Abstract
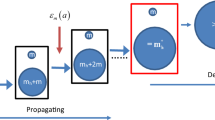
One-dimensional simulations of the nonlinear growth of structure in a universe dominated by a population of nonrelativistic collisionless particles such as massive neutrinos show that a subpopulation of slowly moving particles exists within the ‘pancakes’ that form1. These particles can cluster in a low velocity condensate around any seed perturbation which may be present. The schematic calculation of this aggregation presented here suggests that the properties of neutrino clusters depend only weakly on seed mass but substantially on seed separation. Their mass and velocity dispersion may be quite comparable with the values inferred for the haloes of ‘dark’ matter surrounding real galaxies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melott, A. L. Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 894–896 (1982).
Lyubimov, V. A., Novikov, E. G., Nozik, V. Z., Tretyakov, E. F. & Kozik, V. S. Phys. Lett. B94, 266–268 (1980).
Reines, F., Sobel, S. W. & Pasierb, E. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1307–1311 (1980).
Faber, S. M. & Gallagher, J. S. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 17, 135–187 (1979).
Bond, J. R., Efstathiou, G. & Silk, J. I. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1980–1984 (1980).
Doroshkevich, A. G., Khlopov, M. Yu., Sunyaev, R. A., Szalay, A. S. & Zel'dovich, Ya. B. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 375, 32–42 (1980).
Peebles, P. J. E. Astrophys. J. 258, 415–424 (1982)
Bond, J. R. & Szalay, A. S. Astrophys. J. (in the press).
Zel'dovich, Ya.B. Astr. Astrophys. 5, 84–89 (1970).
Doroshkevich, A. G. et al. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 192, 321–327 (1980).
Sunyaev, R. A. & Zel'dovich, Ya. B. Astr. Astrophys. 20, 189–200 (1972).
White, S. D. M. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 189, 831–852 (1979).
van Albada, T. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 201, 939–955 (1982).
Melott, A. L. Nature 296, 721–723 (1982).
Tremaine, S. D. & Gunn, J. E. Phys. Rev. Lett. 42, 407–410 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bond, J., Szalay, A. & White, S. How galaxies acquire their neutrino haloes. Nature 301, 584–585 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/301584a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/301584a0
This article is cited by
-
Dark matter-systematics of its distribution
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (1986)
-
Formation of galaxies and large-scale structure with cold dark matter
Nature (1984)
-
Is the Universe flat?
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (1984)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.