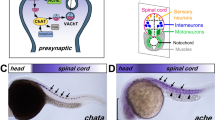
Abstract
Specific to the vertebrate embryo, the neural crest is a transitory structure whose constituent cells migrate extensively through the developing animal and ultimately give rise to many distinct cell types, including the components of the peripheral nervous system1,2. The earliest clear indices of their differentiation have so far been detected only when cells from the crest have reached their destination. This is exemplified by the acquisition of the ability to synthesise and store catecholamines; absent from crest cells before and during their dorso–ventral migration, this ability appears concomitantly with their aggregation into the primary sympathetic ganglia3–6. The chronology of cholinergic maturation, however, is less well defined. Appropriate biochemical markers are demonstrable as soon as parasympathetic or enteric ganglia are formed3–6, but the lack of a suitable cytochemical method is a major obstacle to the identification of any cholinergic cells before then. Although acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is present in migrating neural crest10, choline acetyltransferase (CAT), the enzyme catalysing acetvlcholine (ACh) synthesis, is a much more relevant correlate7,11,12, and definitive evidence for cholinergic differentiation should include the demonstration of ACh-synthesising activity in intact cells13,14 or their extracts. We show here that neural crest, as soon as it begins migration, can synthesise ACh.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weston, J. A. in Advances in Morphogenesis Vol. 8 (eds Abercrombie, M., Brachet, J. & Kind, T. J.) 41–114 (Academic, New York, 1970).
Le Douarin, N. M. Med. Biol. 52, 281–319 (1974); in Embryogenesis in Mammals (CIBA Fdn Symp.) 71–101 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1976); Curr. Topics dev. Biol. (in the press).
Enemar, A., Falck, B. & Håkanson, R. Devl Biol. 11, 268–283 (1965).
Cochard, P., Goldstein, M. & Black, I. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2986–2990(1978).
Rothman, T. P., Gershon, M. D. & Holtzer, H. Devl Biol. 65, 322–341 (1978).
Teitelman, G., Baker, H., Joh, T. H. & Reis, D. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 509–513(1979).
Chiappinelli, V., Giacobini, E., Pilar, G. & Uchimura, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 257, 749–766 (1976).
Smith, J., Cochard, P. & Le Douarin, N. M. Cell Differentiation 6, 199–216 (1977).
Le Douarin, N. M., Teillet, M.-A., Ziller, C. & Smith, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2030–2034 (1978).
Drews, U. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 7, 1–52 (1975).
Hebb, C. O. J. Physiol., Lond. 133, 566–570 (1956).
Burt, A. M. J. exp. Zool. 169, 107–112 (1968).
Hildebrand, J. G., Barker, D. L., Herbert, E. & Kravitz, E. A. J. Neurobiol. 2, 231–246 (1971).
Mains, R. E. & Patterson, P. H. J. Cell Biol. 59 329–345 (1973).
Ziller, C., Smith, J. Fauquet, M. & Le Douarin, N. M. Prog. Brain Res. (in the press).
White, H. L. & Wu, J. C. Biochemistry 12, 841–846 (1973).
Roskoski, R., Mayer, H. E. & Schmid, P. G. J. Neurochem. 23, 1197–1200 (1974).
Sanes, J. R. & Hildebrand, J. G. Devl Biol. 52, 105–120 (1976).
Welsch, F. & McCarthy, S. K. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 56 C, 163–169 (1977).
Haubrich, D. R. in Biology of Cholinergic Function (eds Goldberg, A. M. & Hanin, I.) 239–268 (Raven, New York, 1976).
Tuček, S. Acetylcholine Synthesis in Neurons, Ch. 2 (Chapman and Hall, London, 1978).
Narayanan, C. H. & Narayanan, H. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 47, 137–148 (1978).
Noden, D. M. Devl Biol. 67, 313–329 (1978).
Filogamo, G. & Marchisio, P. C. Neurosci. Res. 4, 29–64 (1971).
Dunant, Y., Gautron, J., Israel, M., Lesbats, B. & Manaranche, R. J. Neurochem. 19, 1987–2002 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J., Fauquet, M., Ziller, C. et al. Acetylcholine synthesis by mesencephalic neural crest cells in the process of migration in vivo. Nature 282, 853–855 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/282853a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/282853a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.