, with effectiveness proportional to their lipid solubility. The cationic or anionic amphipaths were able to compensate for each other's effect. After a channel was activated by an amphipath of one charge, if that amphipath was gradually replaced by one with the opposite charge, the channel first inactivated before reactivating. These findings support the view that the mechanical gating force can come from the surrounding lipids.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinac, B., Buechner, M., Delcour, A. H., Adler, J. & Kung, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 2297–2301 (1987).
Zoratti, M. & Petronilli, V. FEBS Lett. 240, 105–109 (1988).
Gustin, M. C., Zhou, X.-L., Martinac, B. & Kung, C. Science 242, 762–765 (1988).
Falke, L. C., Edwards, K. L., Pickard, B. G. & Misler S. FEBS Lett. 237, 141–144 (1988).
Guharay, F. & Sachs, F. J. Physiol., Lond. 352, 685–701 (1984).
Sigurdson, W. J., Morris, C. E., Brezden, B. L. & Gardner, D. R. J. exp. Biol. 127, 191–209 (1987).
Hudspeth, A. J. Hearing Res. 22, 21–27 (1986).
Ohmori, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 350, 561–581 (1984).
Kirber, M. T., Singer, J. J. & Walsh, J. V. Jr, Biophys. J. 51, 252a (1987).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, Y., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigwrorth, F. J. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Sheetz, M. P. & Singer, S. J. J. Cell Biol. 70, 193–203 (1976).
Deuticke, B. Biochim. biophys. Acta 163, 494–500 (1968).
Sheetz, M. P. & Singer, S. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4457–4461 (1974).
Rothman, J. E. & Lenard, J. Science 195, 743–753 (1977).
Verkleij, A. J. et al. Biochim. biophys. Acta 323, 178–193 (1973).
Buechner, M., Delcour, A. H., Martinac B., Adler, J. & Kung, C. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1024, 111–121 (1990).
Raetz, C. R. A. Rev. Genet. 20, 253–295 (1986).
Nikaido, H. & Vaara M. in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Cellular and Molecular Biology Vol. 1 (eds Neidhardt, F. C. et al.) 7–15 (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington DC, 1987).
Lugtenberg, B. & van Alphen L. Biochim. biophys. Acta 737, 51–115 (1983).
Hille, B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes (Sinauer, Sunderland, MA, 1984).
Delcour, A. H., Martinac, B., Adler, J. & Kung, C. Biophys. J. 56, 631–636 (1989).
Berrier, C., Coulombe, A., Houssin, C. & Ghazi, A. FEBS Lett. 259, 27–32 (1989).
Opsahl, L. R., Mak, D. D. & Webb, W. W. Biophys. J. 57, 321a (1990).
Cooper, K. E., Tang, J. M., Rae, J. L. & Eisenberg, R. S. J. memb. Biol. 93, 259–269 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinac, B., Adler, J. & Kung, C. Mechanosensitive ion channels of E. coli activated by amphipaths. Nature 348, 261–263 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/348261a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/348261a0
This article is cited by
-
A mechanical-coupling mechanism in OSCA/TMEM63 channel mechanosensitivity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Examining Mechanisms for Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Channel-Mediated Secretion Events in Bone Cells
Calcified Tissue International (2023)
-
Deciphering the role of mechanosensitive channels in plant root biology: perception, signaling, and adaptive responses
Planta (2023)
-
Asymmetric effects of amphipathic molecules on mechanosensitive channels
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
2021 Nobel Prize for mechanosensory transduction
Biophysical Reviews (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.